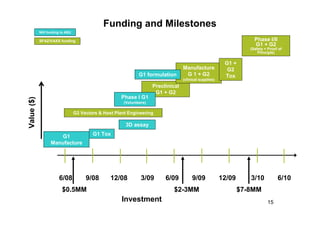
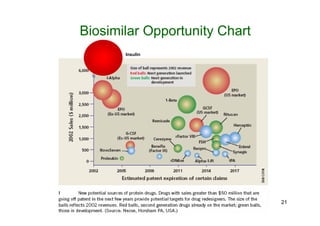
1. Plant-based production of pharmaceuticals is a disruptive technology that could challenge traditional mammalian production methods. Over 400 biotech proteins are currently in development, mostly produced in microbial or animal systems.
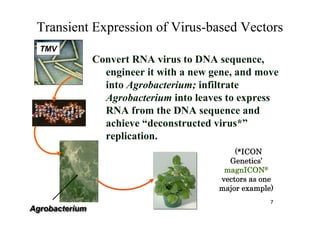
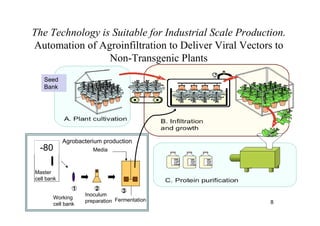
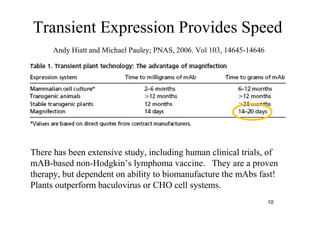
2. Plants have been investigated as an alternative production platform since the 1980s and offer rapid, low-cost scalable production without the risks of using animal pathogens.
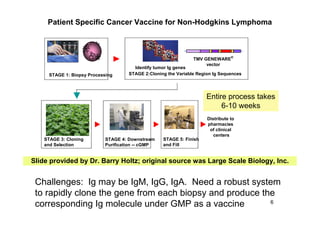
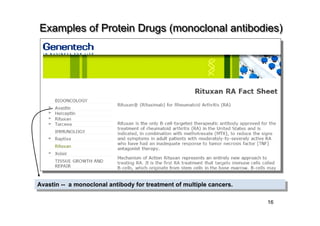
3. The first licensed human vaccine may combine plant and insect cell approaches for a cancer therapeutic, demonstrating the potential of plant-made pharmaceuticals.