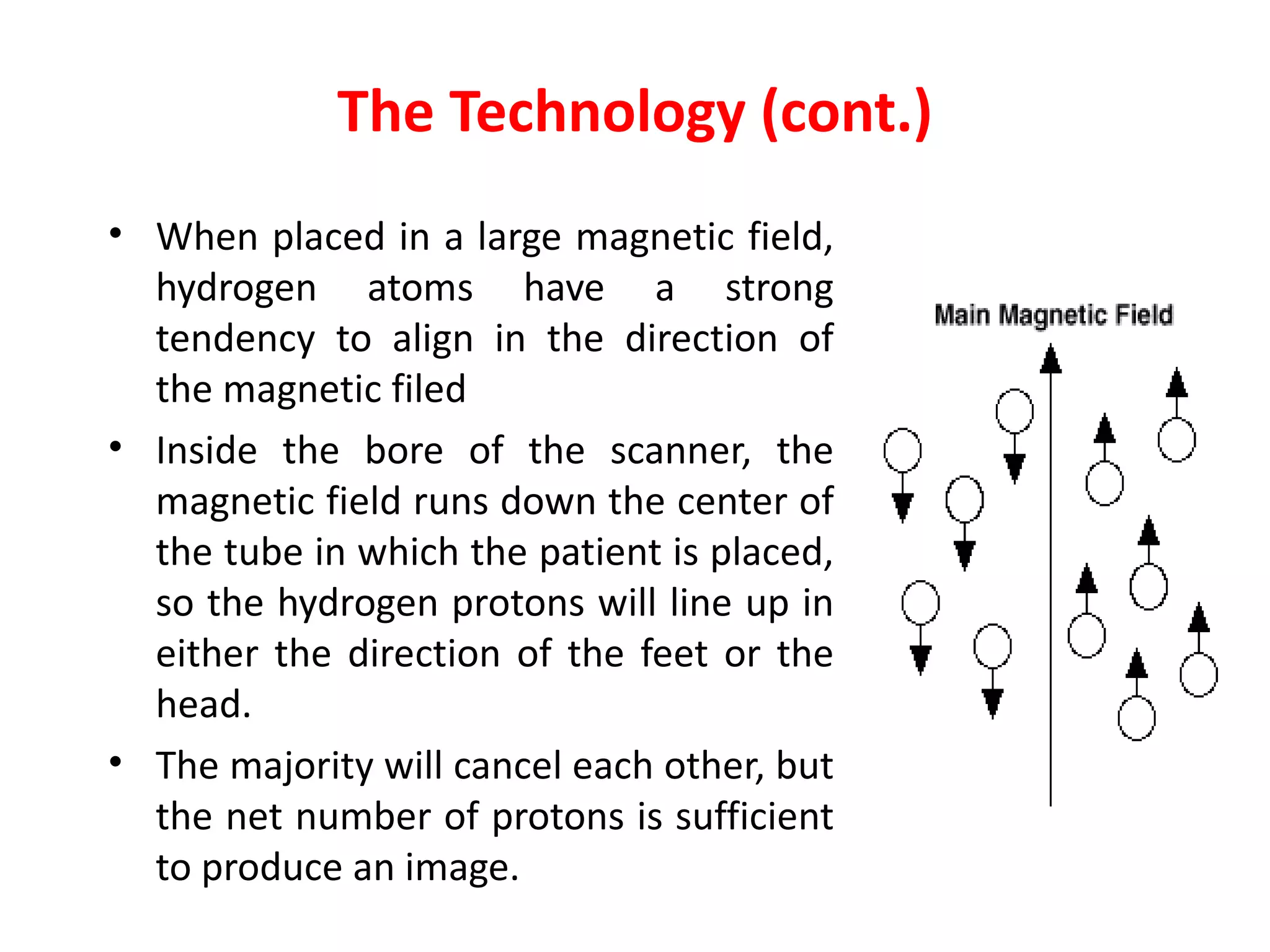
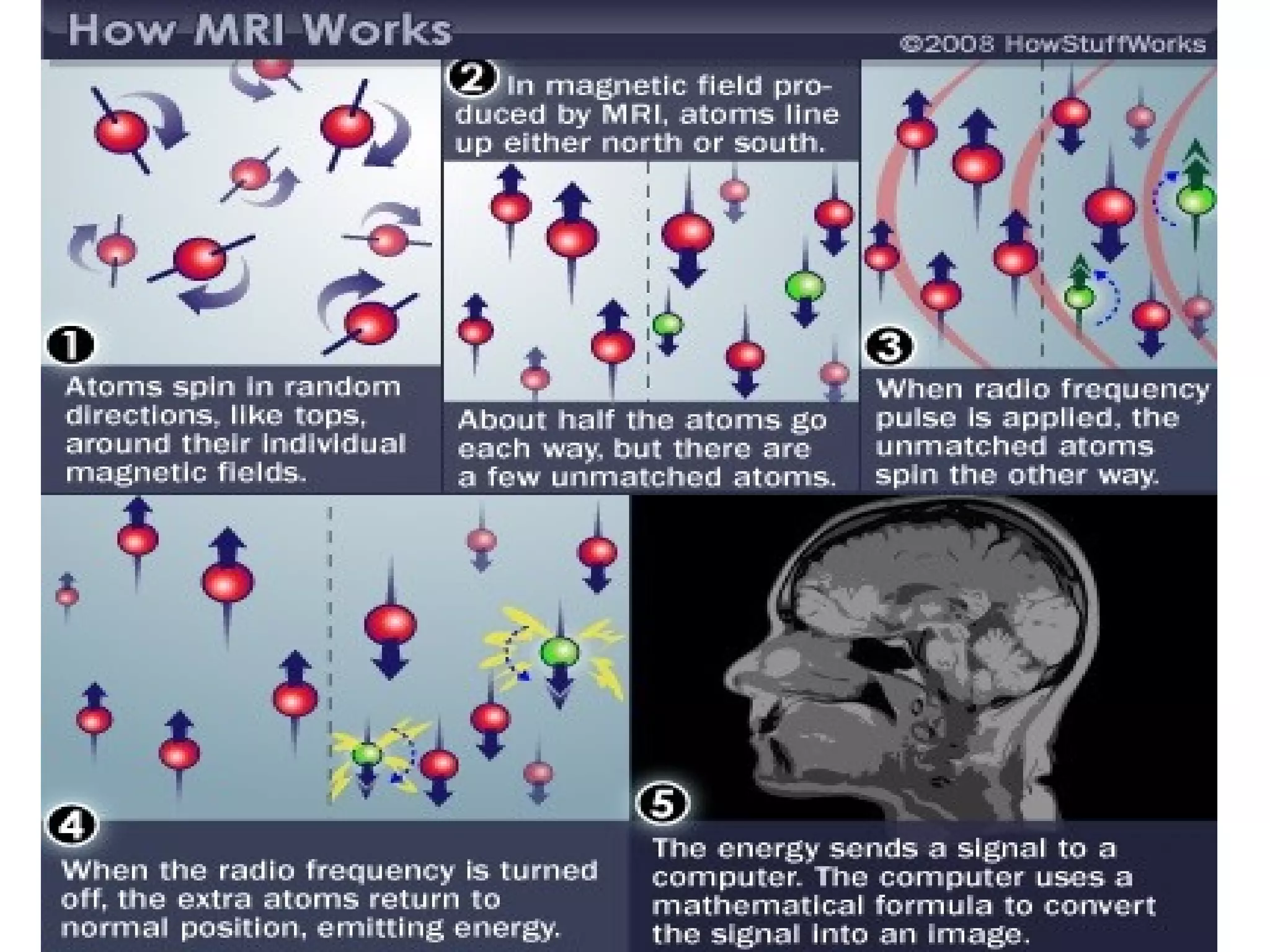
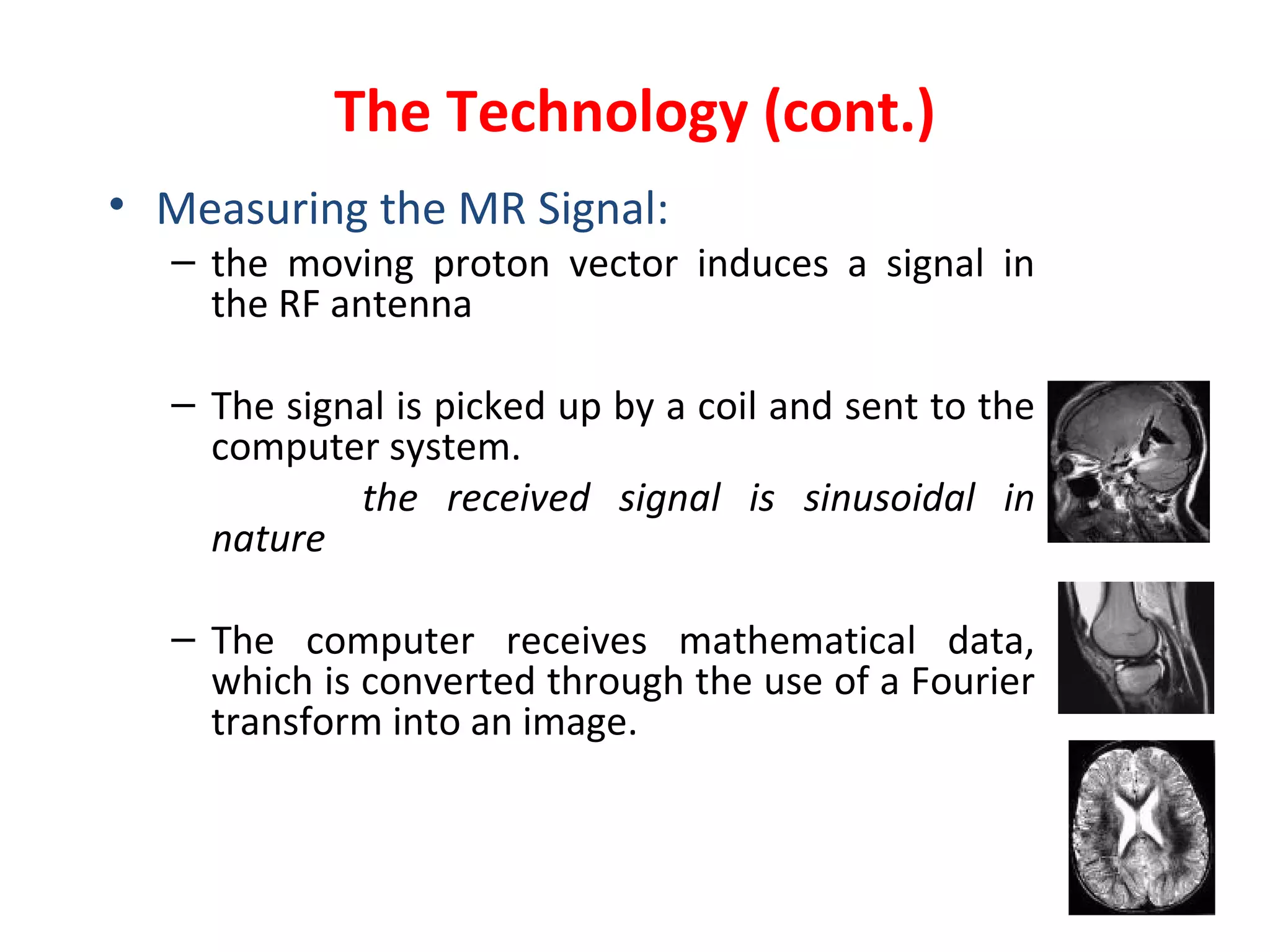
