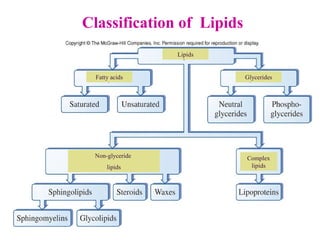
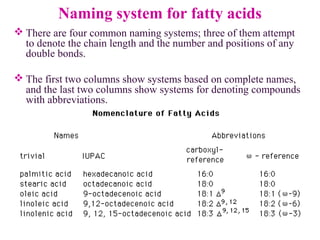
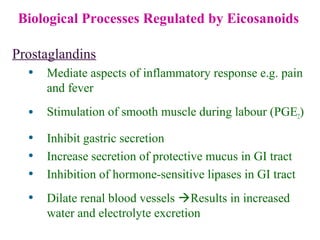
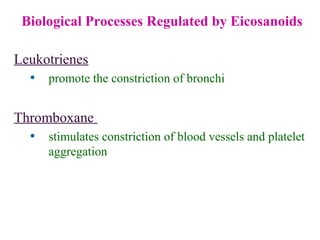
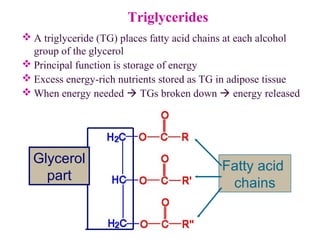
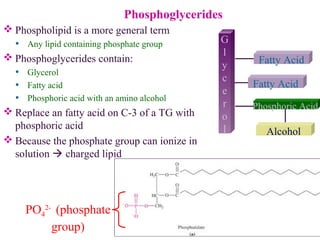
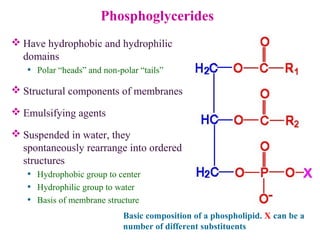
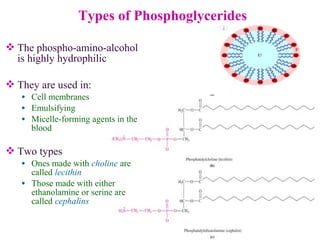
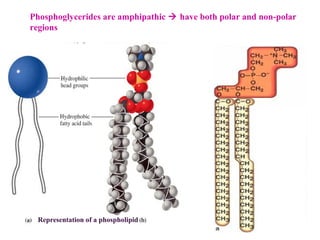
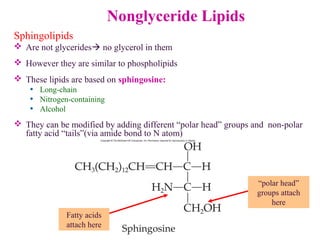
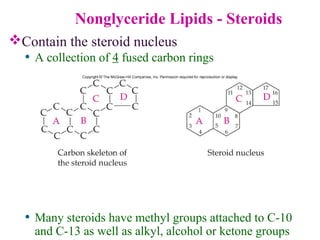
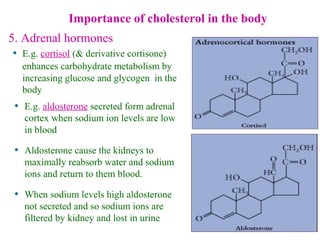
This document provides an overview of lipids, including their classification, properties, and functions. It defines lipids as organic compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Lipids are classified into glycerides (including triglycerides and phosphoglycerides), non-glyceride lipids (such as sphingolipids and steroids), and waxes. Key points covered include the structures of fatty acids and how their properties depend on saturation; essential fatty acids that must be obtained from diet; roles of triglycerides and phosphoglycerides; and biological functions of lipids as energy sources, structural components of cell membranes, and steroid hormones.