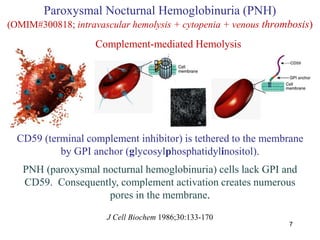
The document outlines various bone marrow failure syndromes, including idiopathic aplastic anemia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), and myelodysplastic syndrome, detailing their causes, clinical manifestations, and treatments. Key points include the role of autoreactive T-cells in aplastic anemia, stem cell transplantation for treatment, and PNH's association with complement-mediated hemolysis. Additionally, the document highlights genetic disorders like Fanconi anemia and Diamond-Blackfan anemia, emphasizing the need for proper diagnosis and supportive care.

![Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes: Definition
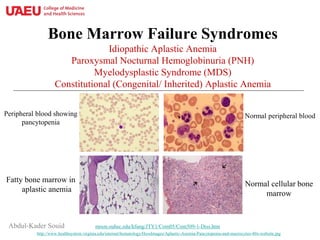
• These disorders are characterized by “near absence of hematopoietic
cells”. The marrow is replaced by fat cells (“fatty marrow”).
• Clinical manifestations include various severities of anemia,
neutropenia, lymphopenia, and thrombocytopenia.
• In most cases, the disease occurs without a known precipitating
cause (termed “idiopathic aplastic anemia”), resulting from
“autoreactive T-cells” that destroy the hematopoietic cells.
• Severe aplastic anemia is defined as “bone marrow cellularity <25% with 2
of the following cytopenias: neutrophil count <0.5 x109/L, platelet counts
<20 x109/L, and reticulocyte count <40 x109/L.
• All patients need bone marrow biopsy, cytogenetic studies for clonal abnormalities,
chromosome breakage for Fanconi anemia by diepoxybutane [DEB] test, flow
cytometry for CD55/59 for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), and
telomere length study for dyskeratosis congenita (DC).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-3-320.jpg)


![Idiopathic Aplastic Anemia: Treatment
• Supportive care include blood and platelet transfusions, antibiotics,
and growth factors [granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF),
thrombopoietin, erythropoietin].
• The disease is curable with hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation
from allogeneic HLA-matched (usually sibling) donor.
• About 80% of patients with no HLA-matched donor show
hematopoietic recovery after transient T-cell depletion by anti-
thymocyte immunoglobulins (ATG, cytolytic antibodies) +
cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant that reduces T-cell function);
relapse usually responds to repetitive treatment.
9/26/2018 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-6-320.jpg)




![Myelodysplastic Syndrome (OMIM#614286):
“Clonal Cytopenia + Oligoblastic Leukemia”
• MDS (myelodysplasia) is ineffective hematopoiesis (cellular bone
marrow + pancytopenia) resulting from an evolving clone of
genetically injured hematopoietic stem cells.
– Cytogenetic abnormalities exist in most patients; most commonly involving
chromosomes 5, 7 and 8.
• Cases could be sporadic (de novo) or result from stem cell injuries, e.g.,
– Cyclophosphamide (AML-associated with monosomy 5 or 7; (del)5q or (del)7q)
– Etoposide (AML-associated with rearrangements involving the mixed lineage
leukemia, MLL [MIM#602409], gene on chromosome 11q23)
• Patients present with uni-lineage, bi-lineage or tri-lineage
(pancytopenia), progressing to acute myelogenous leukemia in many
of the cases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-12-320.jpg)


![• It primarily affects older females. It presents with anemia and dysmorphic
hematopoiesis (lobulated erythroblast nuclei and hypolobulated
micromegakaryocytes). The platelet count is normal or high. The disease is
indolent and has low propensity to evolve into AML.
• It requires supportive care (erythropoietin, granulocyte–colony stimulating
factor, transfusions and antibiotics).
• Allogeneic stem cell transplantation is curative.
Chromosome 5q Deletion Syndrome (OMIM#153550)
[Macrocytic anemia, refractory, due to 5q deletion, somatic]
Hypolobulated micromegakaryocytes
PEIR Digital Library (Pathology image database
Lobulated erythroblast nuclei
pathologyoutlines.com/images/marrow/048.jpg
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-15-320.jpg)
![• DBS is characterized by isolated anemia (↑MCV, ↑erythrocyte adenosine deaminase
[eADA], and ↑hemoglobin F) with severe reticulocytopenia and absence of marrow
erythroid precursors. The neutrophil, lymphocyte and platelet counts are normal.
– It appears in early life and may improve with glucocorticoids.
– Congenital malformations occur in 50% of the patients (e.g., cleft palate, thumb defect).
• Patients have mutations in RPS19 [ribosomal protein S19; OMIM#603474;
autosomal dominant], RPL11 [ribosomal protein L11; OMIM#604175], or GATA1
[OMIM#305371; encodes a zinc finger DNA-binding transcription factor that is
critical for the development of hematopoiesis).
Acquired red cell aplasia:
− Parvovirus infection (cytotoxic to erythroid progenitors)
− “Transient erythrocytopenia of childhood” (TEC, a short-lived suppression of
erythropoiesis due to viral infection).
Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (DBA, OMIM#105650) - Ribosomopathy
DBA in a 3-y-old boy from Pakistan Dr. Diamond](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-16-320.jpg)

![Fanconi Anemia: Natural History and Treatment
[A defect in DNA repair]
• Bone marrow failure occurs in childhood with petechiae, bruising
and hemorrhage from thrombocytopenia; pallor and fatigue from
anemia; and infection from neutropenia.
• The major cause of death is bone marrow failure, followed by
leukemia (AML) and solid tumors (most commonly liver
adenomas and hepatomas in patients treated with oral
androgens). The projected median survival is ~20 years.
• Treatment: Supportive care (transfusions, antibiotics, growth
factors), androgen therapy and stem-cell transplantation. [Blood
2003;101:1249-1256]
9/26/2018 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-bonemarrowfailuresyndromes-180926043250/85/Bone-marrow-failure-syndromes-ppt-18-320.jpg)



