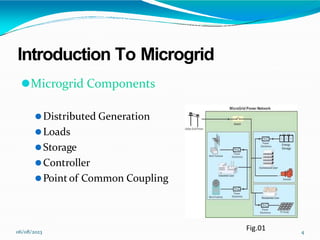
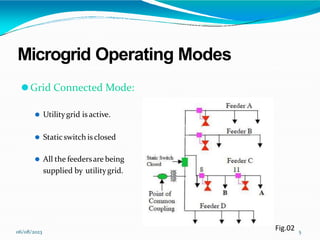
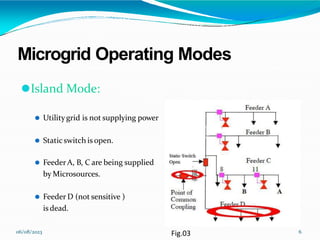
This document provides an overview of microgrids, including their definition, components, operating modes, advantages, and future research directions. A microgrid is a small-scale power supply network that enables local power generation for local loads from various small power sources. Microgrids can operate connected to or isolated from the main utility grid. They provide more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly power compared to conventional grids. Future research will focus on developing control and protection standards to facilitate the growth of microgrids.