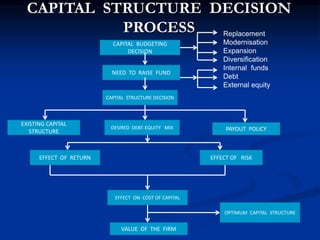
This document discusses different types of leverage used in capital structure analysis. It defines operating leverage as the use of fixed operating costs to magnify the effect of sales changes on operating profits. Financial leverage is defined as the use of fixed financial charges to magnify the effect of changes in operating profits on earnings per share. Combined leverage is the product of operating and financial leverage and measures total risk. Formulas are provided to calculate the degrees of operating, financial, and combined leverage. The advantages of analyzing each type of leverage are also discussed.