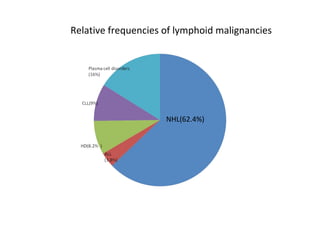
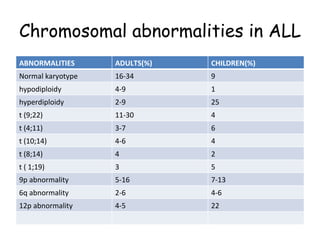
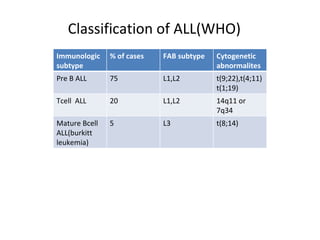
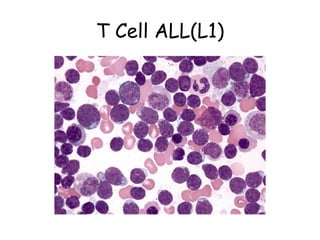
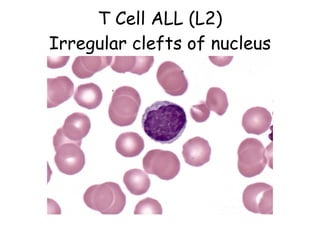
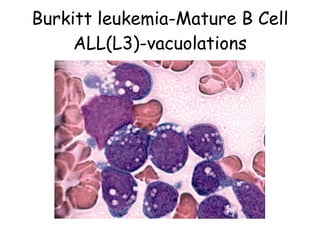
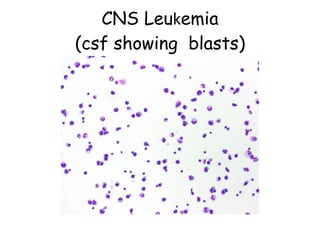
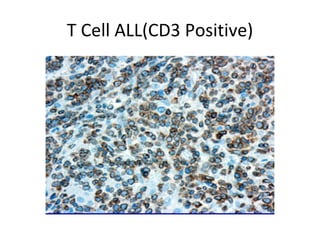
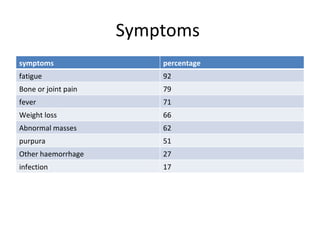
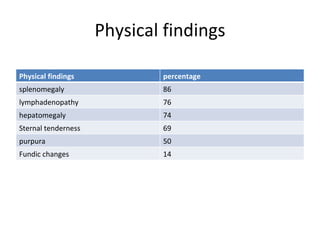
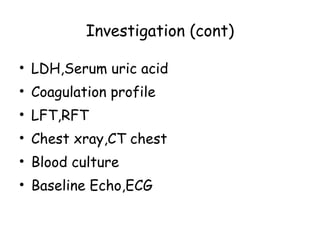
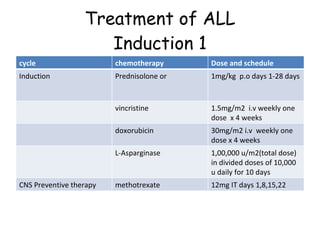
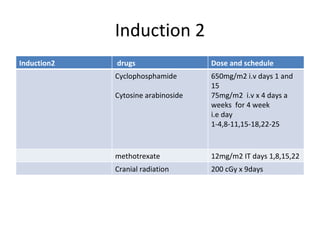
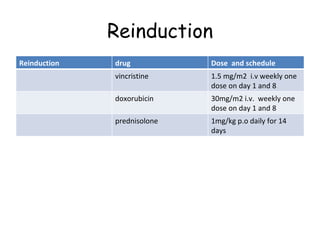
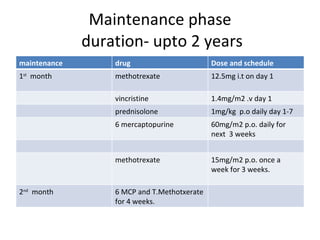
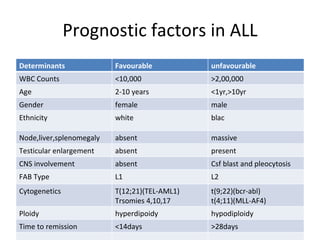
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the proliferation of immature lymphocytes. It most commonly affects children aged 2-6 years and has a peak incidence in adults at around 35 years of age. The disease involves replacement of normal bone marrow by leukemic blasts. Treatment involves chemotherapy with regimens depending on risk stratification including induction, consolidation, CNS prophylaxis and maintenance phases. Prognosis depends on factors like age, white blood cell count, genetics and response to initial treatment.