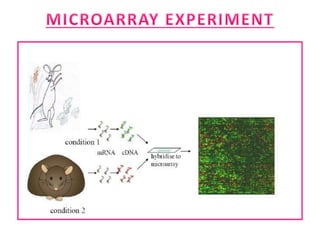
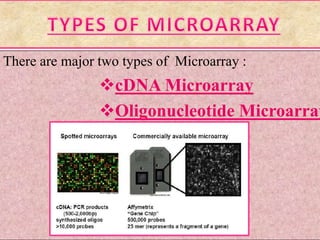
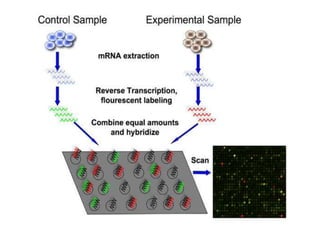
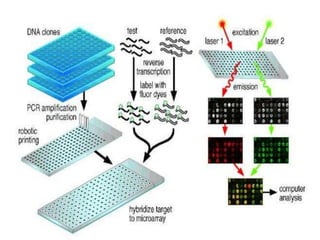
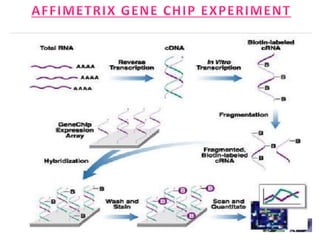
The document explains DNA microarray technology for genome analysis, detailing its principles, types (cDNA and oligonucleotide microarrays), and experimental procedures. It highlights the applications of DNA chips in gene expression profiling, drug discovery, and diagnostics, while also mentioning their advantages and disadvantages, such as cost and complexity in data analysis. Overall, DNA microarrays enable the simultaneous analysis of thousands of genes, contributing to advancements in medical research.