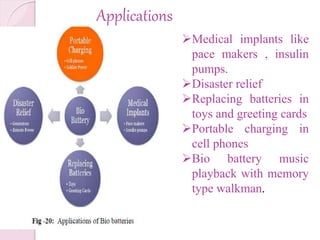
This document presents information on bio batteries. It begins with definitions, explaining that bio batteries generate electricity from renewable fuels like glucose by using enzymes to break glucose down, releasing electrons and protons. It then covers the history, types (passive and active systems), need, principles, and processes of bio batteries. The document discusses using glucose as a fuel, prototypes, applications, and advantages/disadvantages. It envisions bio batteries being used widely in the future.