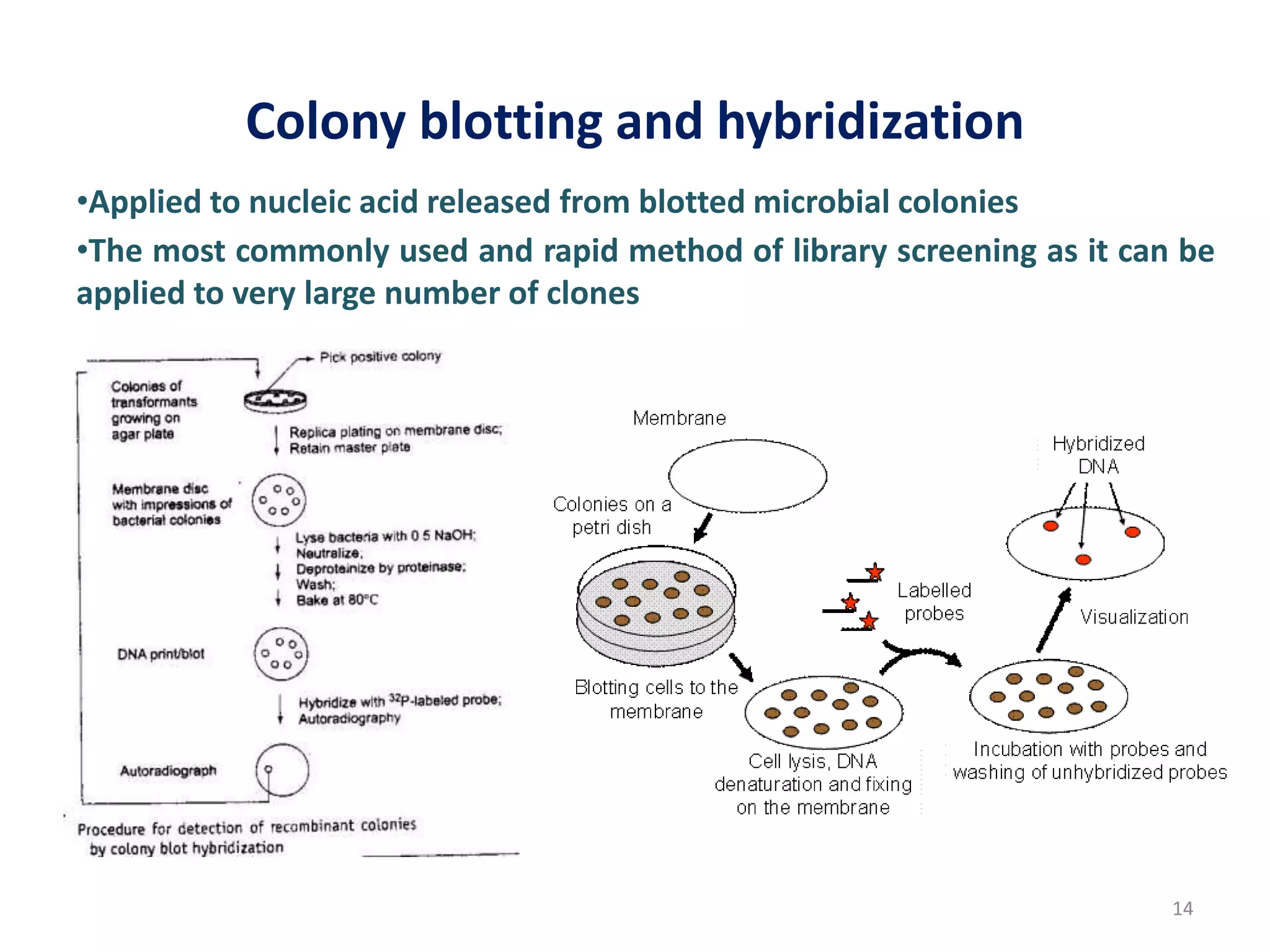