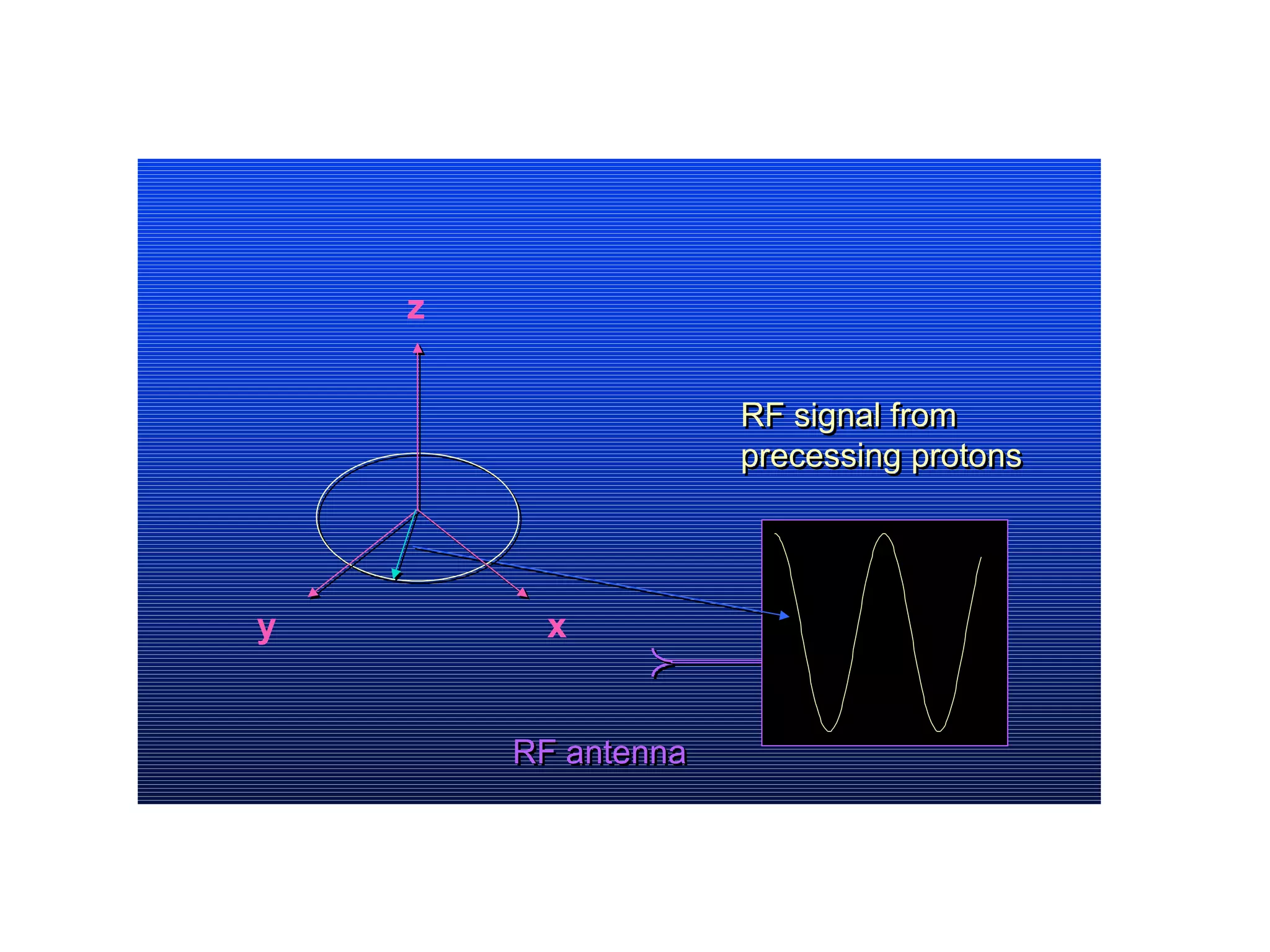
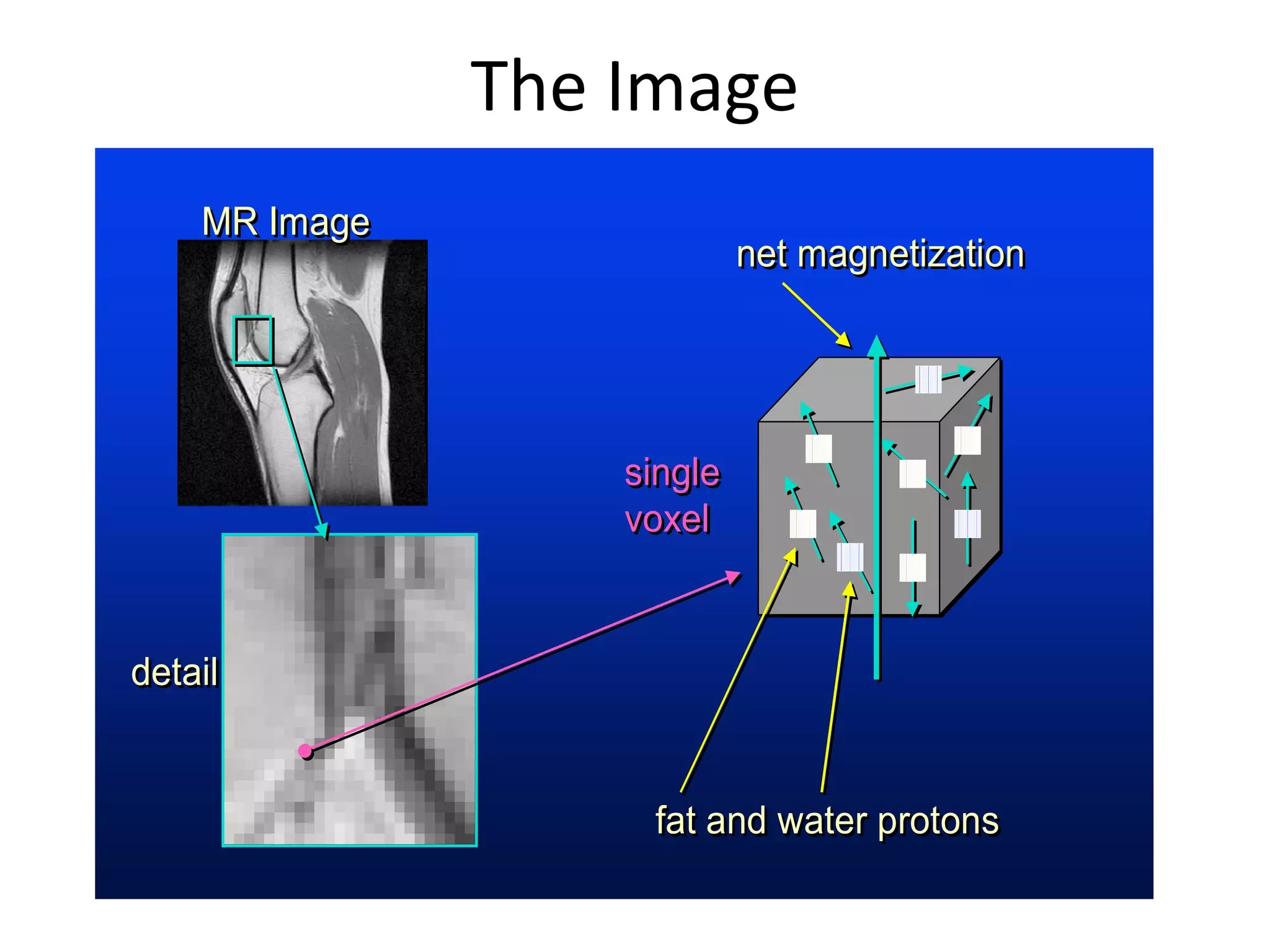
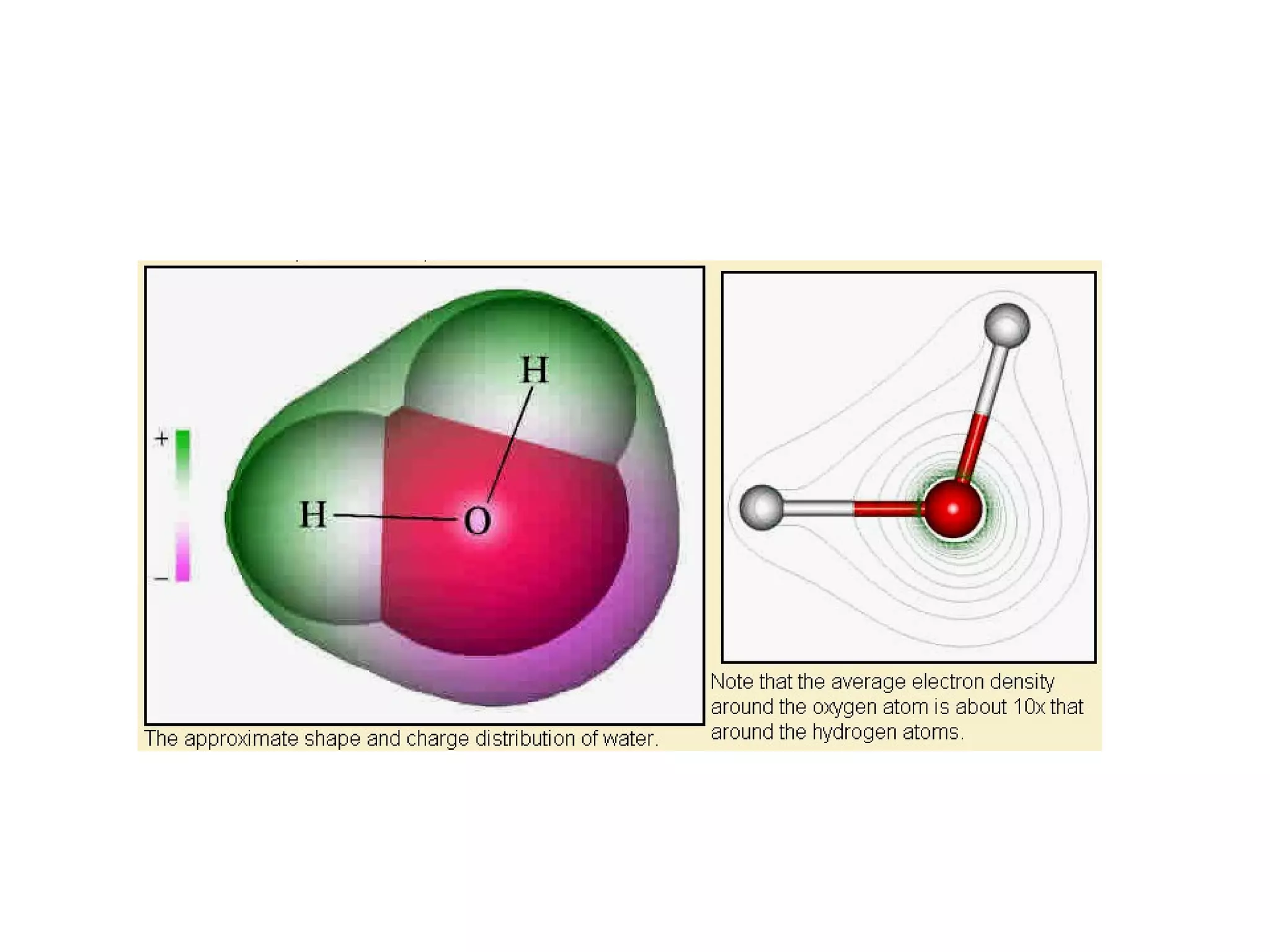
