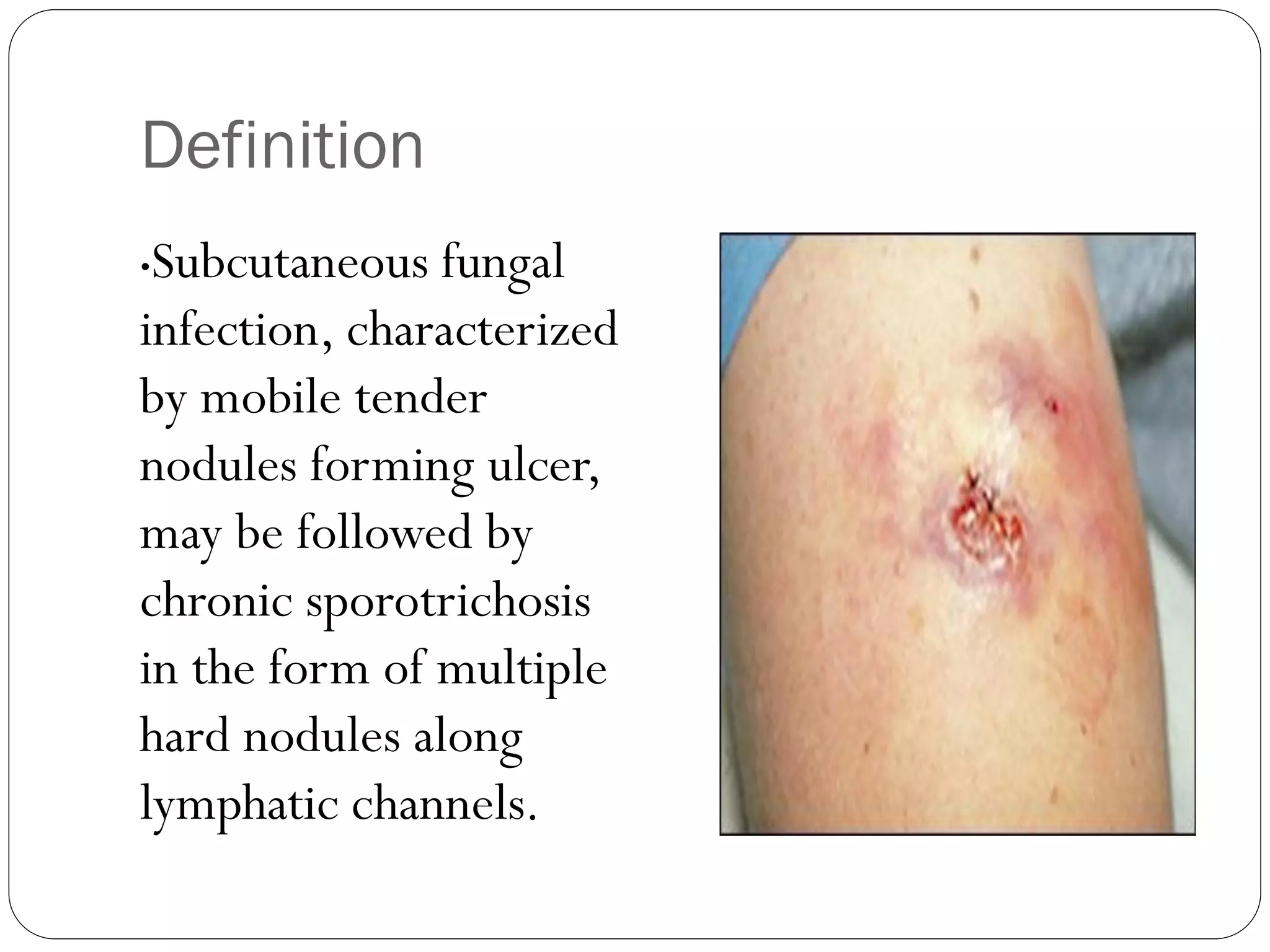
This document provides information about Sporotrichosis, including its definition, etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment. It is caused by the dimorphic fungus Sporothrix schenckii, which can cause subcutaneous nodules and ulceration. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination, culture, histology, and serology to demonstrate the presence of the fungus. Treatment typically involves oral antifungal medication such as itraconazole or potassium iodide for at least 4-6 weeks after symptoms resolve.

















![Laboratory Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by culture as frequently the fungus may not be
demonstrable in pus or tissues.
Collection of Infected Material:
Pus should be aspirated from unruptured nodules.
