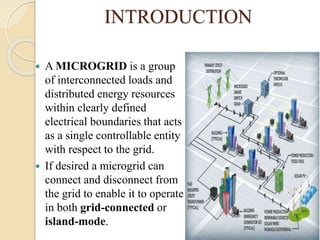
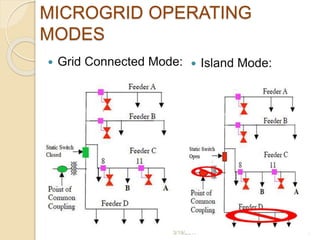
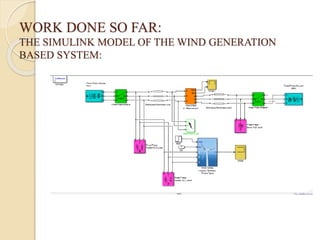
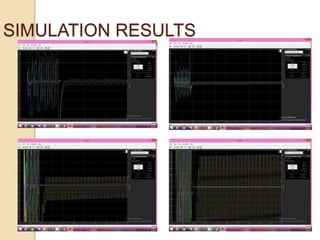
This thesis reviews the performance of hybrid grids that integrate distributed generation sources like solar and wind under various fault conditions. It explores microgrid operations in both grid-connected and island modes, highlighting advantages such as enhanced integration of renewable resources and improved power quality. Key challenges include coordination issues, voltage regulation, and potential high costs, with ongoing work focused on studying transient behaviors and fault responses using simulation tools.



![LITERATURE REVIEW
So far I have reviewed approx. 25 papers on micro grids
[1] F Kanellos et aI., "Micro-grid Simulation during Grid-
connected and Islanded modes of Operation," The
International Conference on Power Systems Transients,
(IPST'05), Montereal, 19-23 June 2005, Paper No. IPST05-113..
[2] Z. Chen and W. Kong, "Protection Coordination Based on
Multi Agent for Distribution Power System with
Distribution Generation Units," 2007, pp. 1-5.
[3] T. Quoce et aI., "Dynamics Analysis of an Insulated
Distribution Network," IEEE Proceedings of Power System
Conference and Exposition, Vol. 2, 2004, pp.815-821.
[4] C.L.T Borges, and D.M. Falcao, "Impact of
Distributed Generation Allocation and Sizing on Reliability,
Losses, and Voltage Profile", 2003 IEEE Bologna Power
Tech Conference Proceedings, Bologna, Volume 2, 23-26 June
2003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modifiedpptformtechproject-170319023411/85/Modified-ppt-for-mtech-project-4-320.jpg)