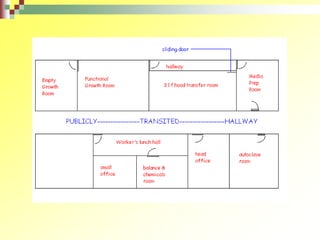
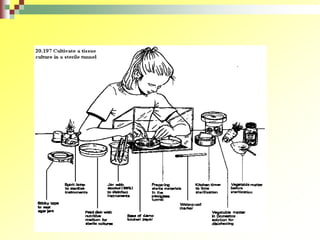
The document outlines the key considerations for designing an effective plant tissue culture laboratory. It discusses that the laboratory should have separate areas for washing and storage, media preparation, aseptic transfer, and primary growth. The aseptic transfer area and primary growth room require stringent cleanliness, with HEPA filters, UV lights, and laminar flow hoods. Other areas require equipment for media preparation, sterilization, and storage. The primary growth room needs temperature, humidity, and lighting controls to suit the plants being cultured. Careful planning of traffic flow and separation of clean and dirty areas is important for success.