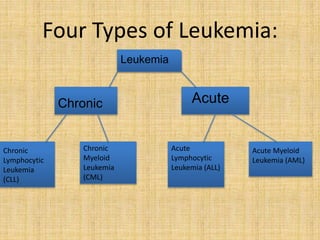
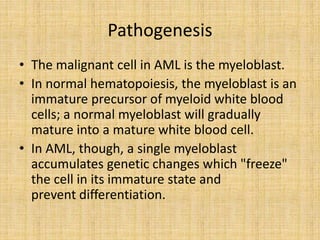
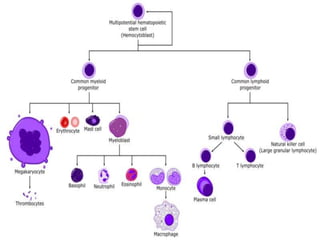
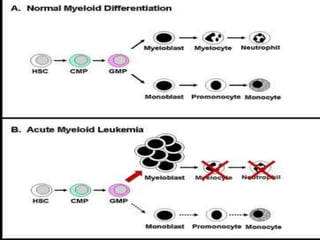
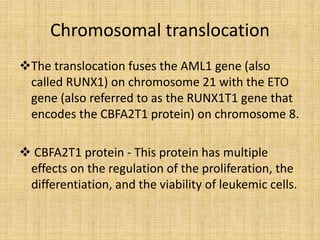
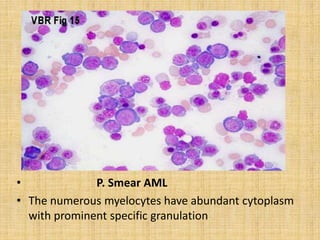
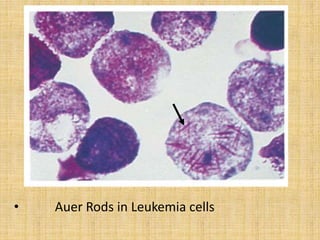
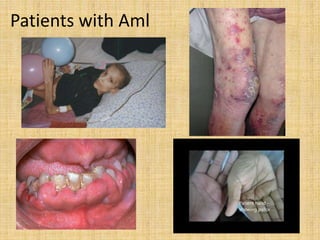
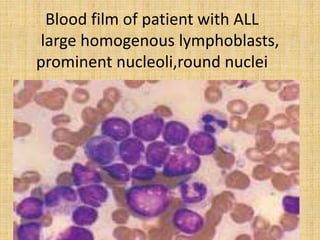
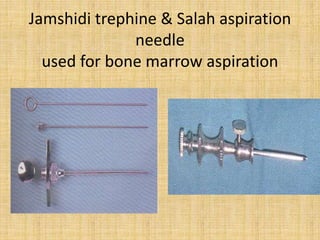
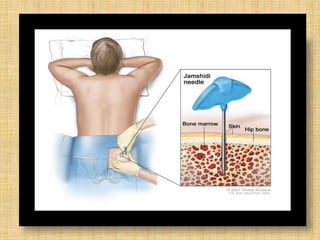
Acute leukemia is a malignant clonal disorder characterized by the accumulation of immature blast cells in the bone marrow, which replaces normal marrow tissue and results in bone marrow failure and peripheral blood cytopenias. There are two main types: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). ALL involves abnormal proliferation of immature lymphocytes while AML involves the myeloid cell lineages. Diagnosis involves physical exam, blood tests, bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. Treatment for both types usually involves intensive multi-agent chemotherapy, while AML may also involve all-trans retinoic acid. Prognosis depends on various risk factors like age, white blood cell count, and cytogenetics.