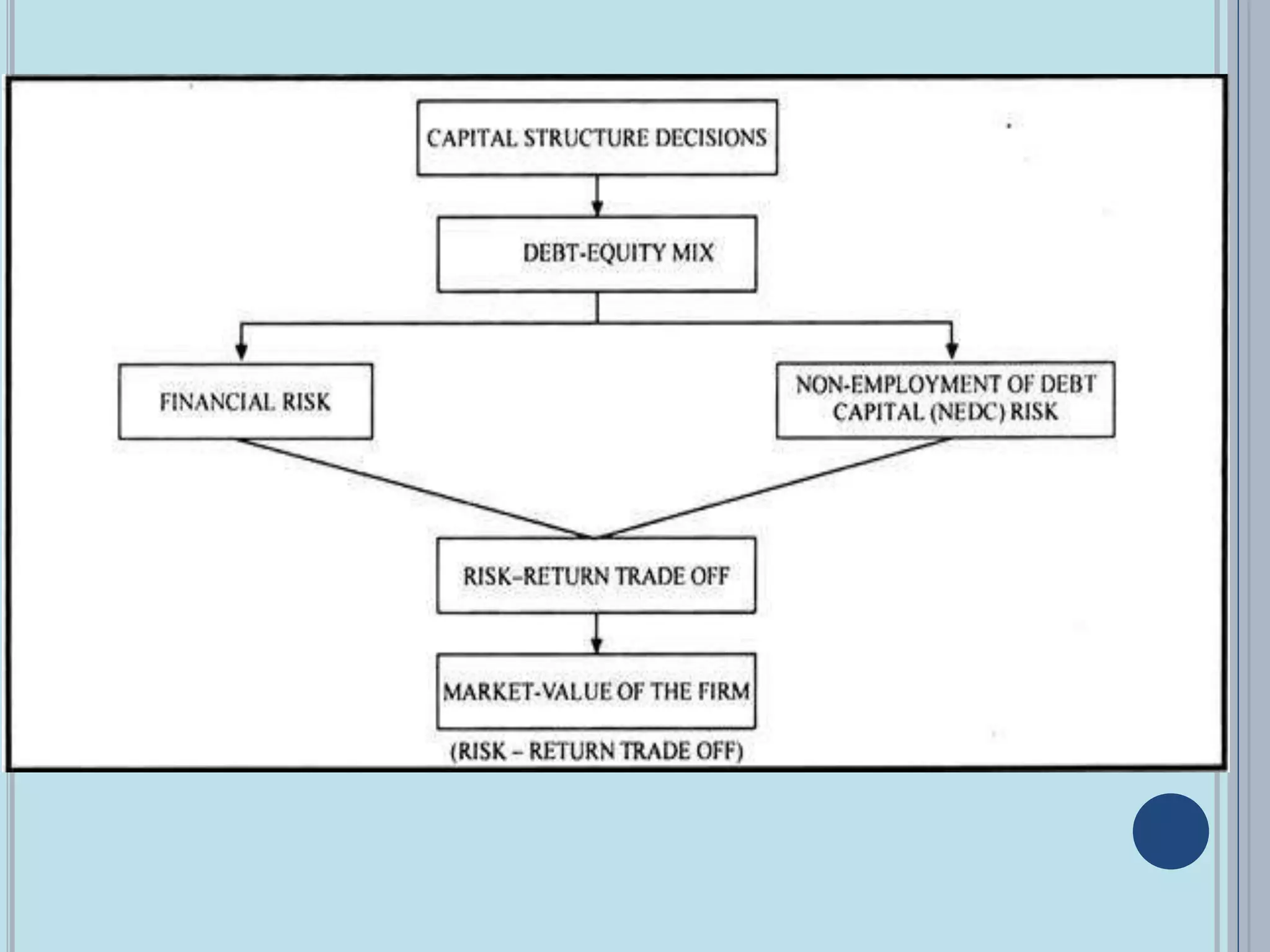
This document discusses capital structure decisions and optimal capital structure. It defines capital structure as the mix of long-term financing sources like debt and equity. An optimal capital structure minimizes costs while maximizing firm value. It balances financial risk from debt against non-employment of debt capital risk. The optimal structure achieves the lowest weighted average cost of capital.