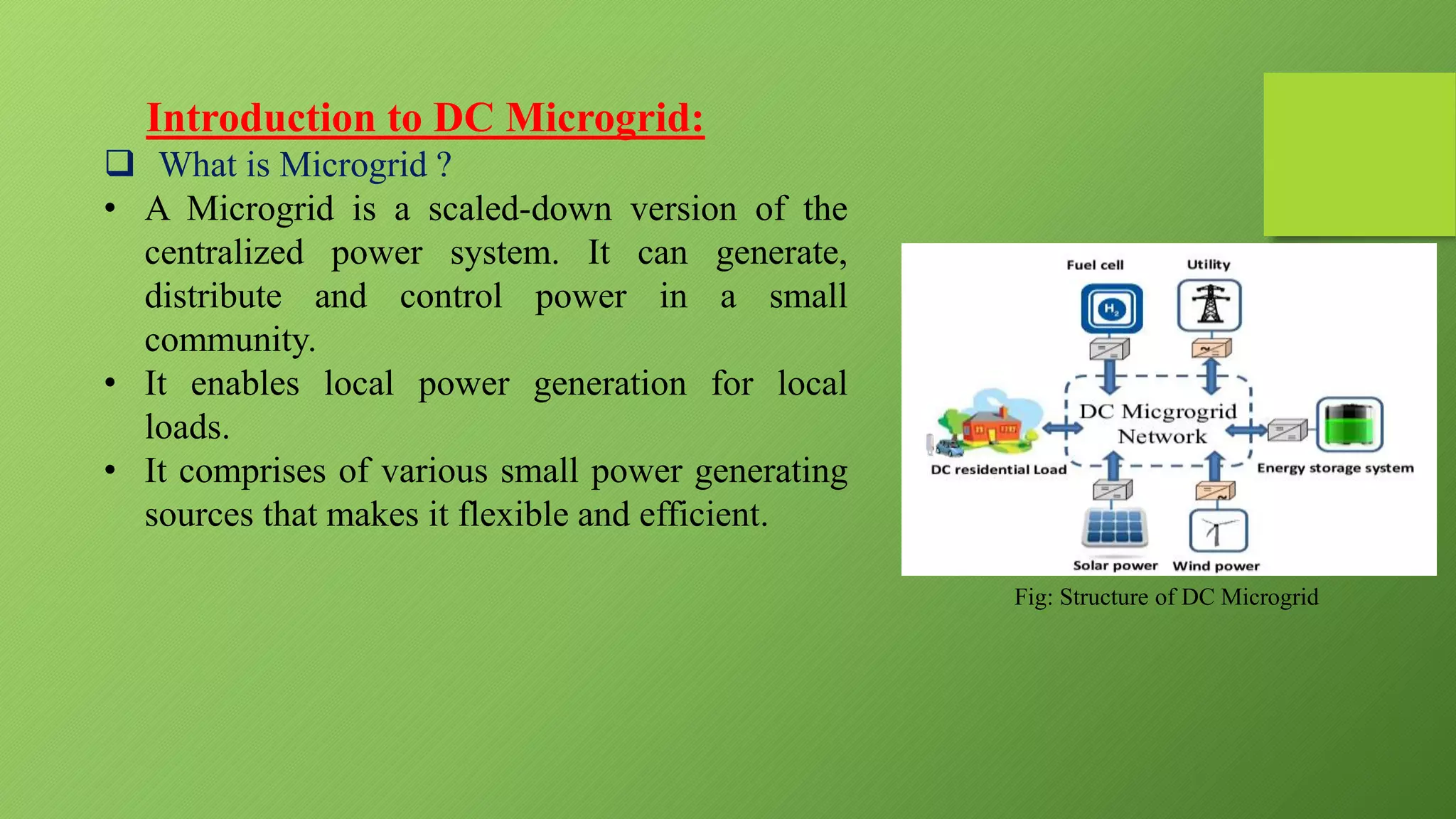
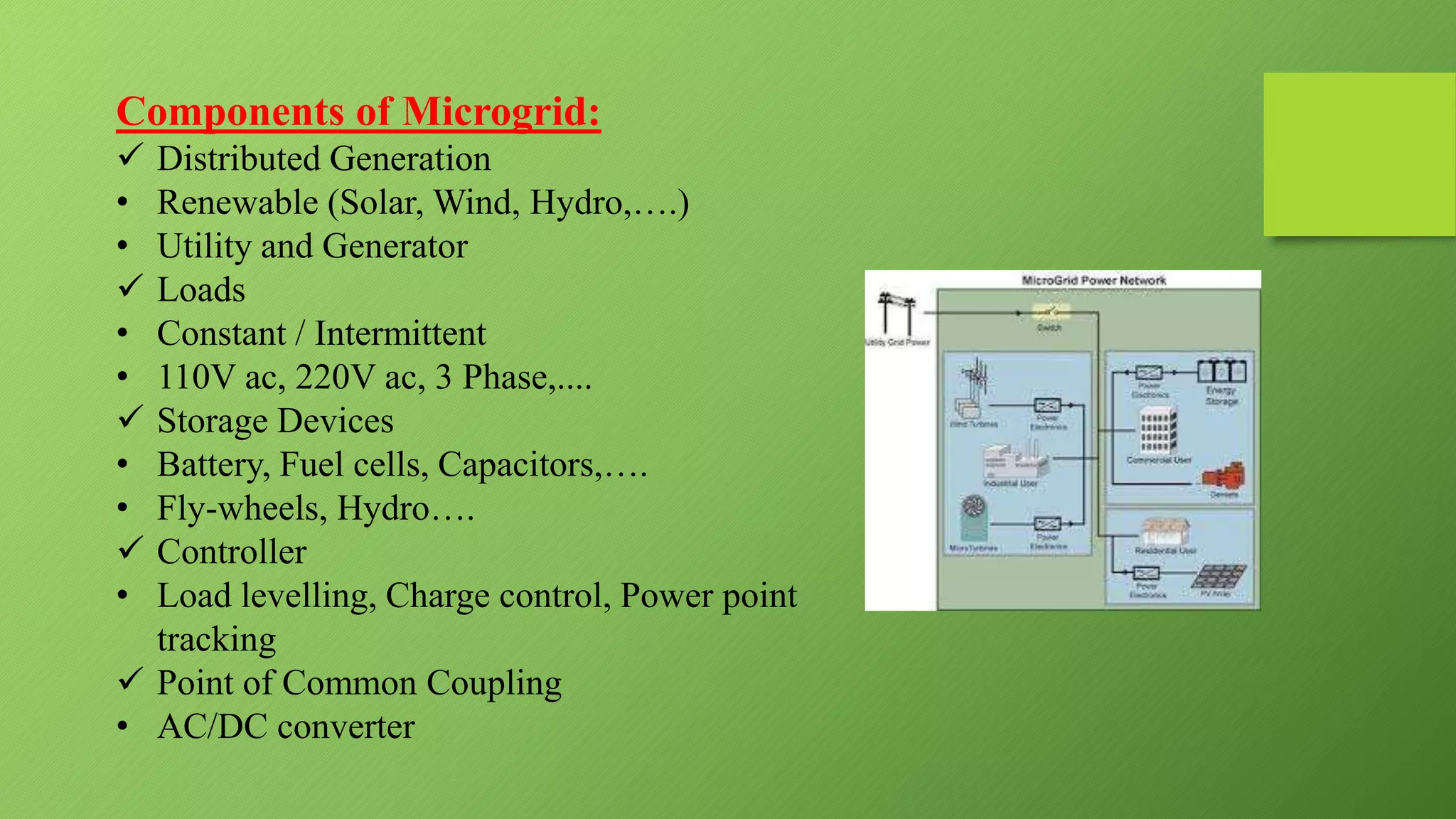
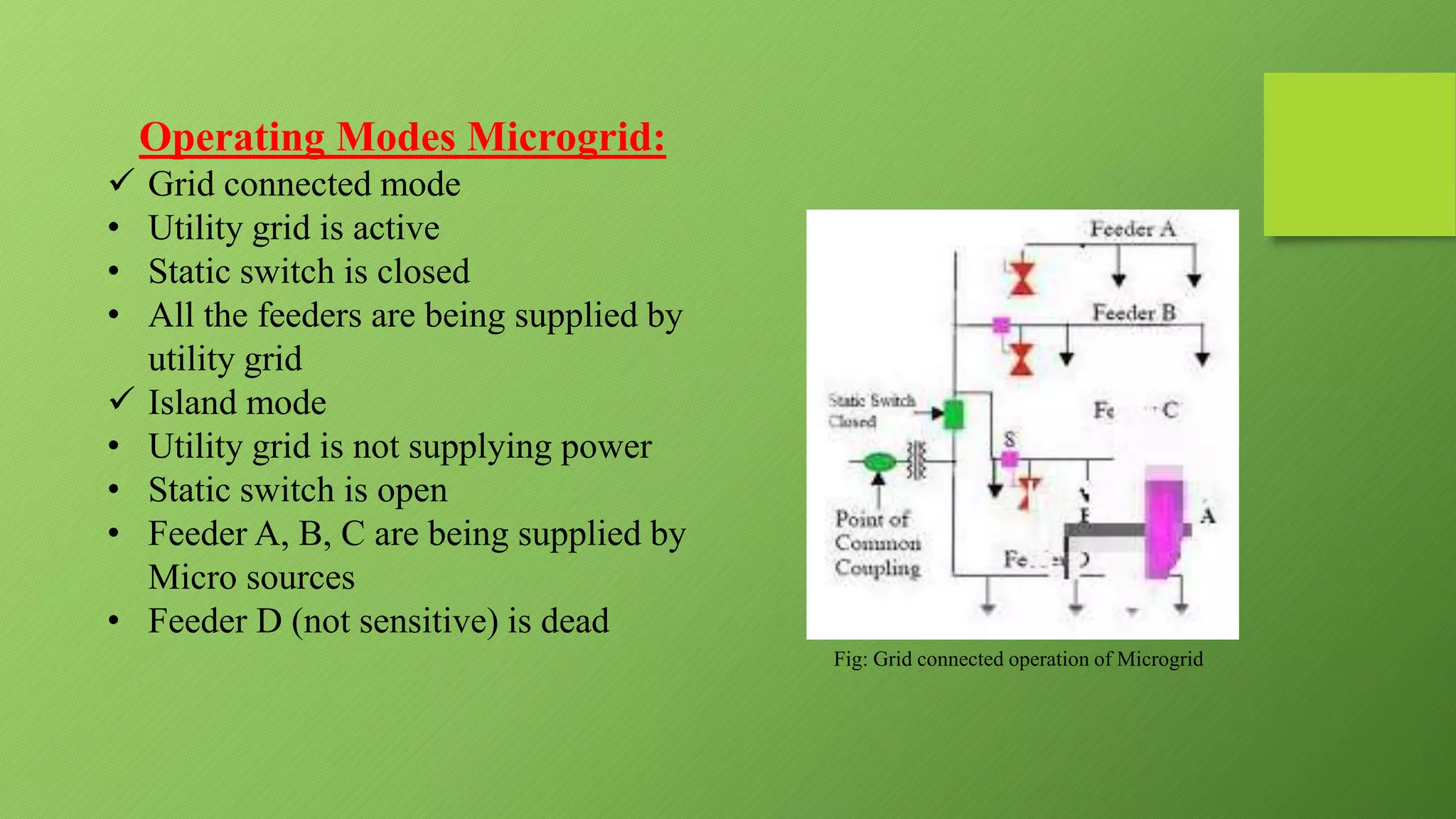
This presentation provides an overview of DC microgrids. It discusses the components of microgrids including distributed generation sources, loads, storage devices, and controllers. It describes the operating modes of microgrids as being either grid-connected or island mode. The presentation outlines the need for microgrids to provide backup power and enhance grid stability and resilience while being more efficient and environmentally friendly than conventional grids. It notes advantages such as improved reliability but also challenges involving battery storage and synchronization.