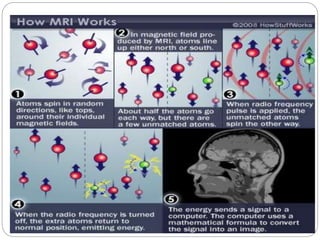
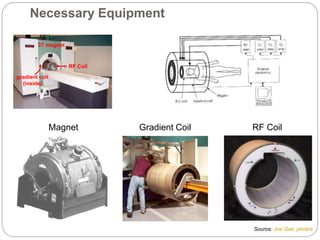
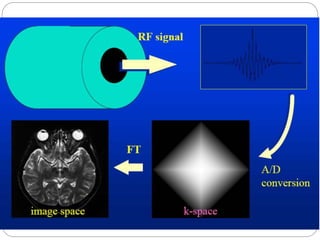
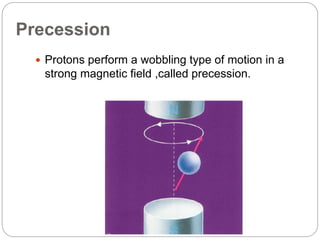
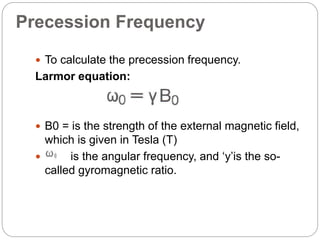
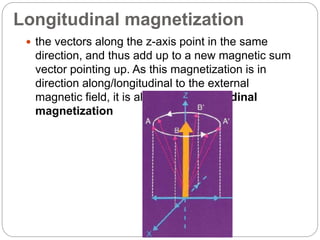
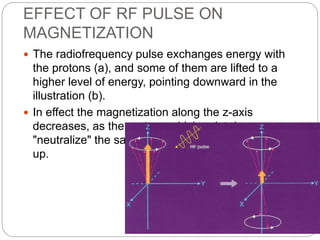
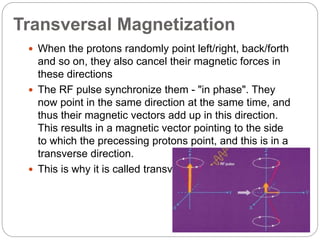
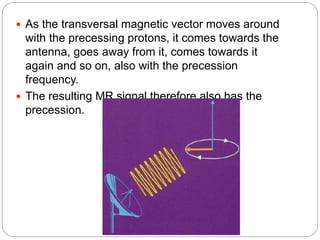
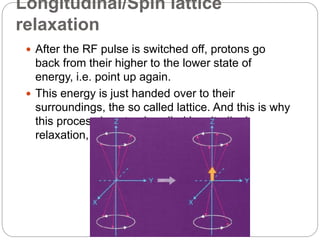
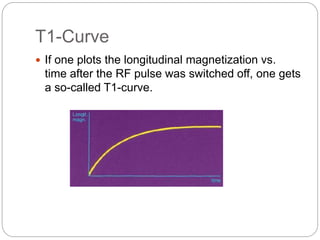
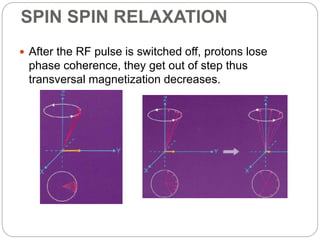
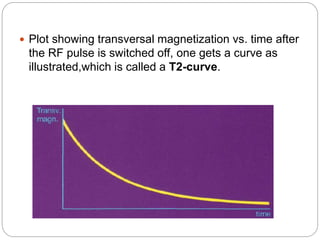
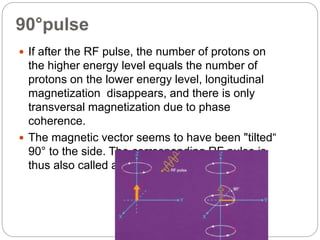
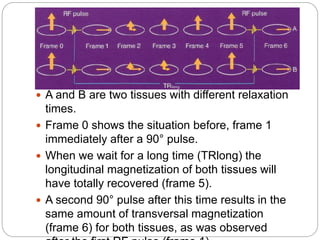
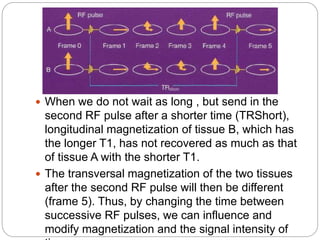
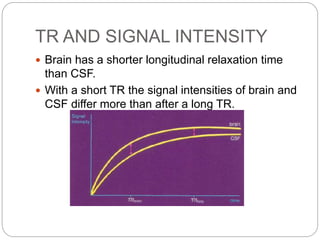
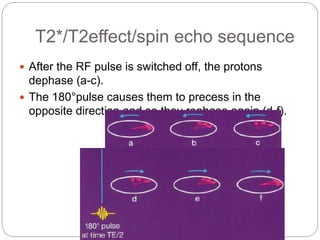
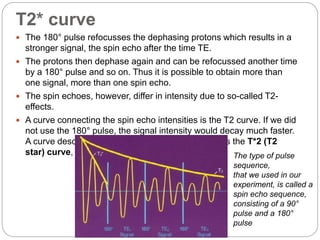
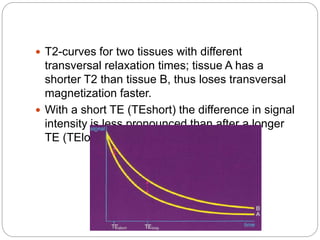
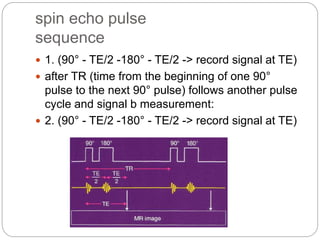
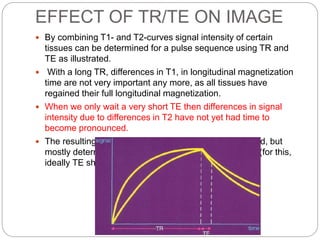
