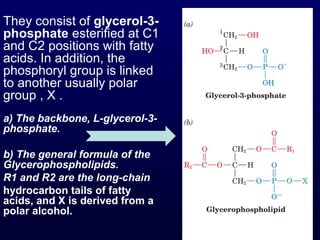
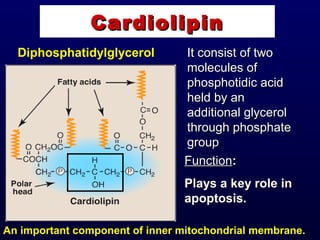
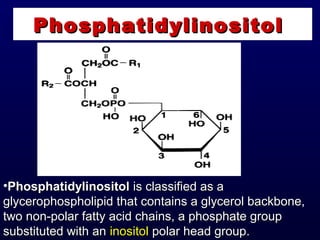
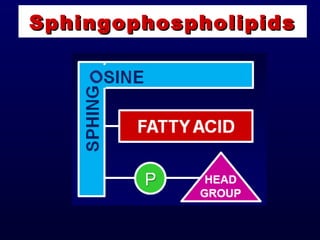
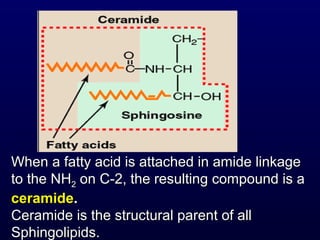
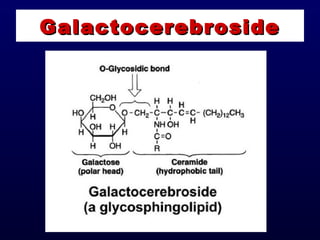
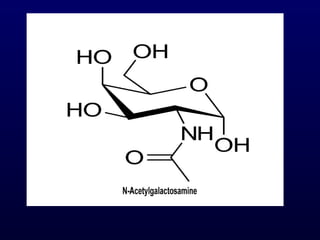
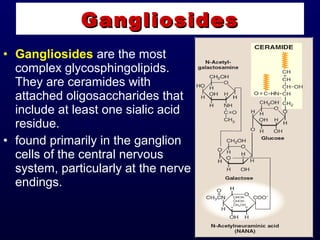
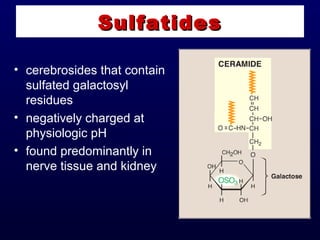
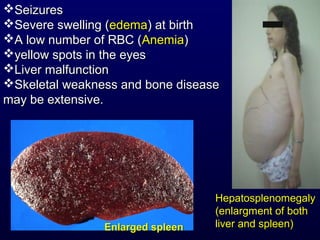
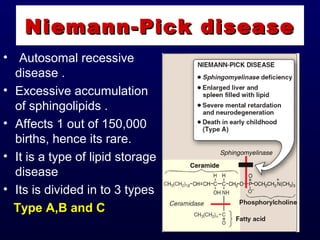
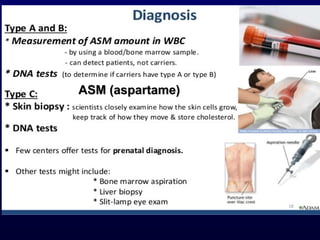
This document discusses compound lipids. It begins by defining compound lipids as lipids that contain fatty acids esterified to an alcohol and an additional group. The document then focuses on phospholipids, dividing them into glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. Glycerophospholipids are discussed in detail, including their structure and common classes like phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, and cardiolipin. Sphingolipids are introduced as containing sphingosine instead of glycerol. Specific sphingolipids like sphingomyelin, cerebrosides, globosides, gangliosides, and sulfatides are