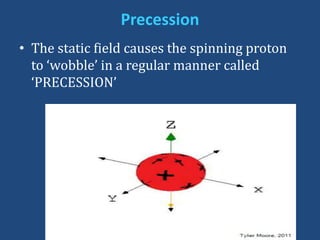
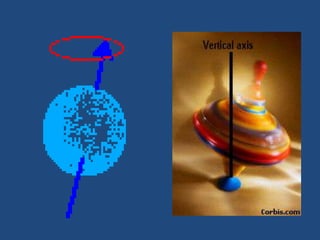
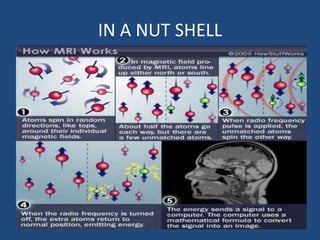
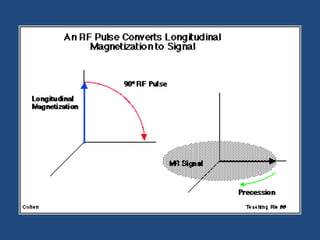
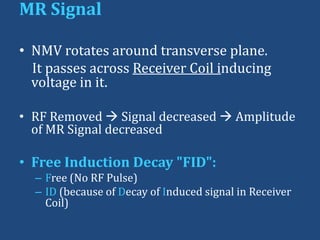
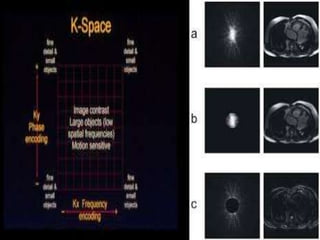
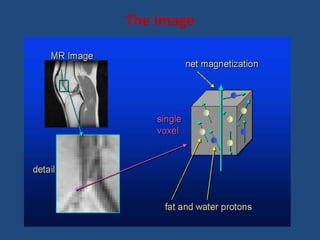
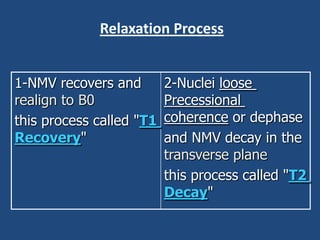
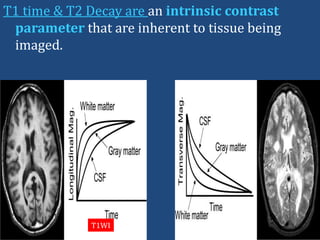
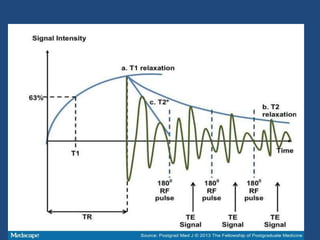
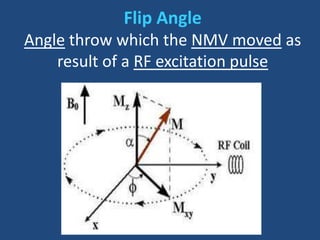
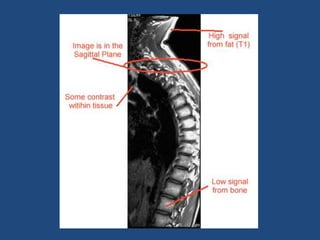
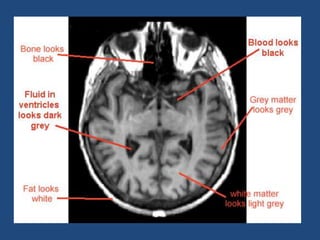
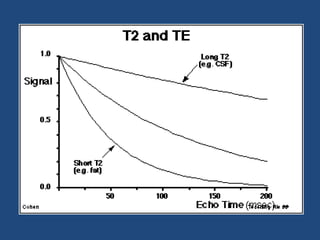
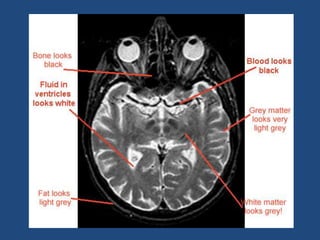
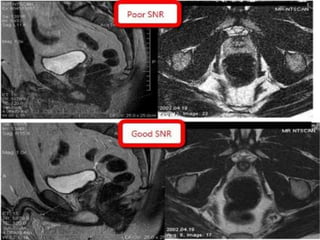
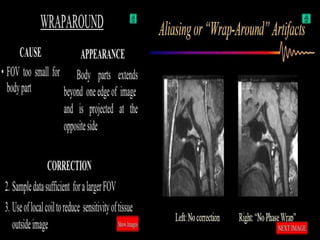
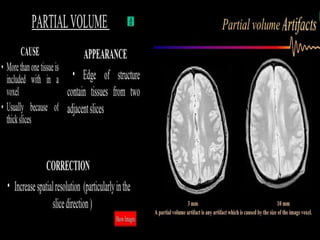
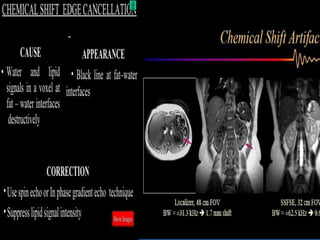
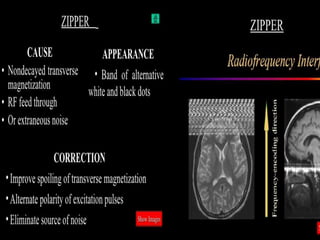
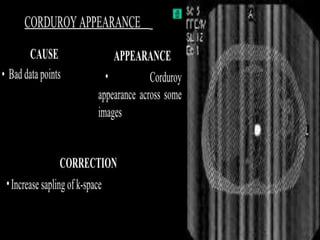
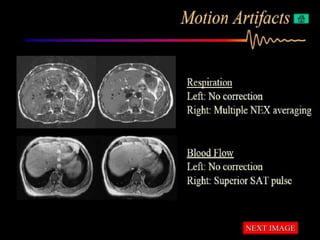
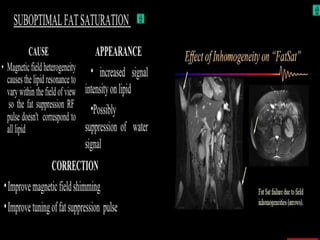