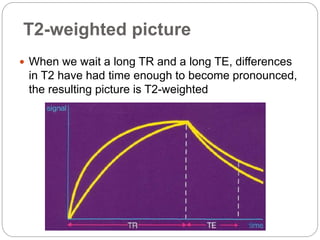
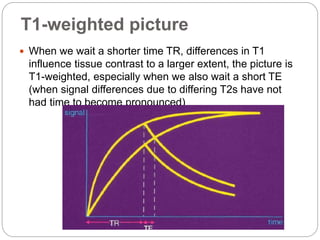
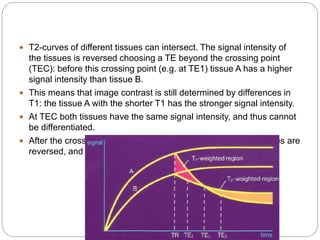
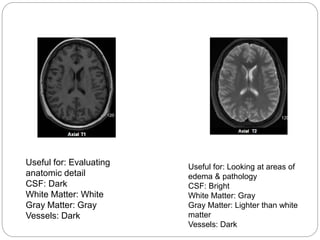
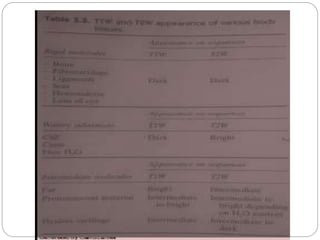
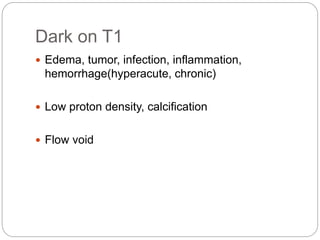
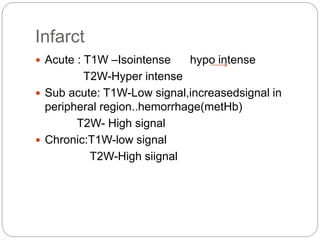
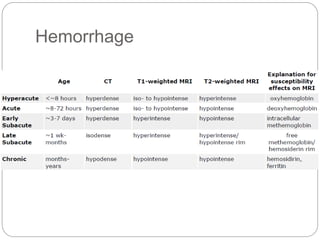
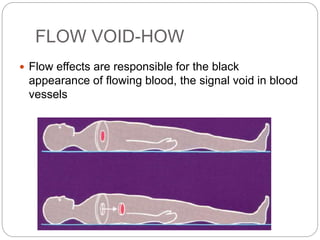
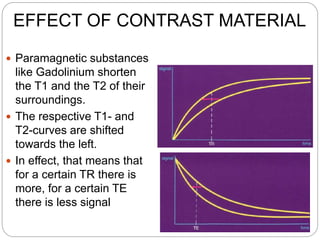
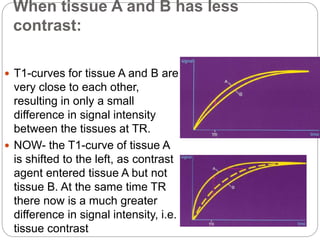
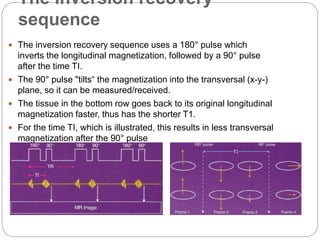
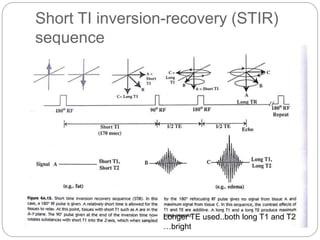
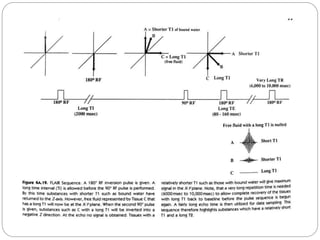
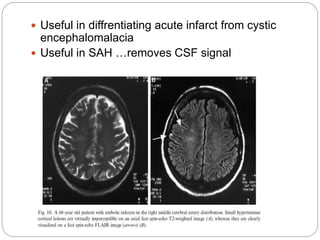
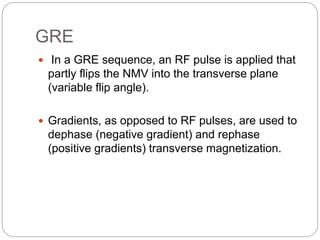
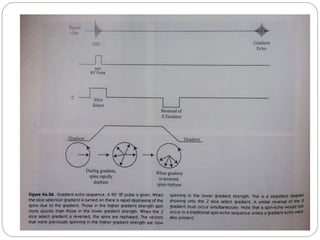
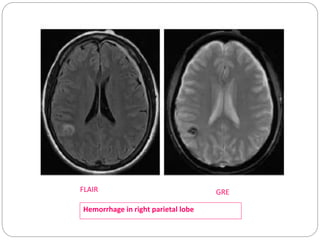
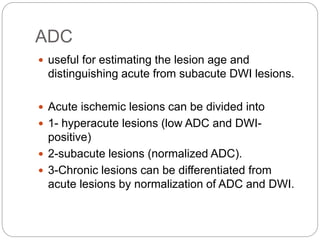
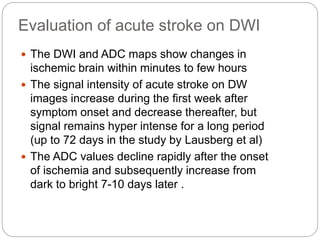
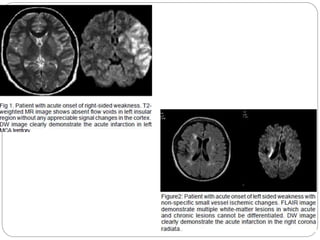
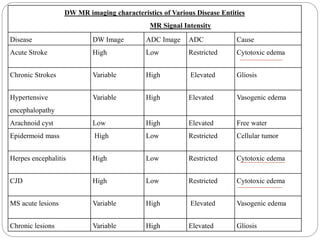
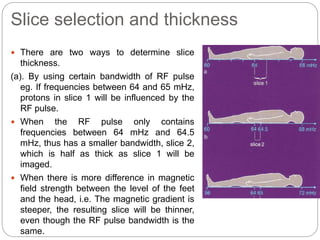
