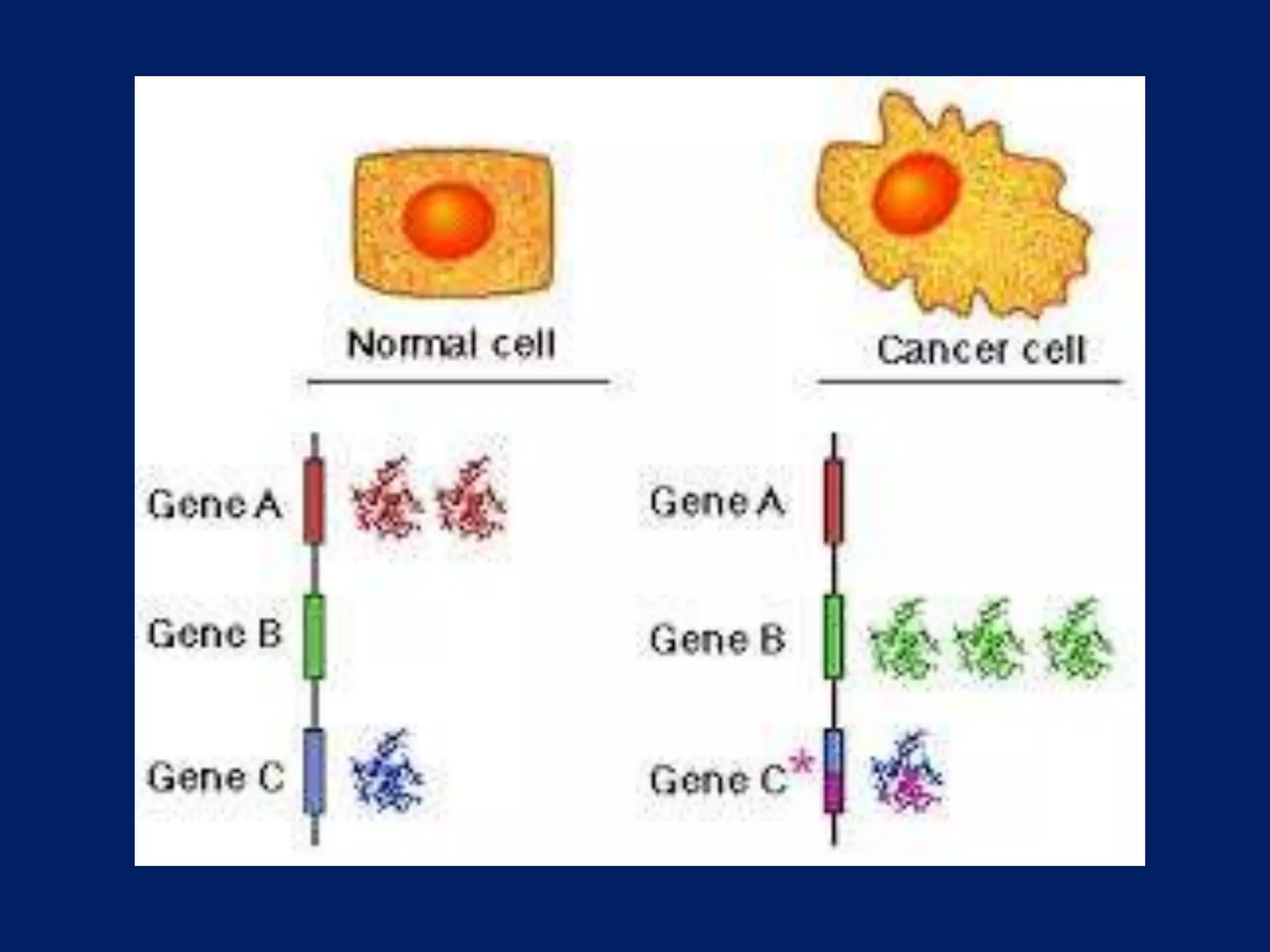
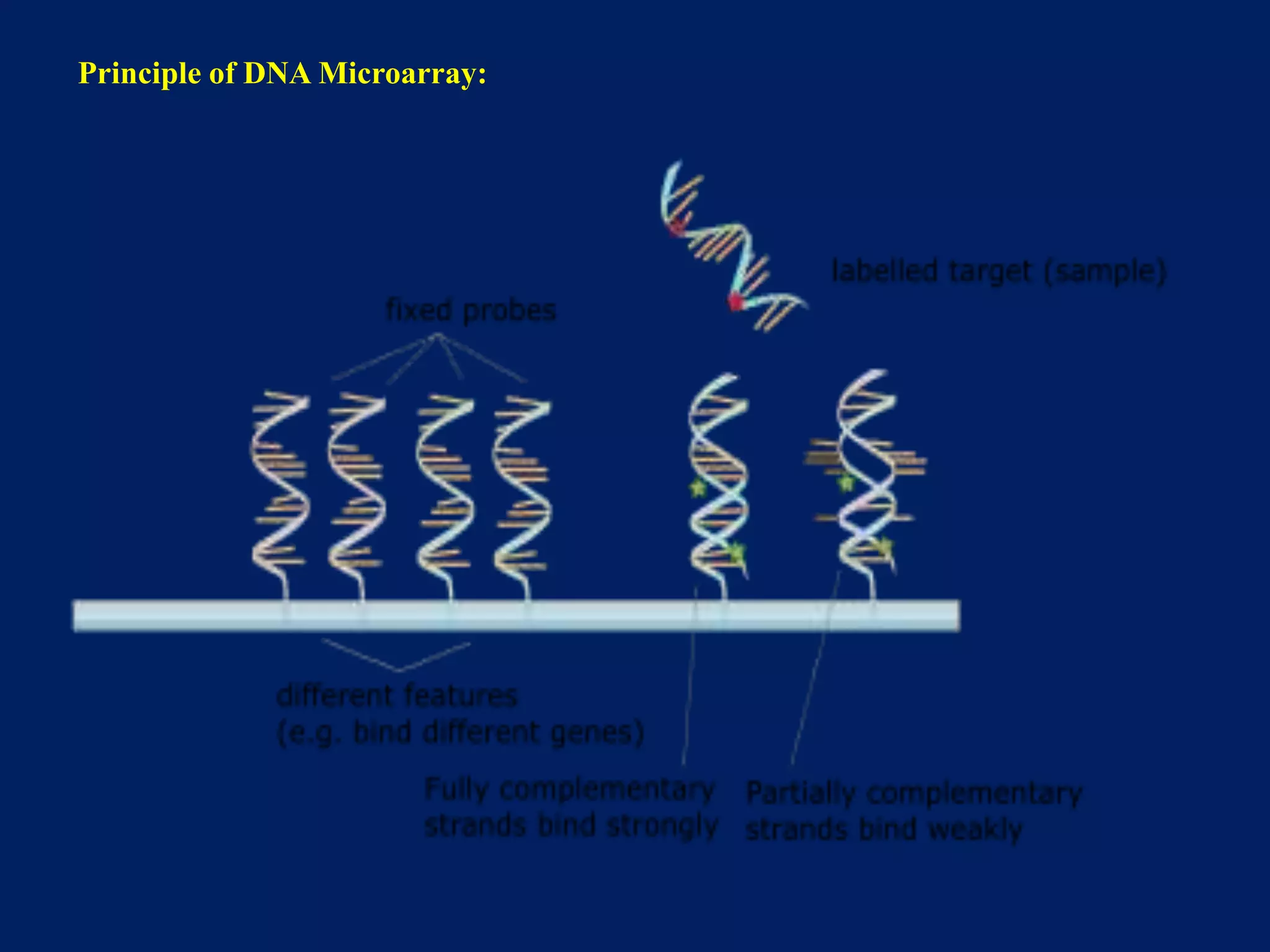
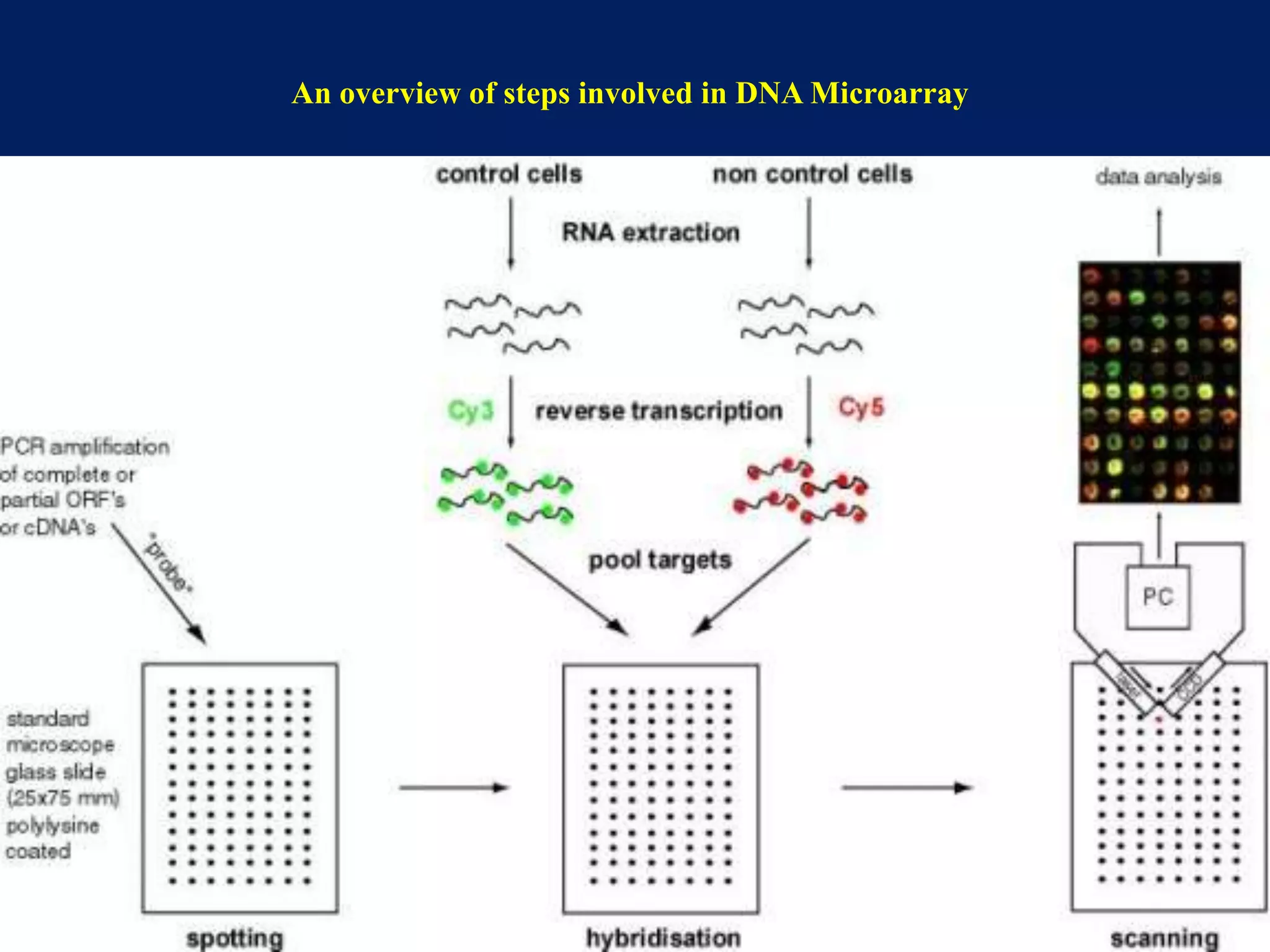
