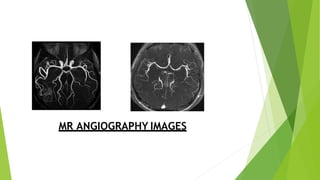
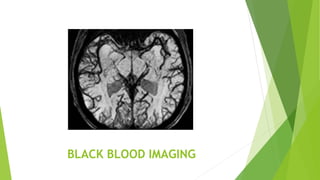
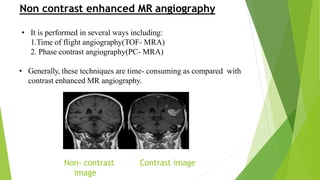
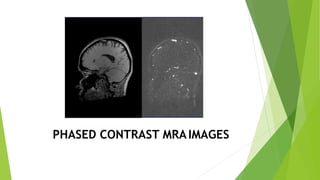
MR angiography is a type of MRI scan that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide pictures of blood vessels without using a catheter. It has advantages over conventional angiography in that it is less invasive, less expensive, and faster. Disadvantages include not depicting small vessels or slow blood flow as well. There are various techniques used in MR angiography including contrast enhanced MRA, which uses gadolinium contrast to visualize vascular structures, and non-contrast MRA such as time-of-flight angiography and phase contrast angiography. Artifacts that can occur include metal artifacts from implanted devices and blooming artifacts around paramagnetic substances.