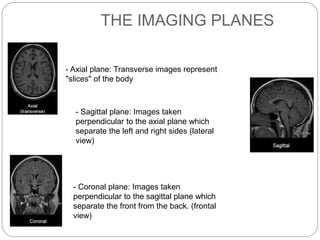
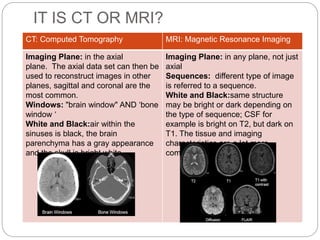
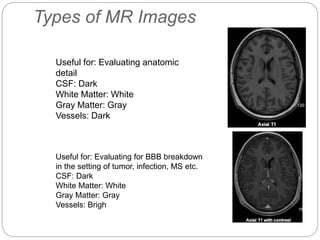
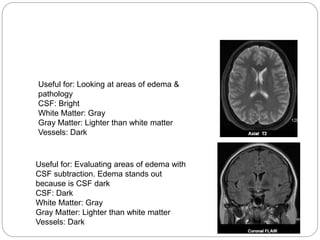
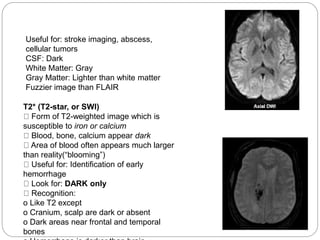
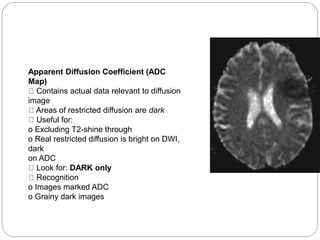
Dr Pawan Kumar presented on MRI principles, techniques, and reading. MRI works by using a strong magnetic field to align proton spins in the body. Radiofrequency pulses excite the protons, causing them to emit signals as they relax back to equilibrium. These signals are used to form MRI images. Key hardware includes magnets, gradient coils, and RF coils. MRI contrast depends on tissue T1 and T2 relaxation times and the chosen TR and TE parameters. Different sequences like T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and FLAIR are used to highlight various tissues and pathologies. Contrast agents can also be used to improve tissue contrast on MRI scans.