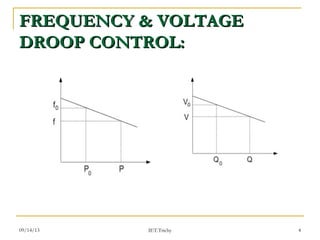
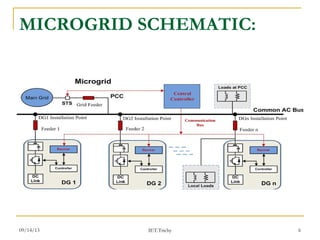
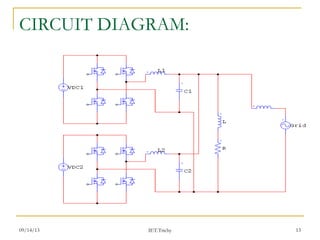
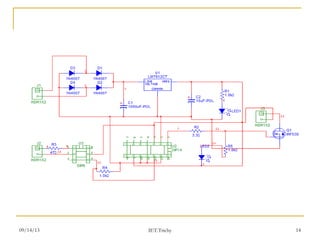
The document discusses voltage droop control in microgrids with distributed generators. It proposes a droop control scheme that uses local power measurements to adjust generator operating points for load sharing. The scheme calculates a reference voltage based on real power output and compares it to actual voltage to create an error signal. This signal is used to control inverters through PWM signals. The proposed system studies two distributed generation subsystems each with two inverters and loads. An integral control term is also used to regulate voltage and maintain reactive power sharing during real power disturbances. This configuration aims to improve power quality by reducing harmonic distortion.