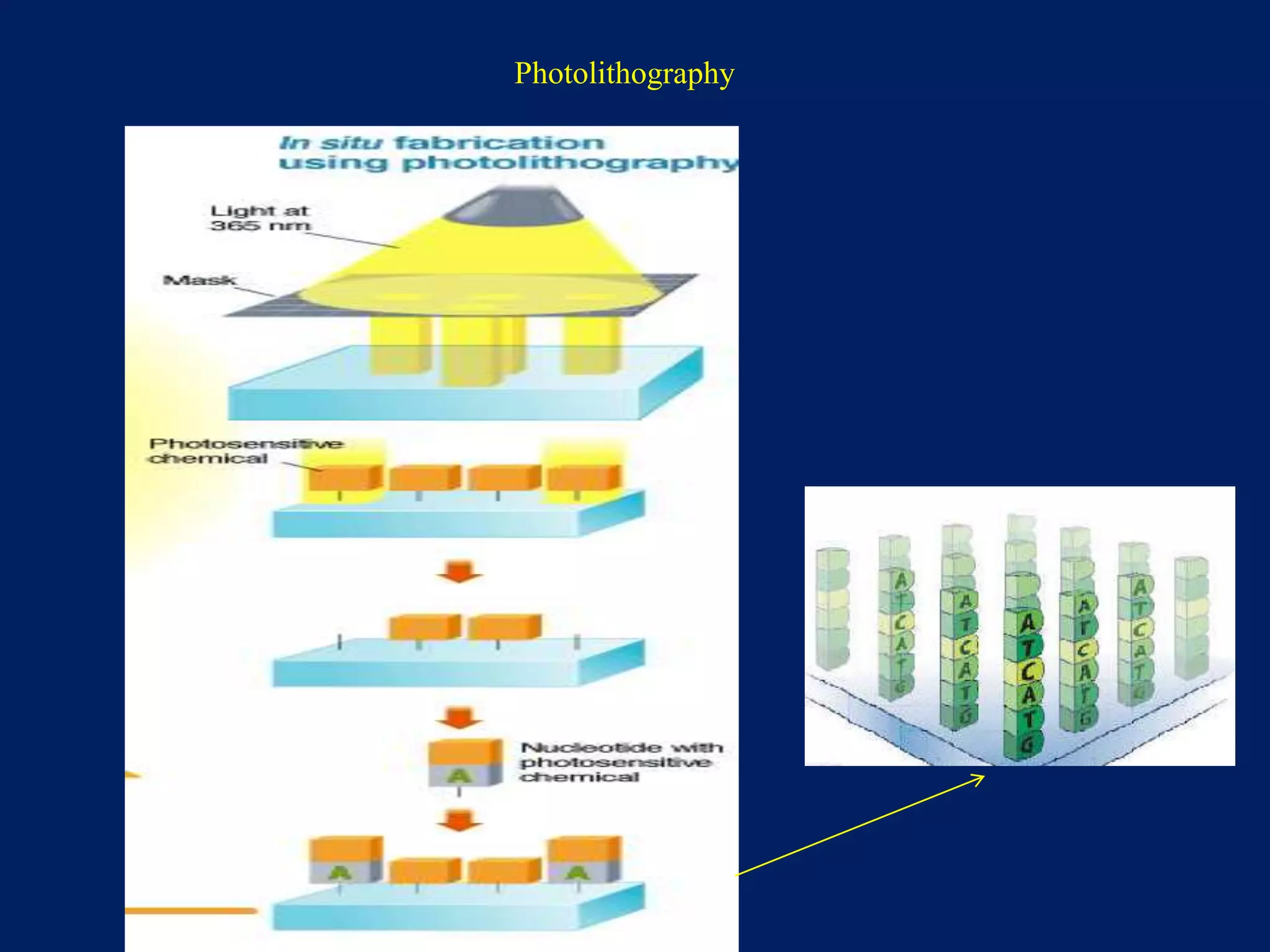
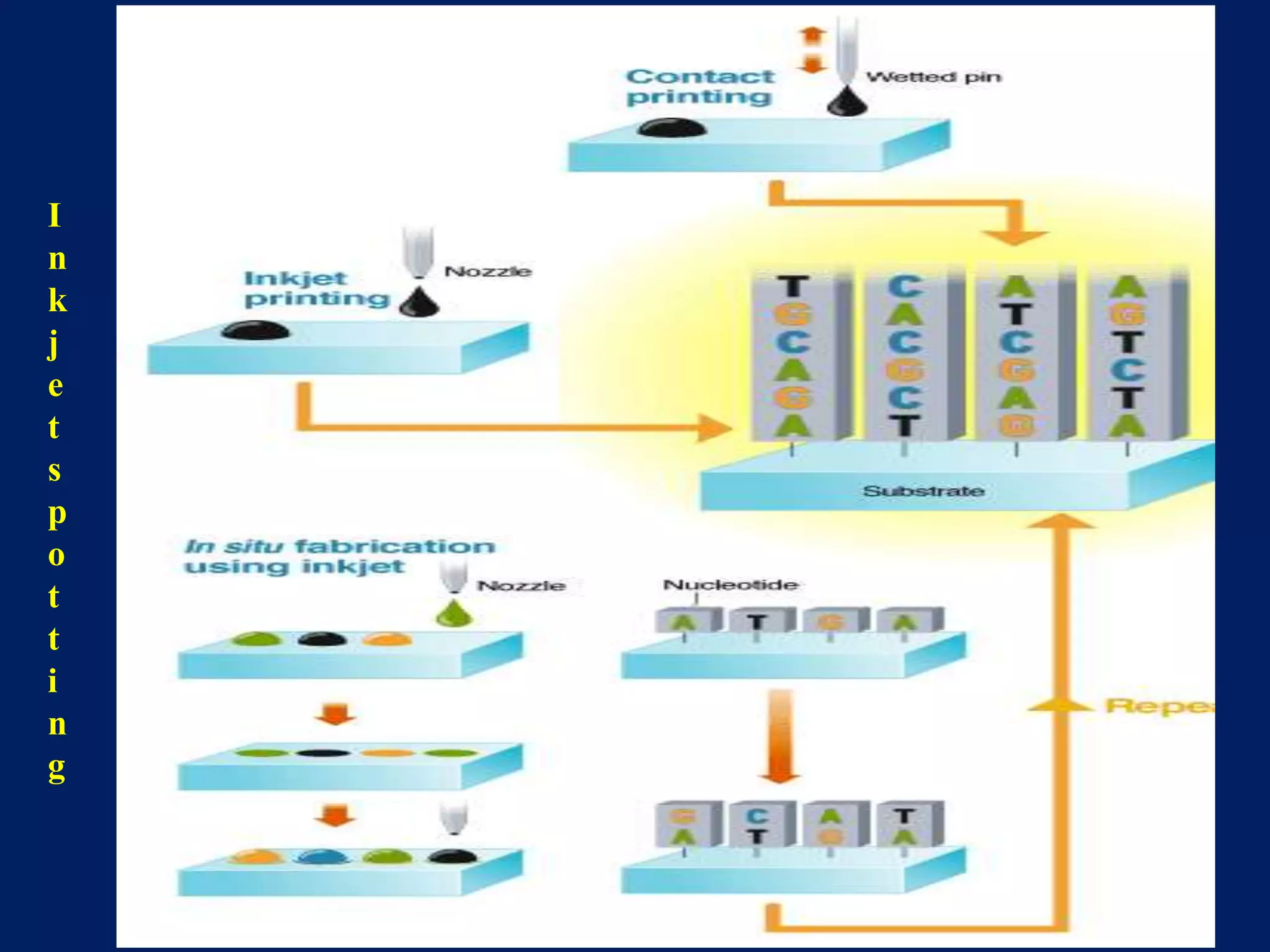
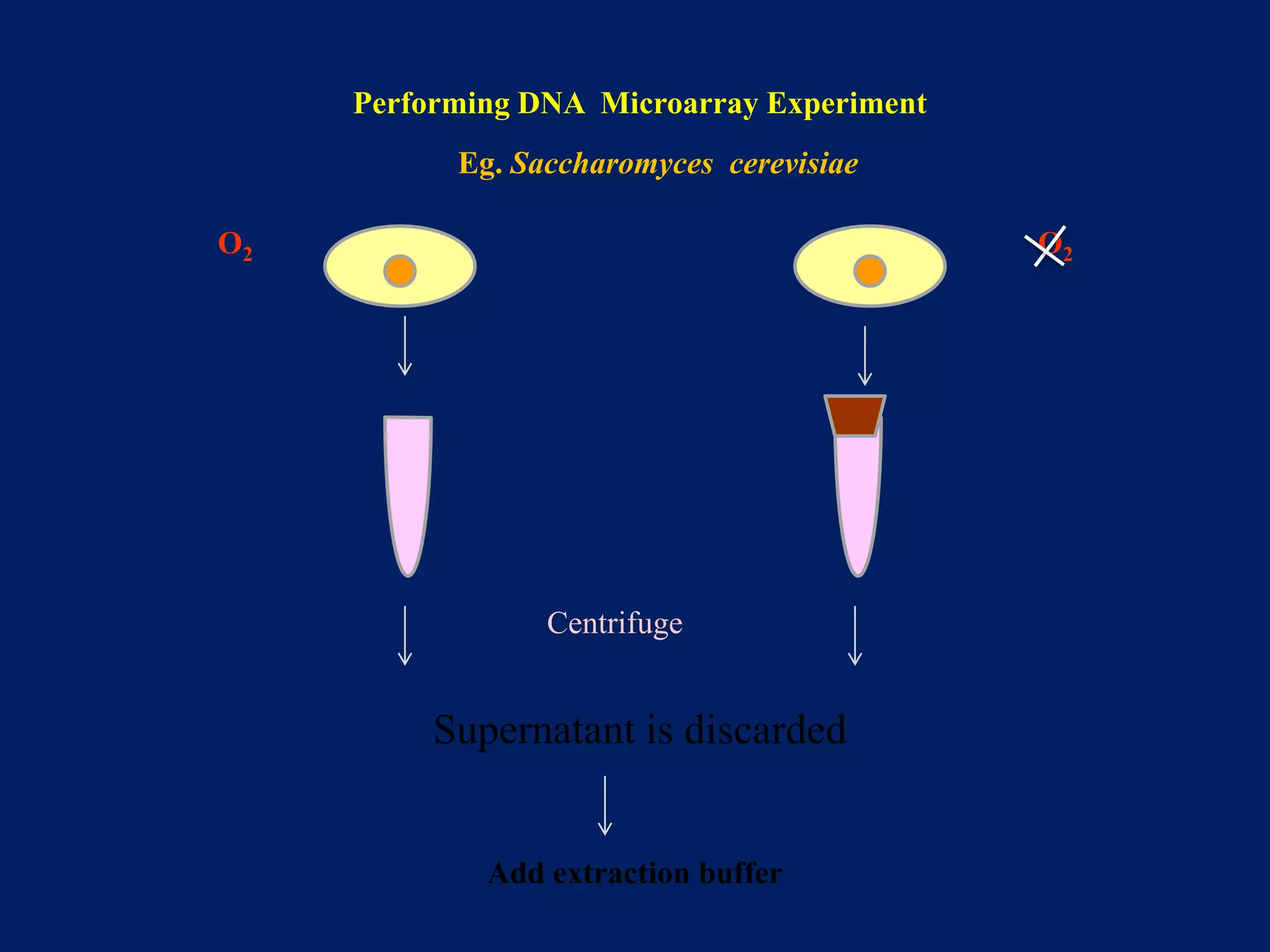