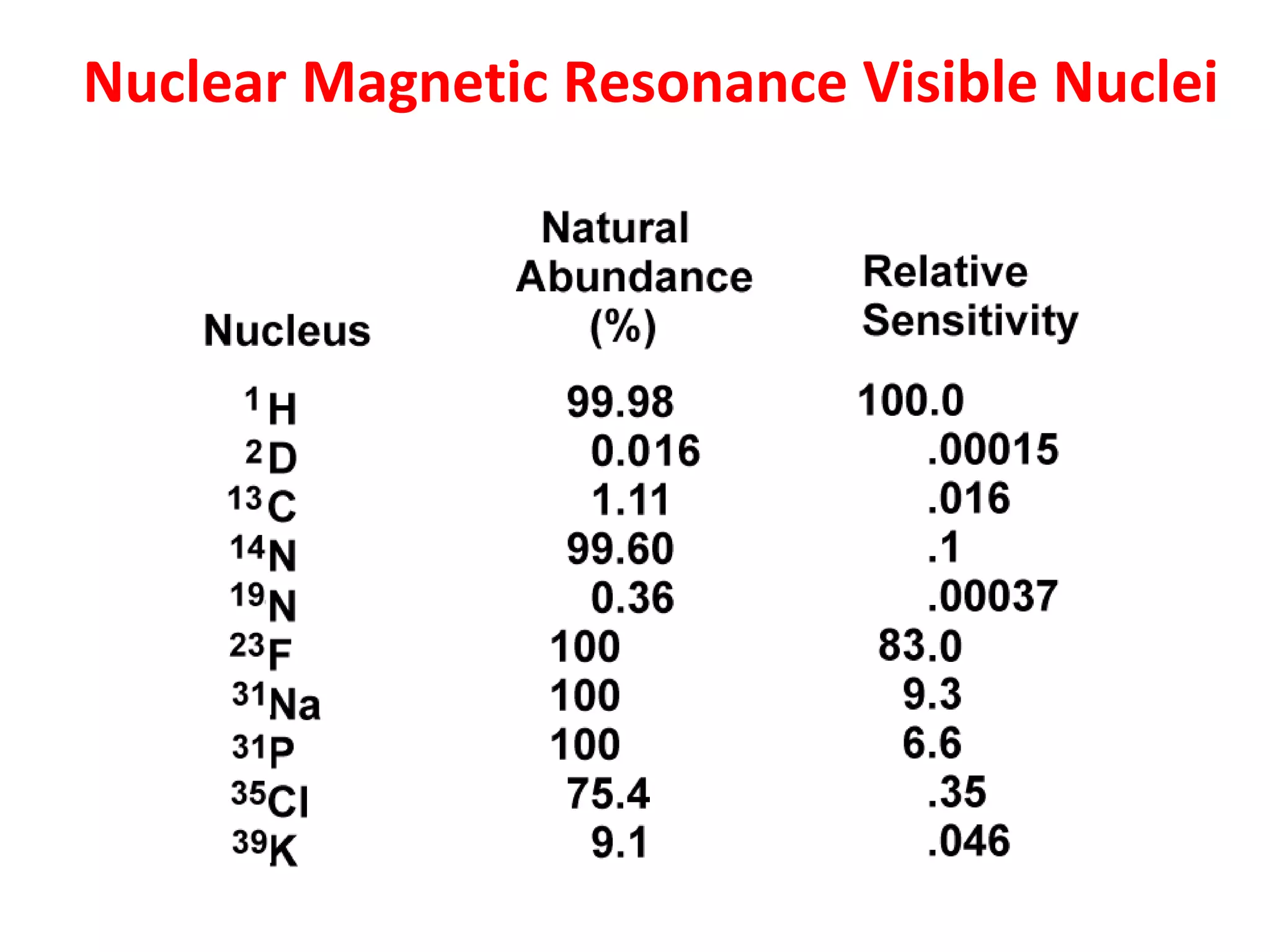
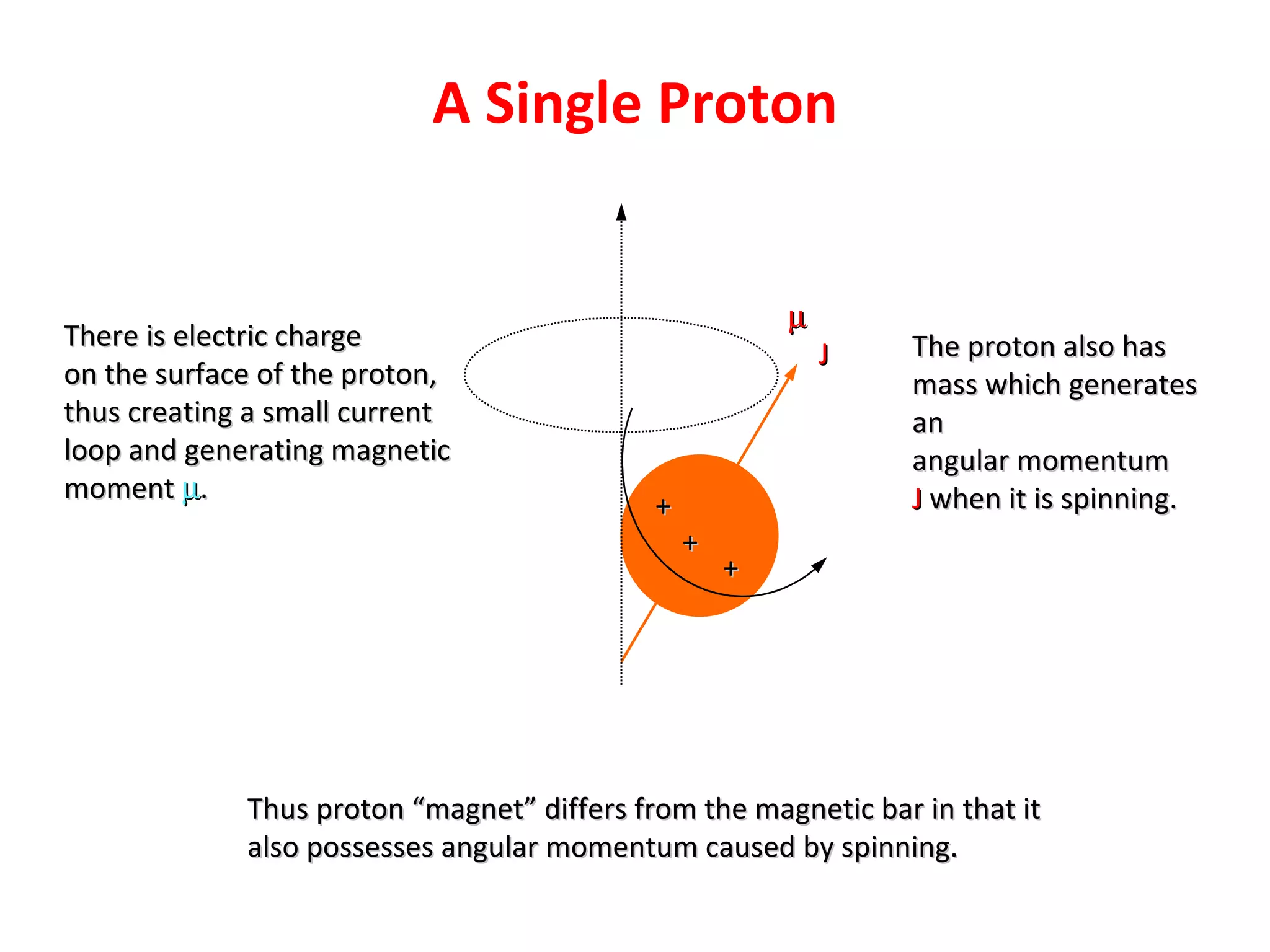
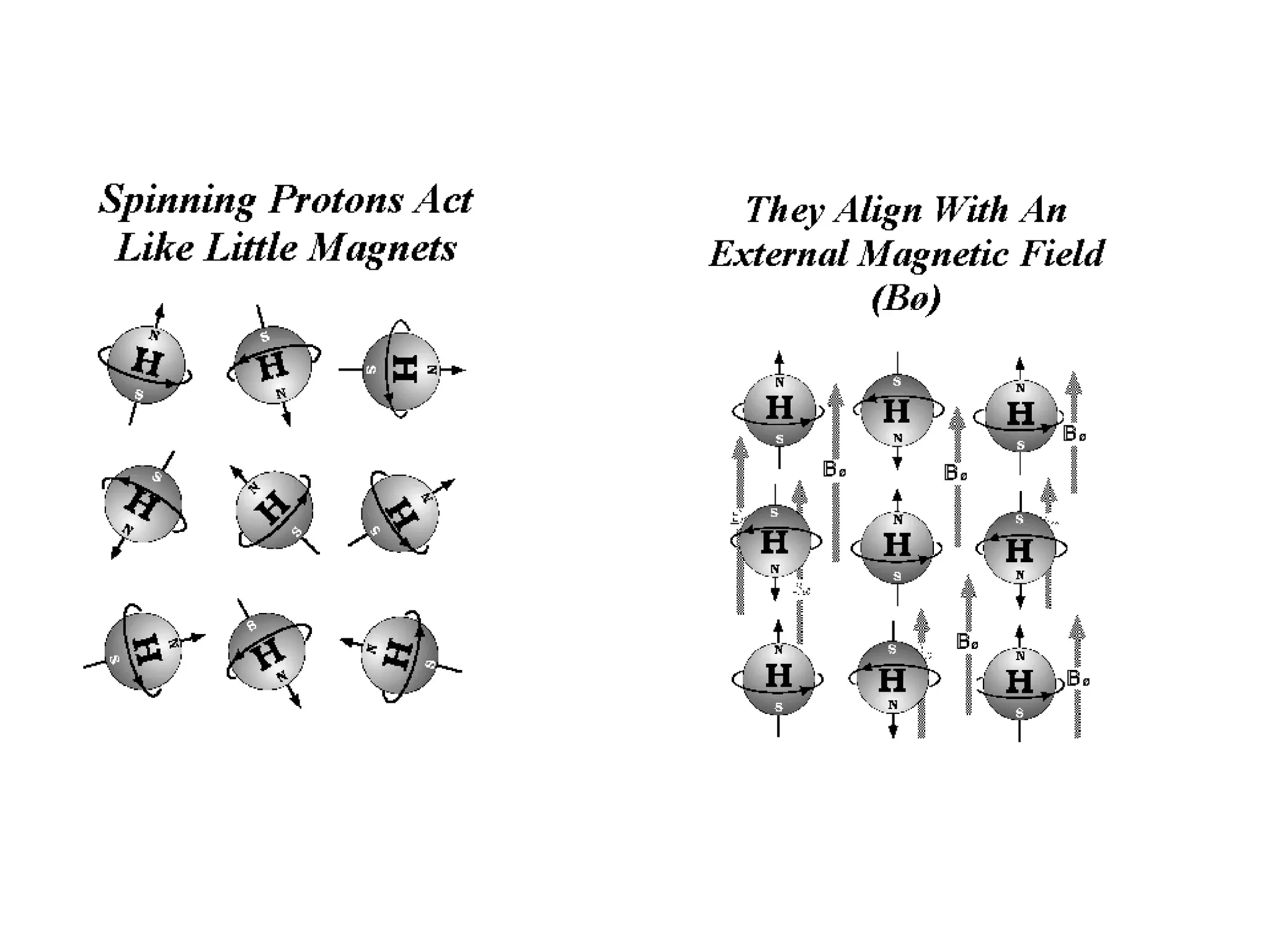
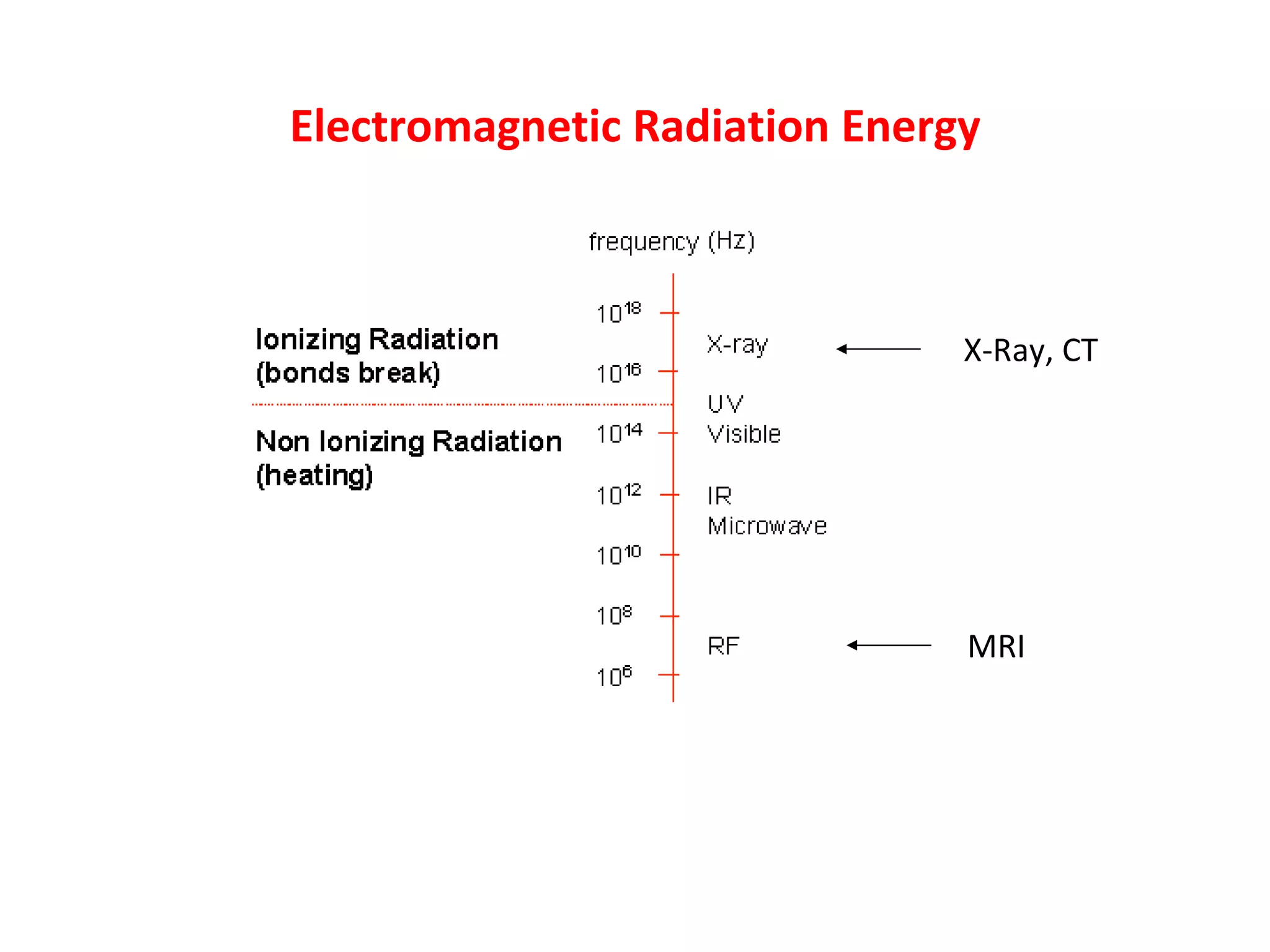
