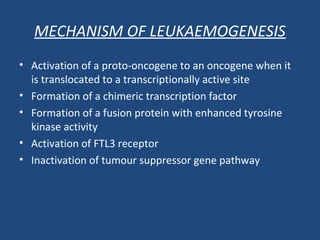
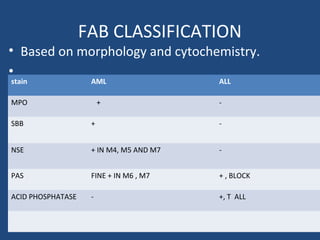
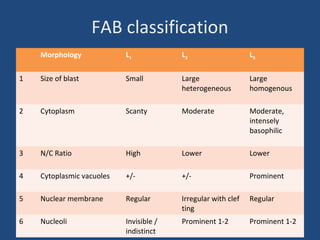
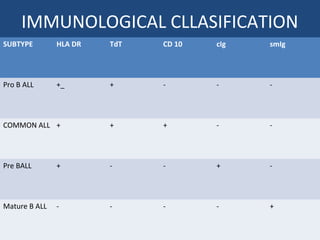
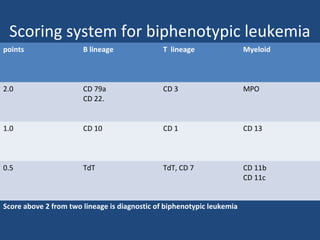
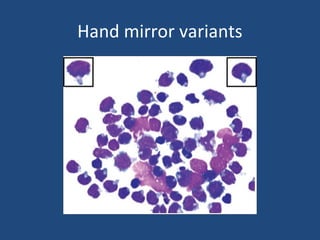
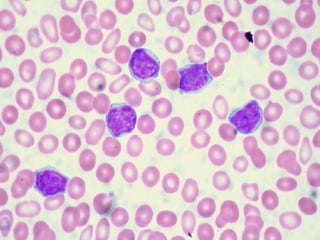
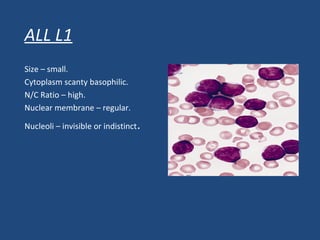
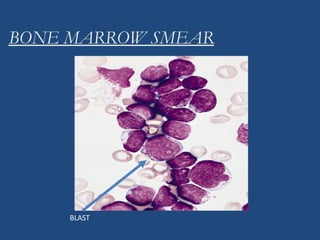
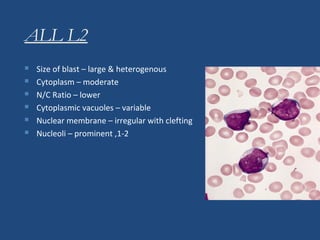
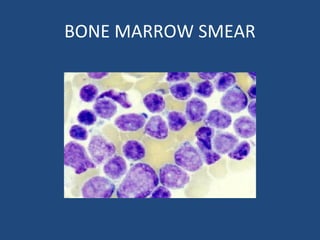
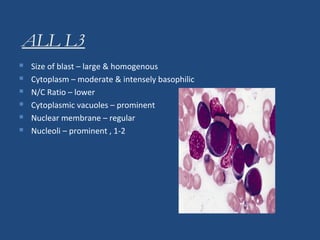
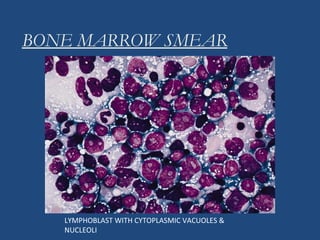
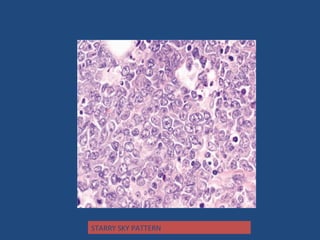
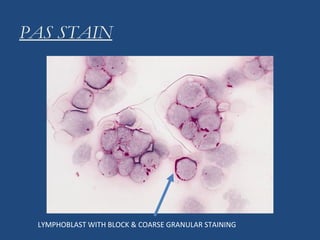
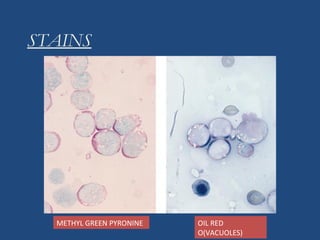
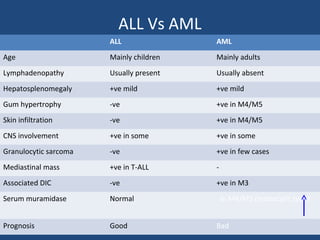
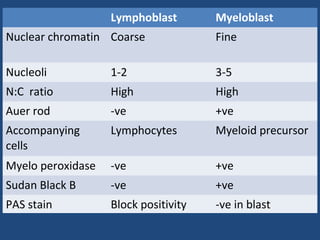
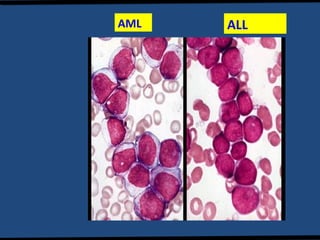
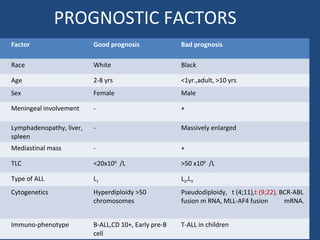
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common malignancy in children. It is characterized by the overproduction of immature white blood cells called lymphoblasts. The disease is classified based on immunophenotyping and cytogenetics. Prognostic factors include age, white blood cell count, cytogenetics, and immunophenotype. Diagnosis involves examination of peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate, immunophenotyping, cytogenetics, and molecular testing. Treatment and monitoring of minimal residual disease is important. Genetic conditions and environmental exposures can predispose children to developing ALL.