Swabs, scrapings or biopsies of ulcerated lesions should be
collected in a sterile container.
A. Micrscopic Examination:
Direct microscopy is of little.
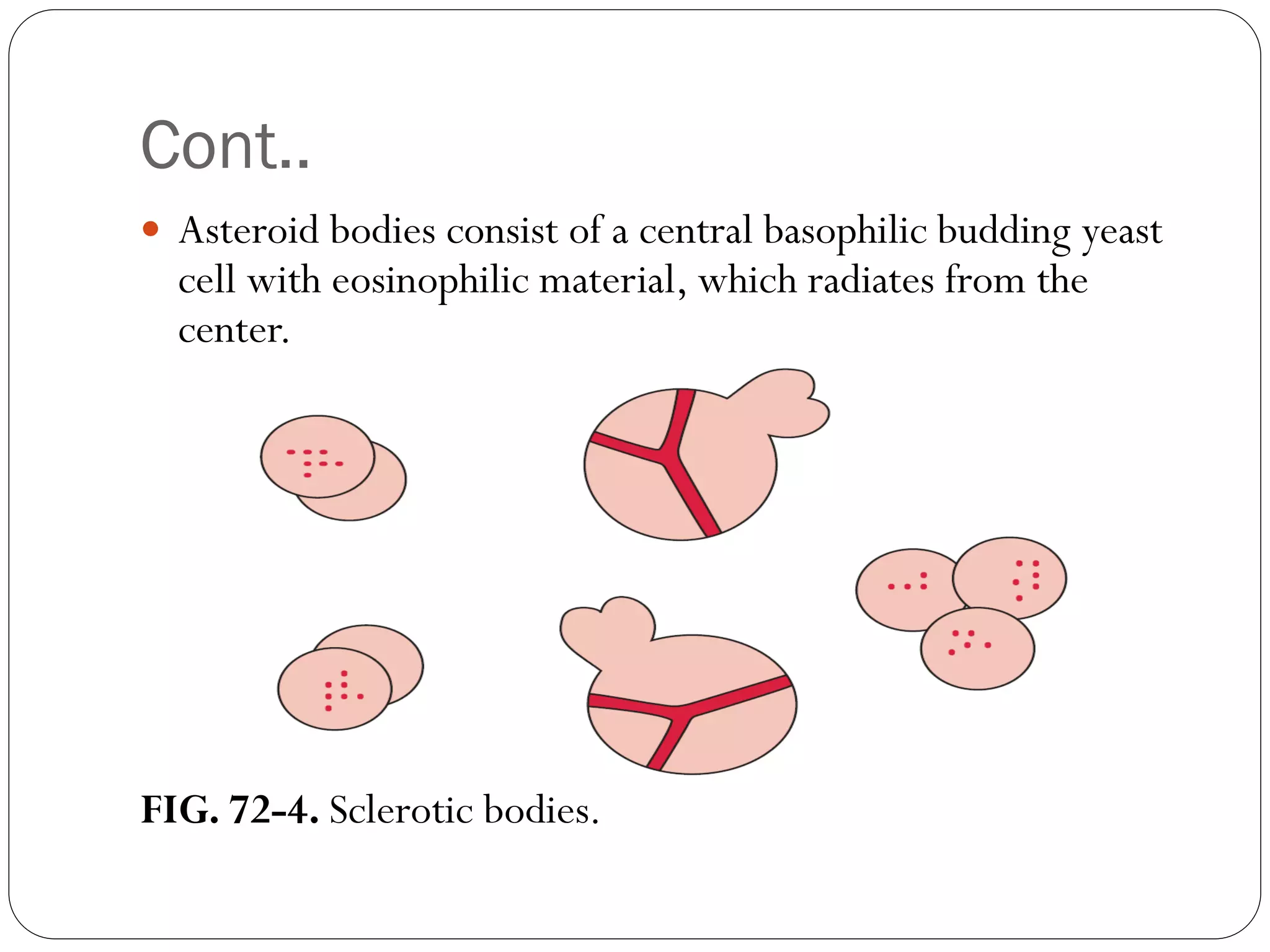
Fine-needle aspiration cytology may show epithelioid cell
granuloma, asteroid bodies and/or yeast cells and cigarshaped
bodies [periodic acid Schiff (PAS) or Grocott‟s methanamine silver
(GMS) stains].
The sensitivity/specificity of direct microscopic examination
remains under evaluated as most studies consider it unhelpful due
to paucity of fungal cells.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sporotrichosis-210301153904/75/Sporotrichosis-22-2048.jpg)
