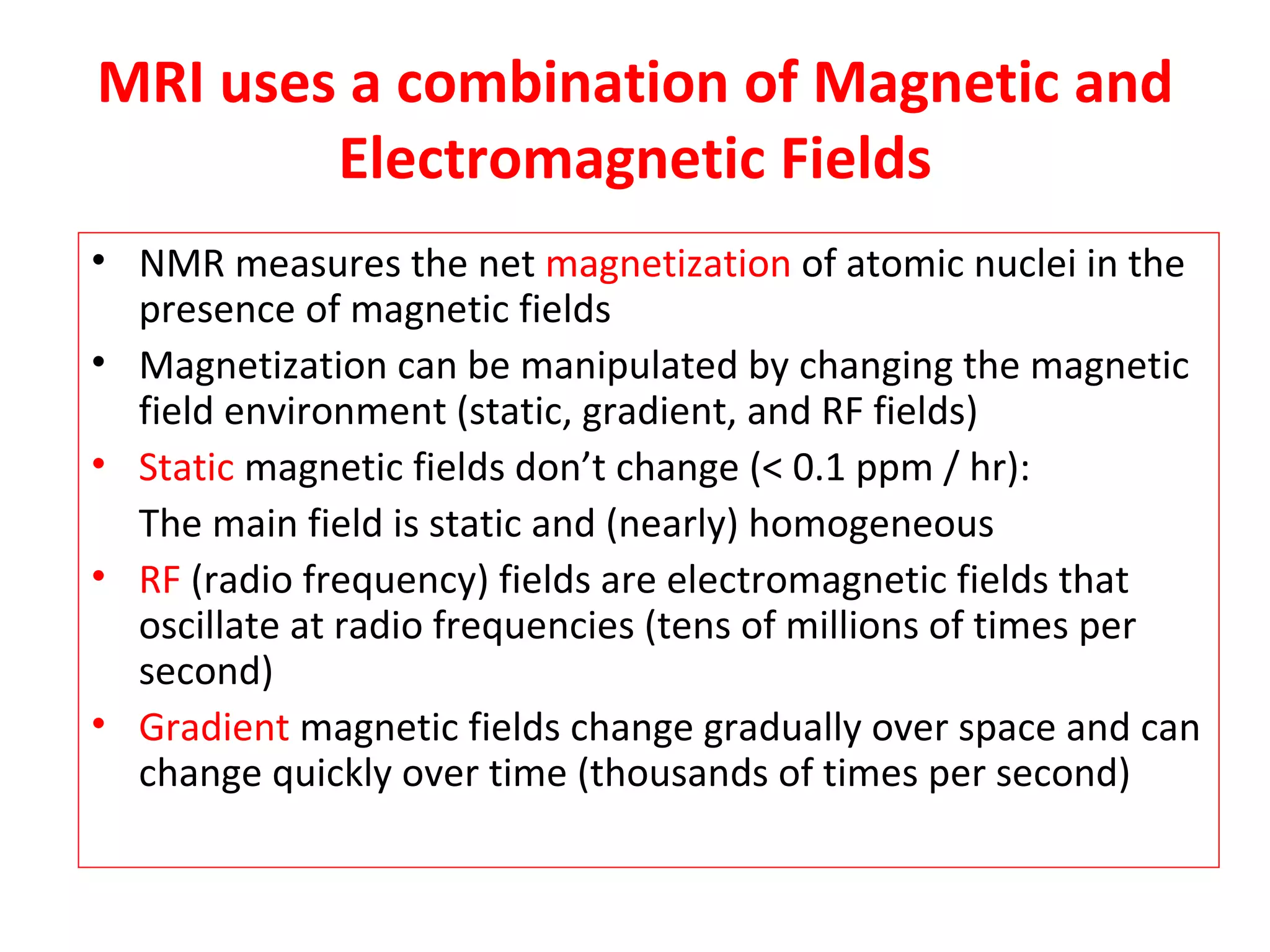
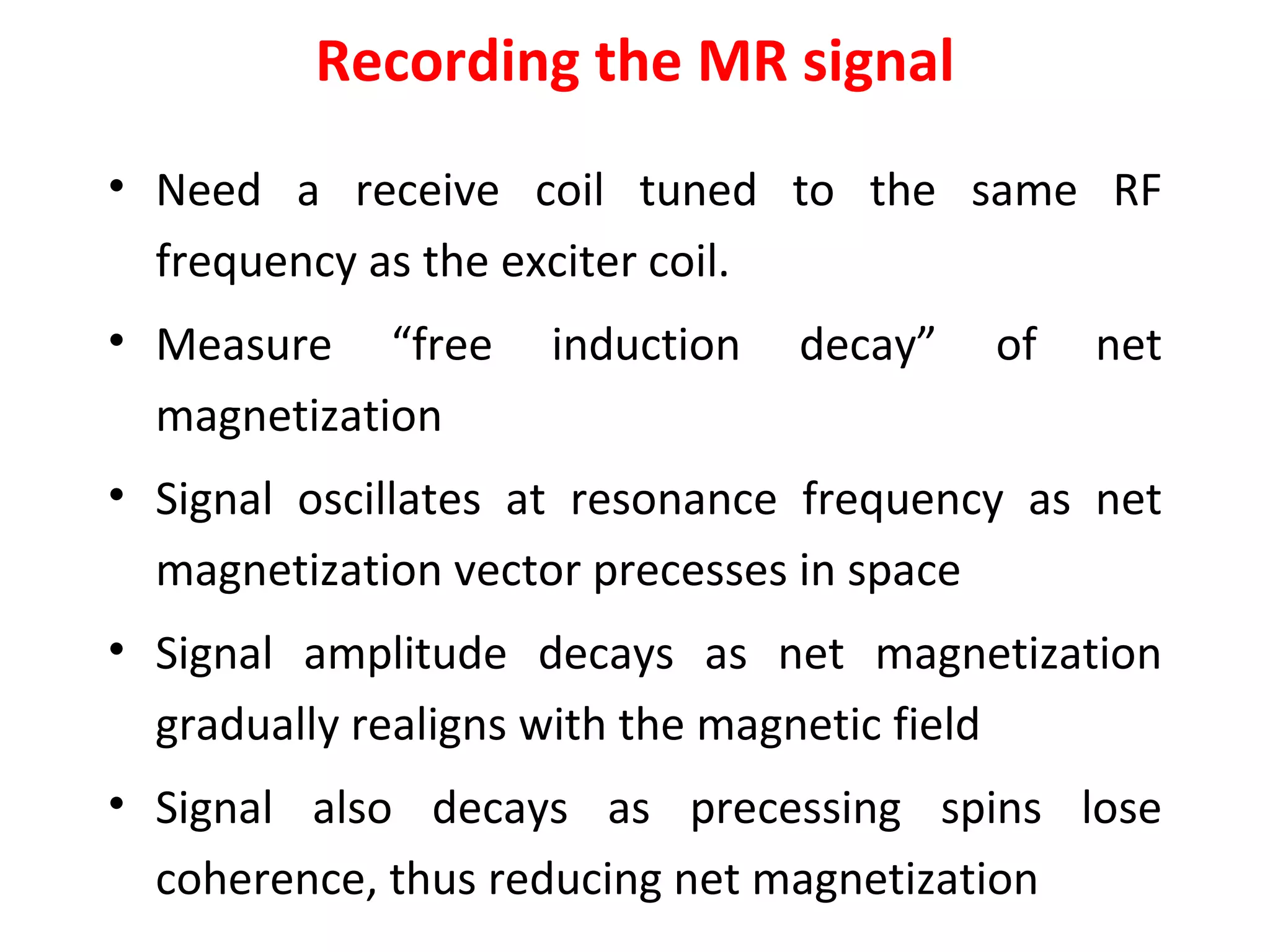
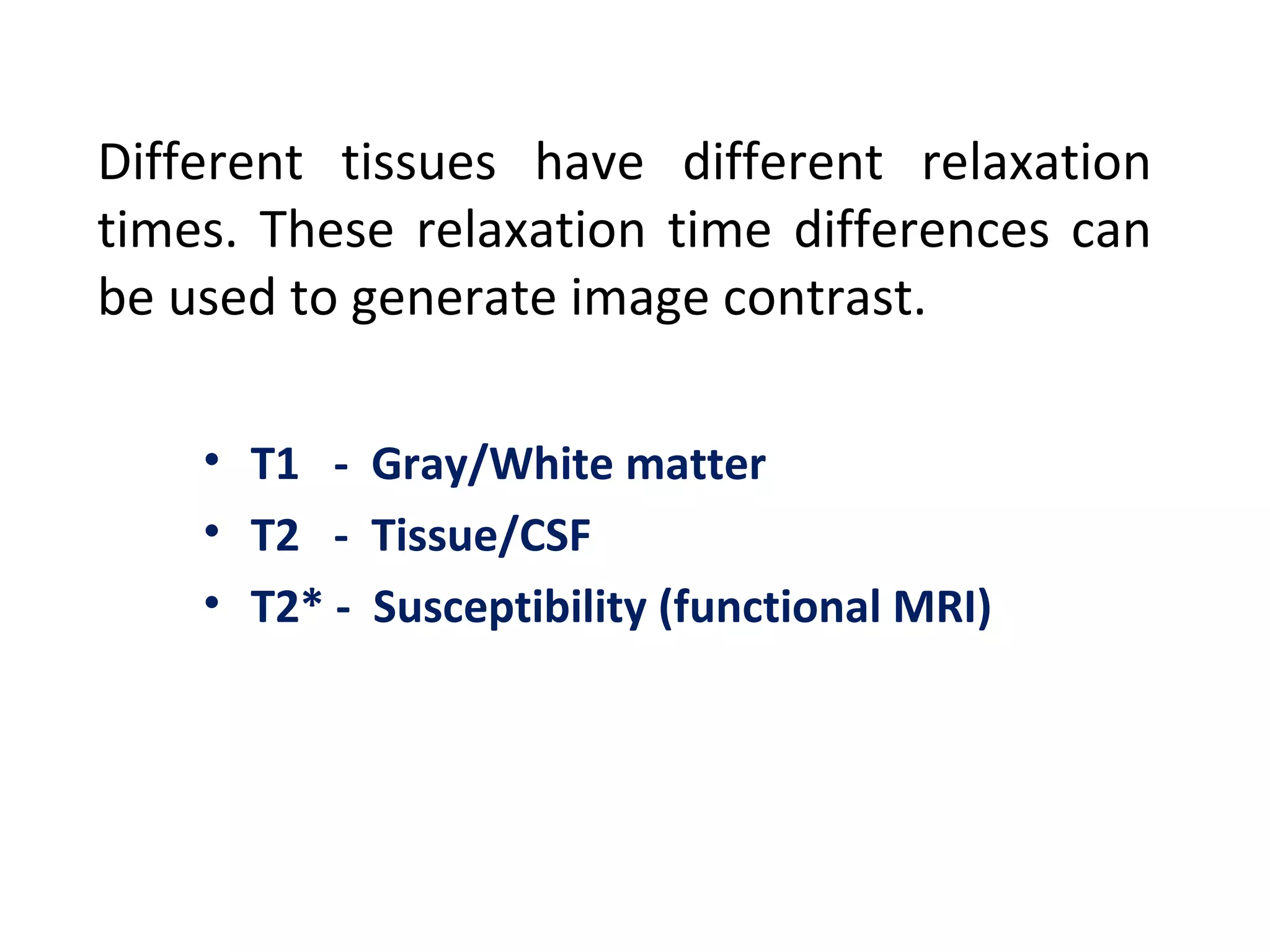