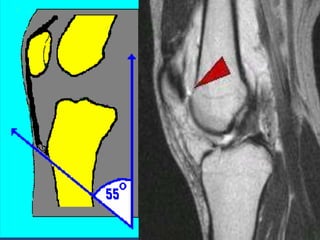
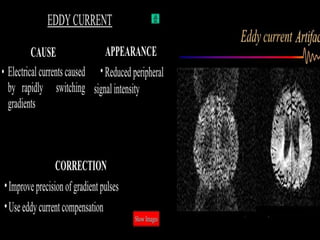
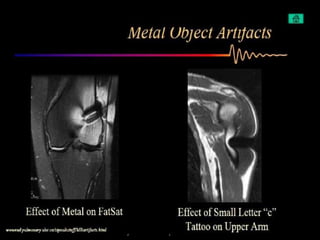
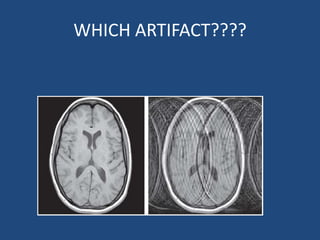
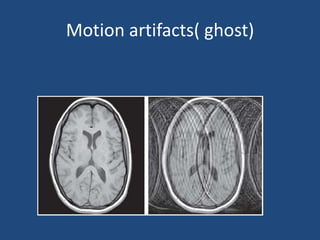
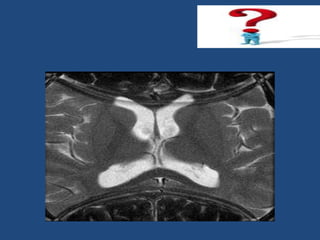
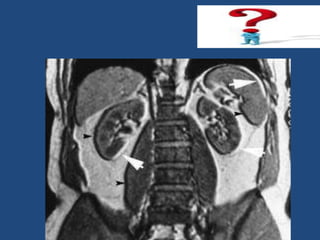
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of the inside of the body. It works by aligning hydrogen atoms in water molecules and fat in tissues when placed in a magnetic field. Radio waves are then used to stimulate the hydrogen atoms, which emit signals as they relax back to their original positions. These signals can be used to construct detailed images of tissues and organs inside the body. The document discusses key concepts in MRI physics including precession, relaxation times T1 and T2, spin echo and gradient echo sequences, and how varying pulse sequence parameters affects contrast in the resulting images.