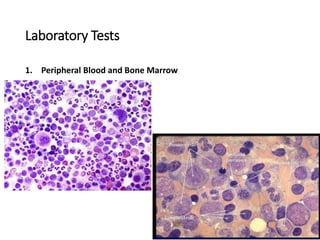
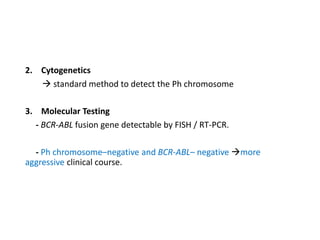
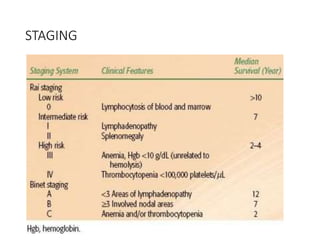
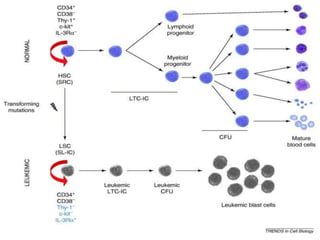
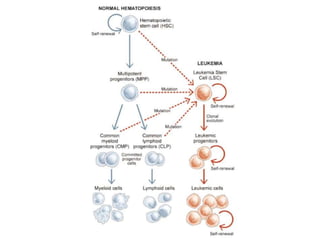
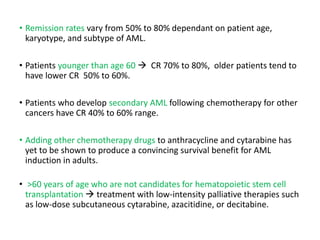
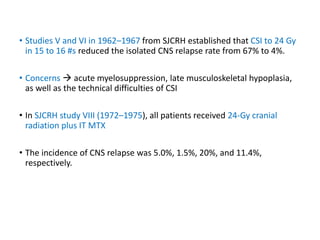
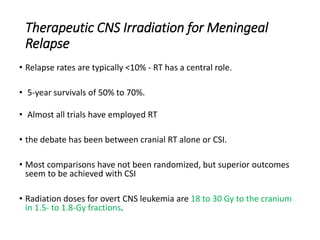
Leukemia are neoplastic disorders of the hematopoietic system characterized by aberrant or arrested differentiation. There are two main types - acute and chronic leukemias. Acute leukemias are further classified as myeloid or lymphoid based on the lineage of the malignant cells. Chromosomal abnormalities are detected in the majority of acute leukemia cases and correlate with specific disease subtypes and clinical outcomes. Treatment involves induction chemotherapy followed by consolidation therapy and stem cell transplantation for eligible patients, with cure rates varying based on disease risk factors.









































![Pathogenesis
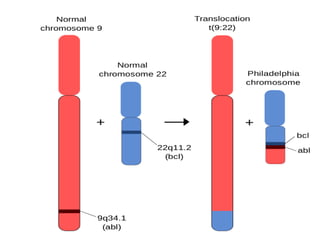
• In 1973, Janet Rowley discovered that Ph is in fact the result of a
reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 [t(9;22)
(q34;q11)].
• The genes juxtaposed by the translocation ABL (Abelson) on 9q34
and breakpoint cluster region (BCR) on chromosome 22q11
• Tyrosine kinase activity of BCR-ABL is required for cellular
transformation
• According to WHO the presence is diagnostic of CML, although the
translocation is also found in ALL and rare cases of AML.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukemia-230805173901-ab3214b8/85/LEUKEMIA-pptx-54-320.jpg)