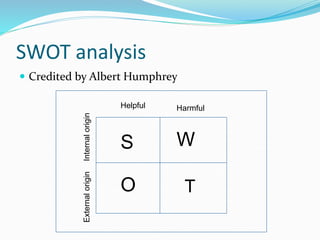
The document discusses the various elements of the external business environment including the micro and macro environment. It provides details on the economic, political, socio-cultural, legal, technological, and physical environment. The economic environment section outlines factors such as the economic system, policies, and indicators of a country. The political environment section describes the political system, laws, and responsibilities of business and government. The socio-cultural environment influences business through factors like family, social class, and culture. Techniques for analyzing the external environment include SWOT and ETOP analysis.