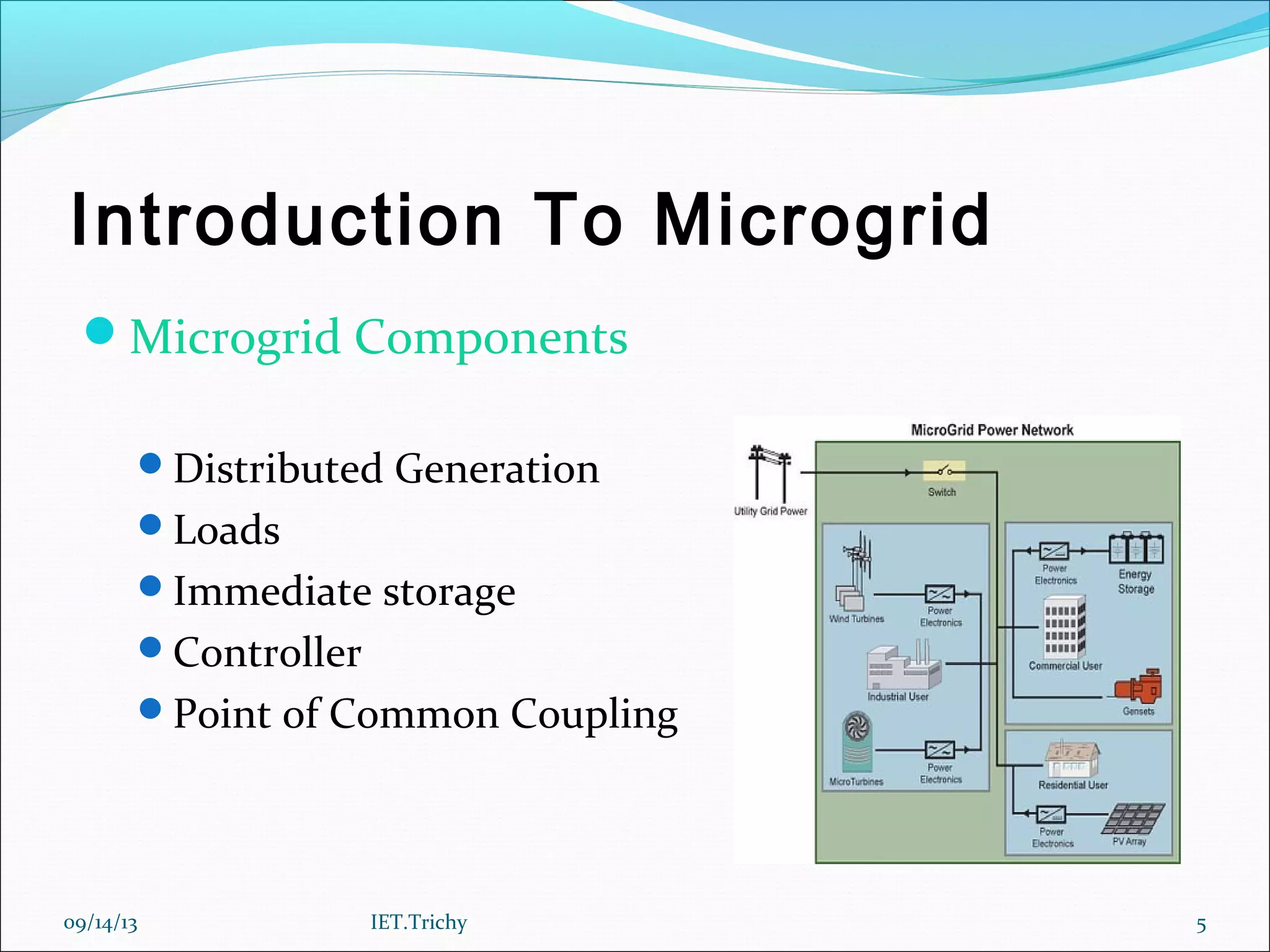
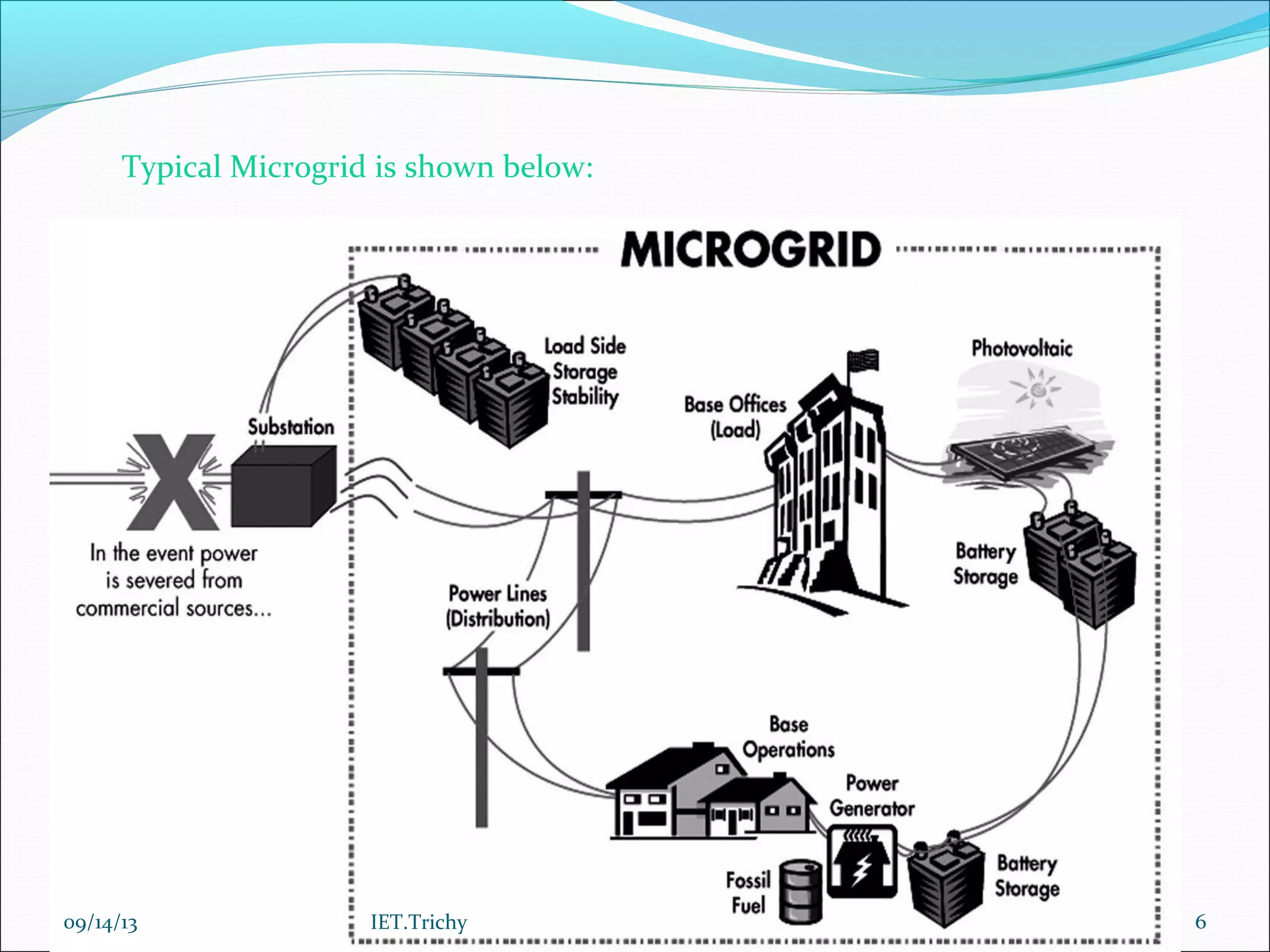
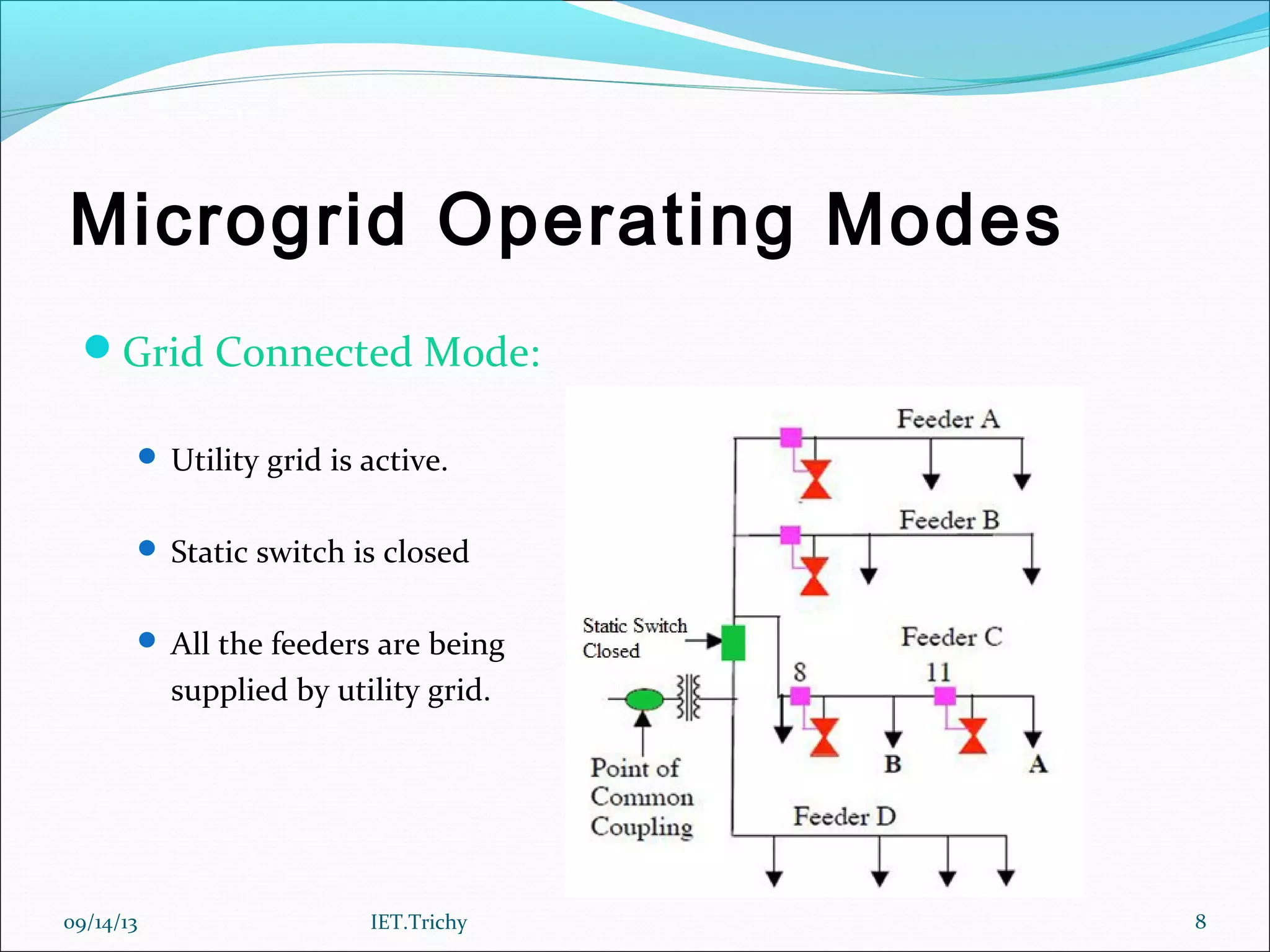
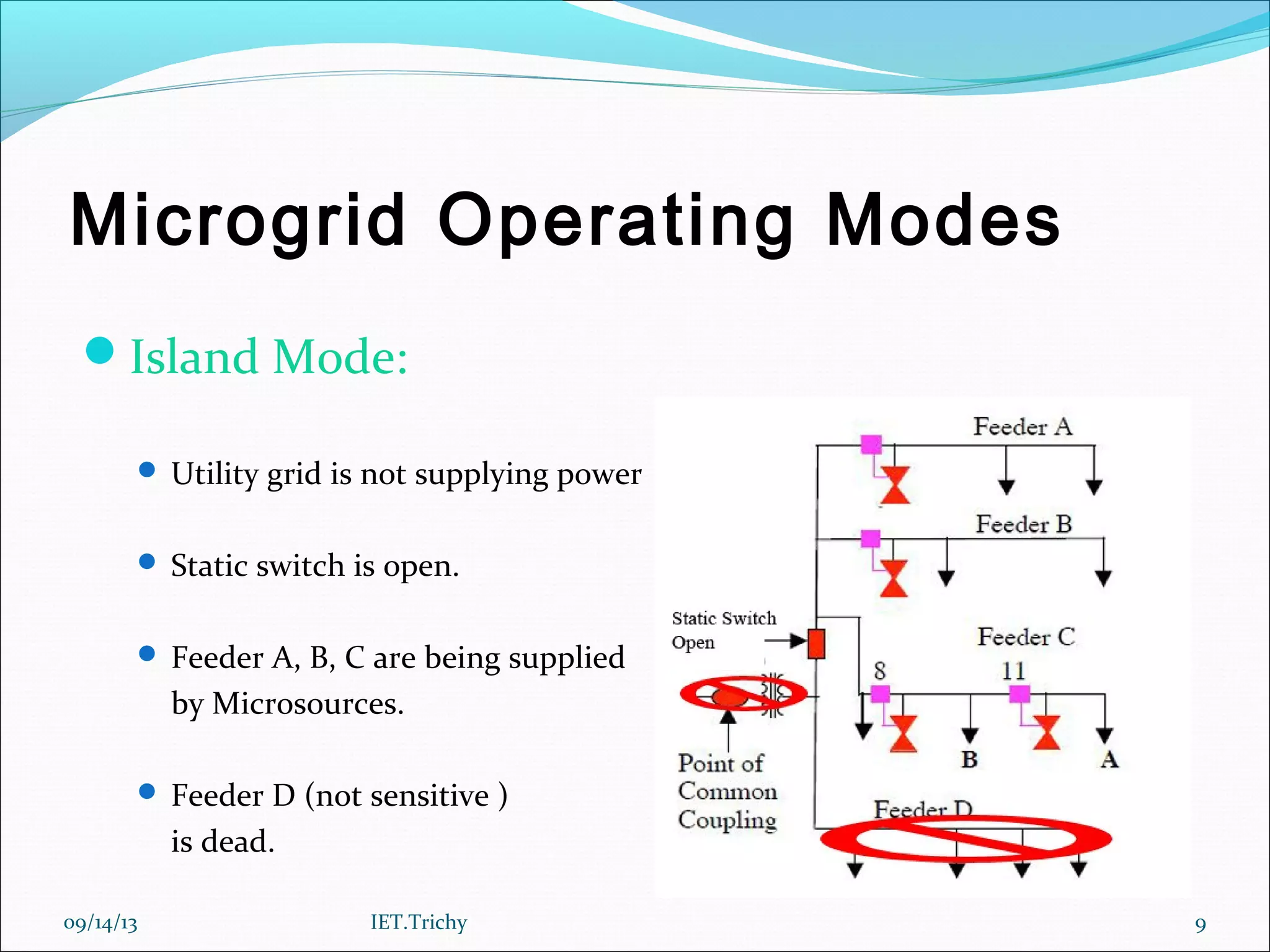
The document outlines a presentation on microgrids. It begins with an introduction that defines a microgrid as a small-scale power supply network designed to provide power for a small community using various distributed energy sources. It then discusses microgrid components and operating modes when connected to or isolated from the main grid. The document also notes the need for microgrids to provide reliable local power and reduce emissions and transmission losses. It concludes by discussing advantages like resilience and environmental benefits, challenges like protection and interconnection standards, and directions for future research.