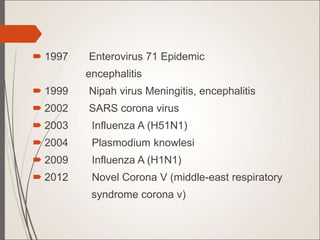
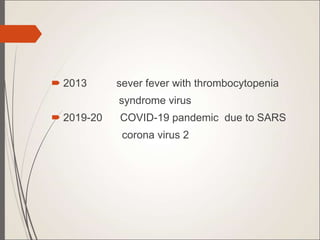
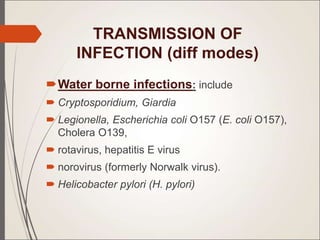
This document defines emerging and re-emerging infections. Emerging infections are those whose incidence in humans has increased in the past two decades or are expected to increase. Re-emerging infections were previously clinically silent but have reappeared. Major causes of emerging infections include changes in human behavior, environments, travel, and antimicrobial resistance in known pathogens. The document lists many bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic pathogens that have emerged since 1972. It describes different modes of transmission including waterborne, foodborne, respiratory, zoonotic, vector-borne and nosocomial.