This document discusses lipids, which are a diverse group of compounds that are nonpolar and hydrophobic. Lipids perform many important functions in cells, including energy storage as fats, insulation, and as building blocks of membranes. The document defines different types of lipids like triglycerides, fatty acids, phospholipids, and steroids. It describes the structures and properties of these lipids, how they are stored and used in the body, and their roles in membrane structure.











![[1] Lipids:
Biological Importance, Structures and Physical properties
More soluble in organic solvents than water.
Nonpolar lipids; (fats or oils) store energy (storage lipids).
(Oxidation of fats is highly exergonic.)
Amphiphilic lipids (Polar); (phospholipids and sterols) help
make up biological membranes.
Steroid Lipid; Steroids (found in membrane) are precursors
to many hormones
Miscellaneous Lipids (other Lipids); Some are involved in
light-absorbing pigments, are enzyme cofactors (vitamin K),
hormones (estrogens, testosterone), signal molecules
(prostaglandins), electron carriers (ubiquinone) or help
solubilize other lipids during digestion (bile acids).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/llipidsslides-231117135844-9849f1ed/85/Llipids-slides-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![(1) Fatty acids: Carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains
(4-36 carbons)
R
C
O
OH
Saturated 18:0 Unsaturated 18:1(9)
[2] Storage Lipids: Fatty acids (FA) and derivatives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/llipidsslides-231117135844-9849f1ed/85/Llipids-slides-pptx-13-320.jpg)



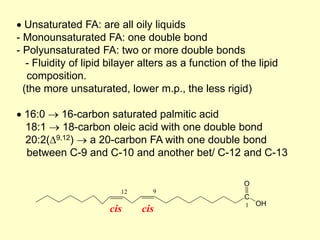

![[2] Storage Lipids: Fatty acids (FA) and derivatives
increase
decrease
increase
double
bonds
decrease
all cis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/llipidsslides-231117135844-9849f1ed/85/Llipids-slides-pptx-19-320.jpg)




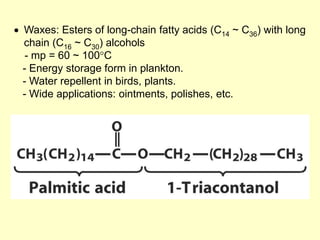
![[3] Structural Lipids in Membranes
All membrane lipids are amphipathic:
hydrophilic head + hydrophobic (bulky) tail
(1) Glycerophospholipids: belong to phospholipids
glycerol + 2 FA (C1 & C2) + phosphate (C3)
The major component of biological membranes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/llipidsslides-231117135844-9849f1ed/85/Llipids-slides-pptx-25-320.jpg)