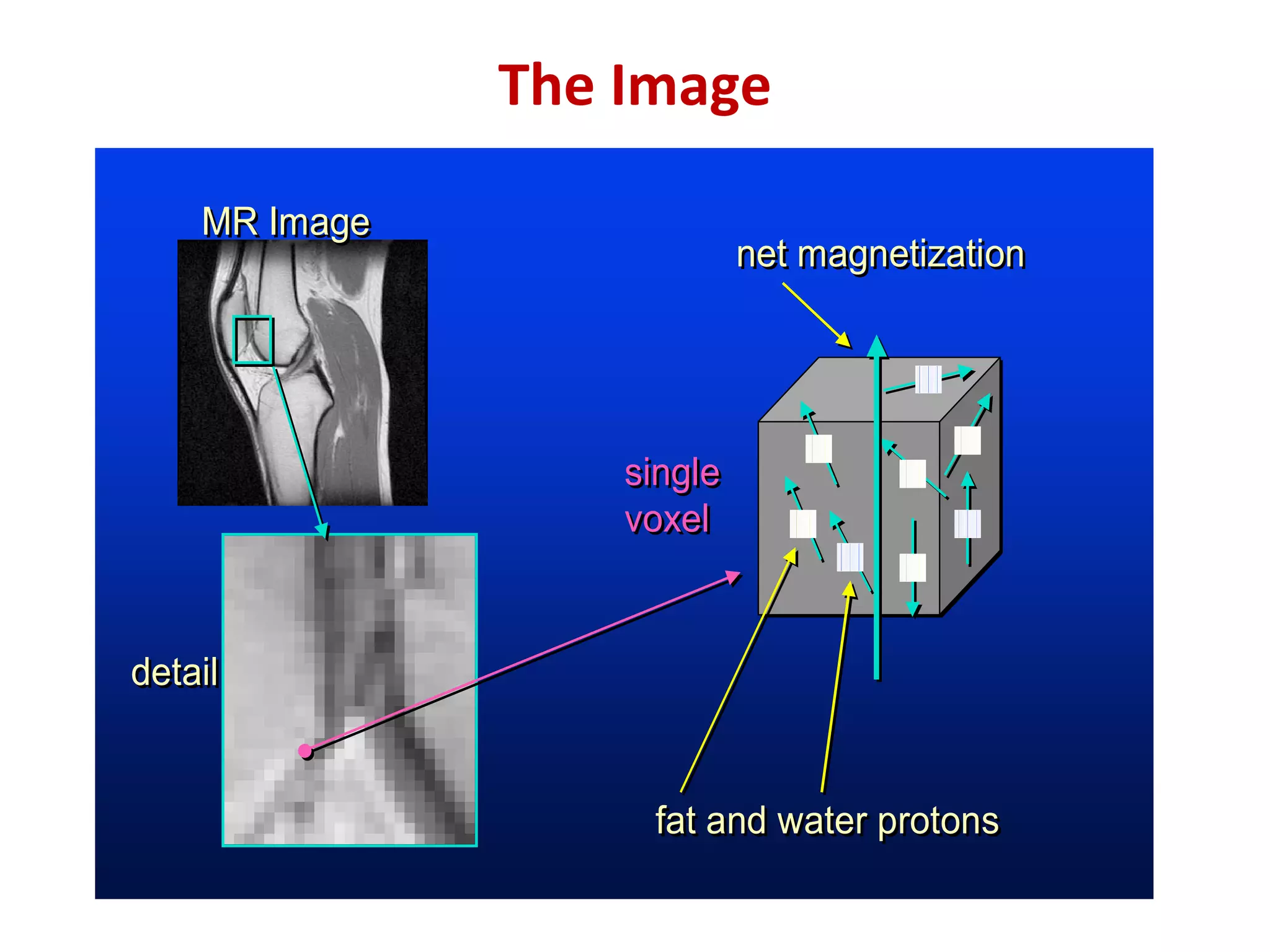
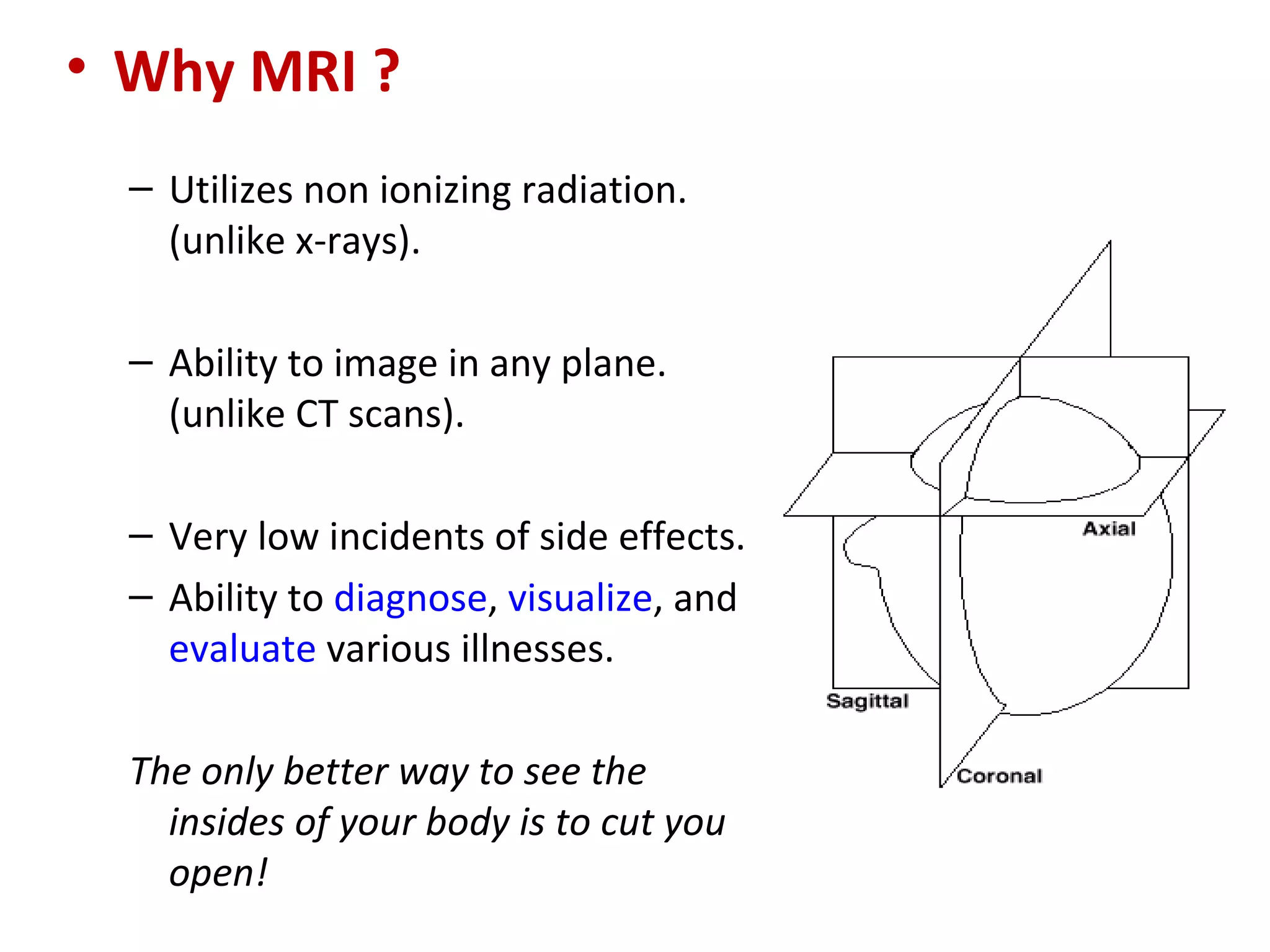
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the body. MRI works by aligning hydrogen atoms in the body using magnetism and radio waves, and detecting the radio signal emitted as the atoms relax back to their normal state. Different tissues produce different signal relaxations, allowing MRI to distinguish between tissues and create detailed images. MRI is useful for examining many parts of the body without using ionizing radiation.