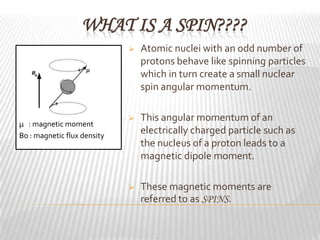
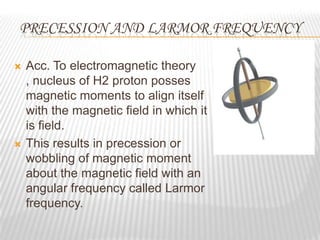
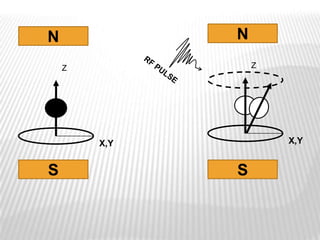
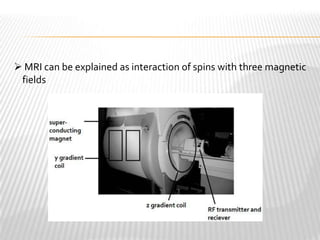
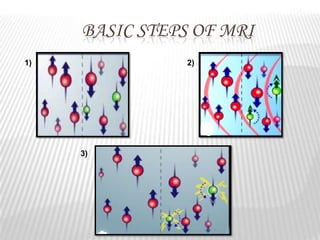
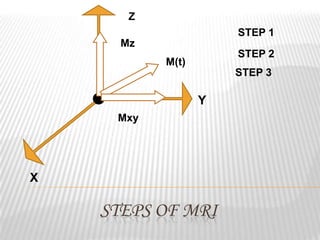
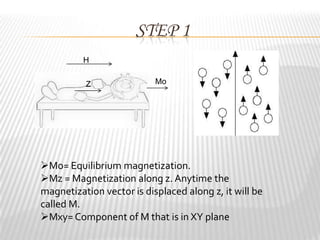
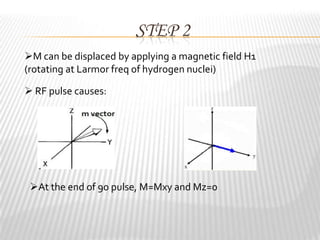
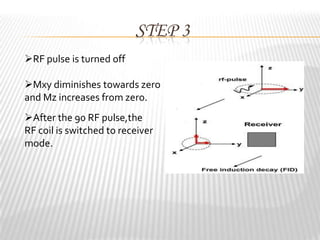
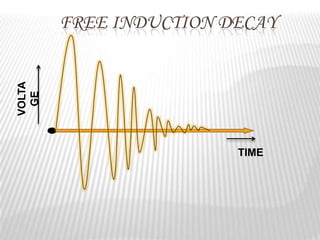
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the internal structures of the body. MRI works by aligning the spin of hydrogen atoms in the body using strong magnetic fields and radio waves. When the radio waves are turned off, the hydrogen atoms send out signals as they relax and return to equilibrium, and these signals can be used to build up a detailed image of tissues and organs in the body. The basic steps of MRI involve applying a magnetic field to align spins, using a radiofrequency pulse to excite the spins and produce a signal, and detecting the signal as spins relax back to equilibrium.