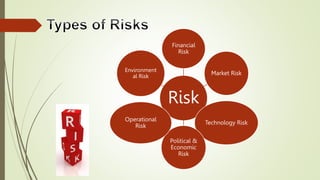
The document discusses the essence of entrepreneurship in India, highlighting the achievements of notable entrepreneurs and the qualities that contribute to their success. It defines entrepreneurship as an innovative and risk-taking endeavor that is essential for economic growth and outlines the differences between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs. Additionally, it details various types of risks faced by entrepreneurs and the advantages of being an entrepreneur.