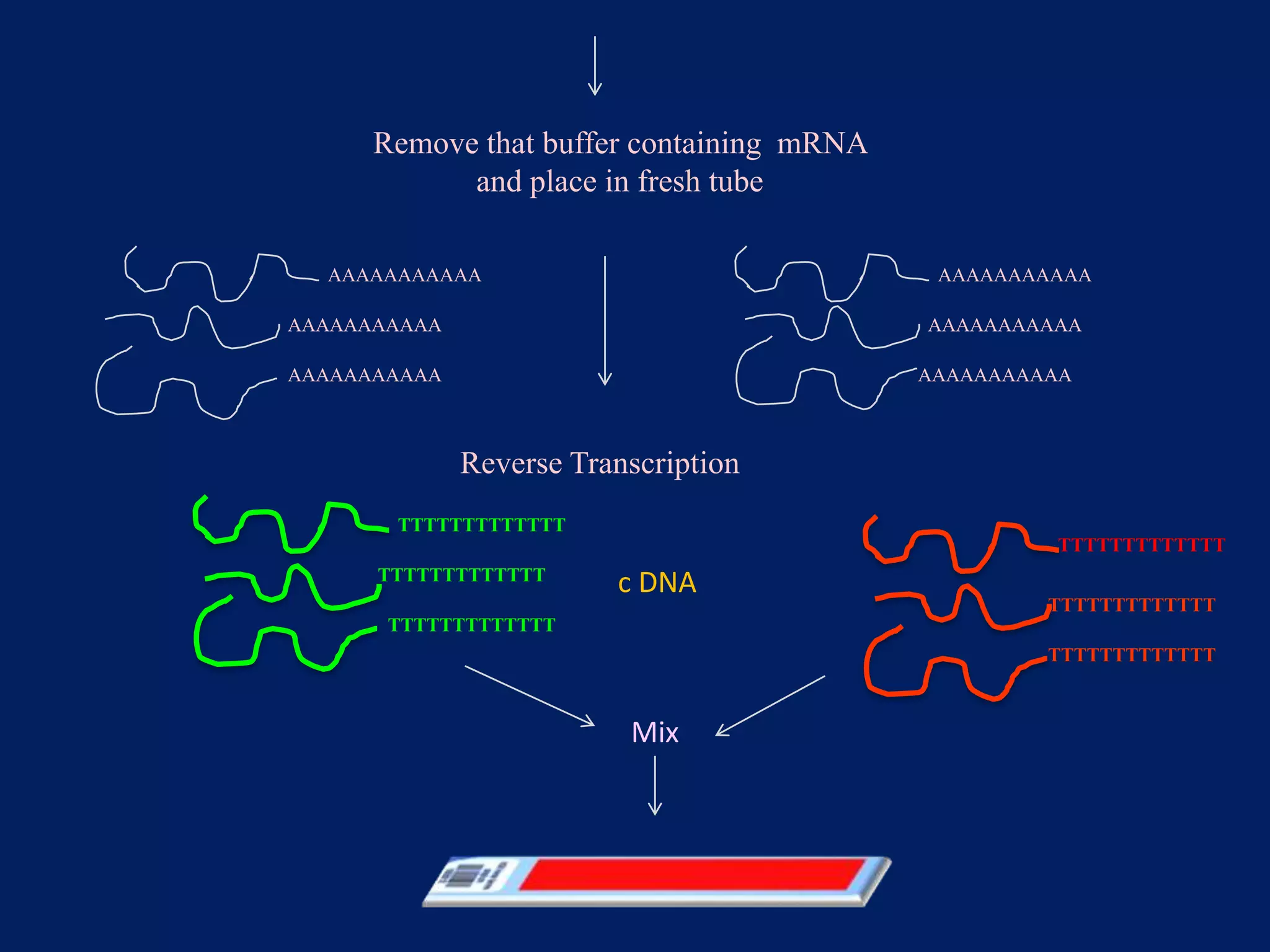
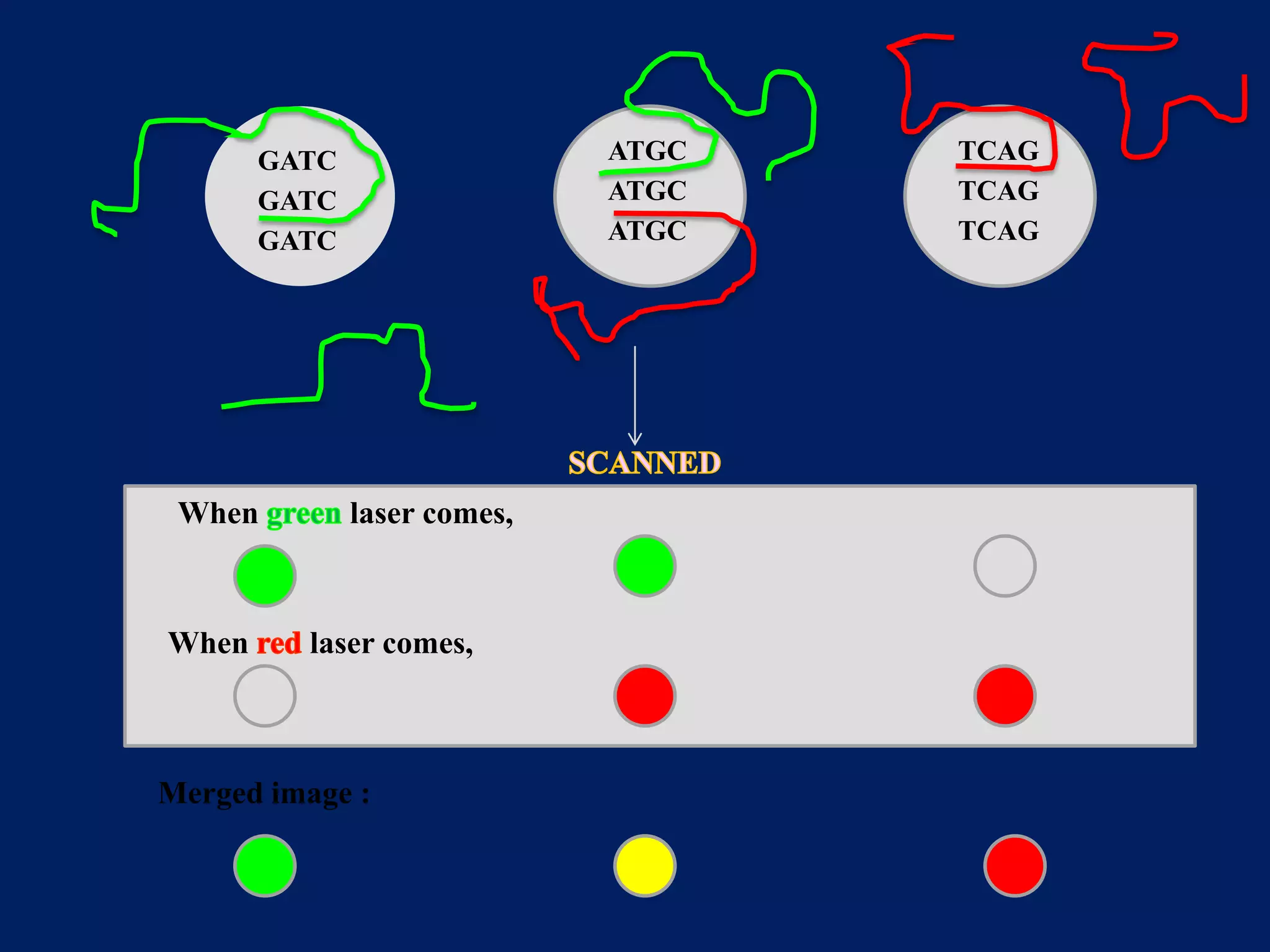
This document provides an overview of DNA microarray technology. It discusses the historical background beginning in the 1970s with Southern blotting and the development of microarrays in the 1980s. The key principles are that DNA microarrays allow analysis of thousands of genes simultaneously and efficiently through orderly arrangement of DNA sequences on a solid surface like glass. The main steps involve preparing the microarray slide through various methods, performing experiments with sample mRNA, fluorescence scanning, and data analysis to understand gene expression patterns. DNA microarray technology has wide applications in studying diseases, toxicology, and stem cell research.