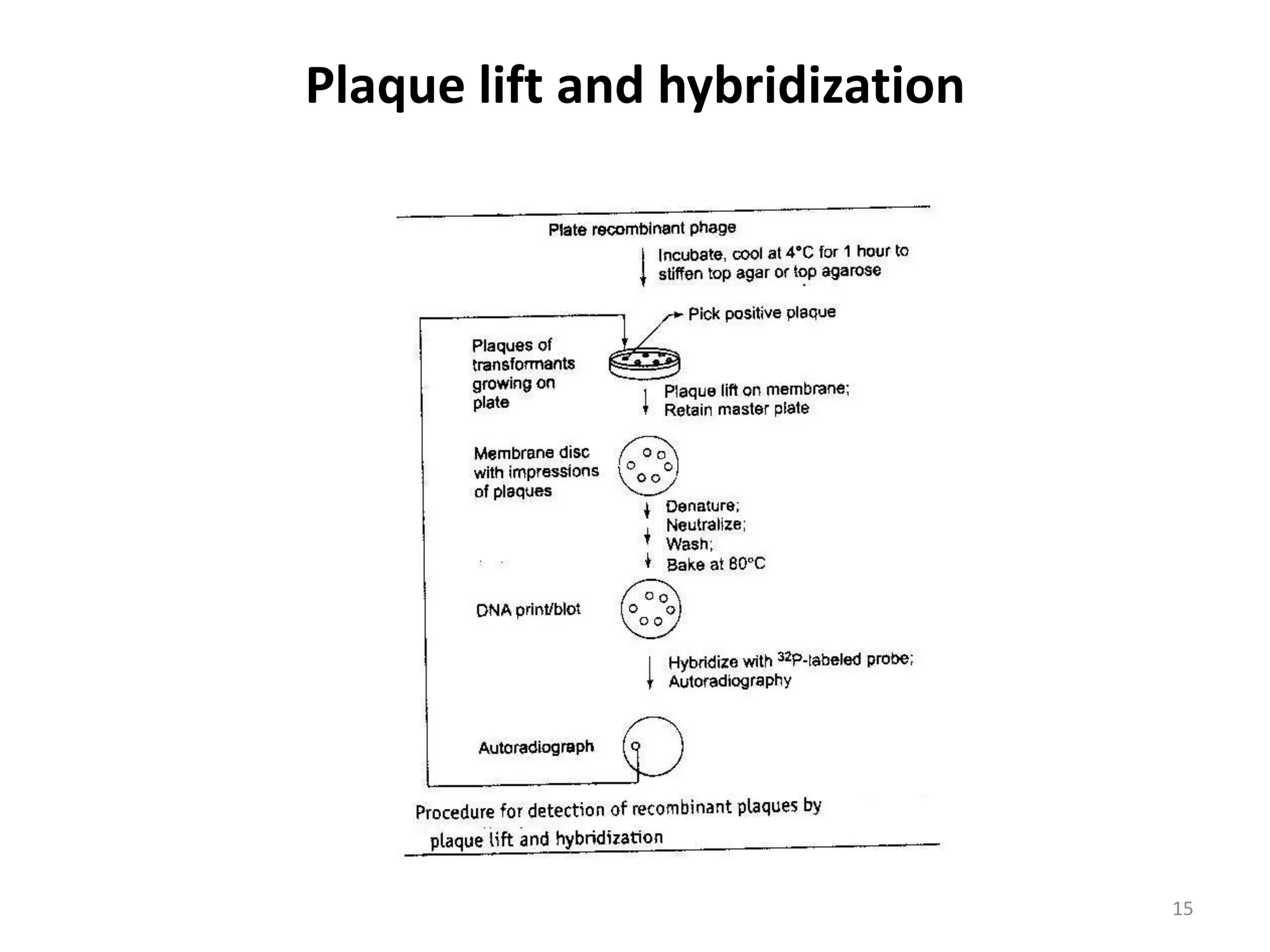
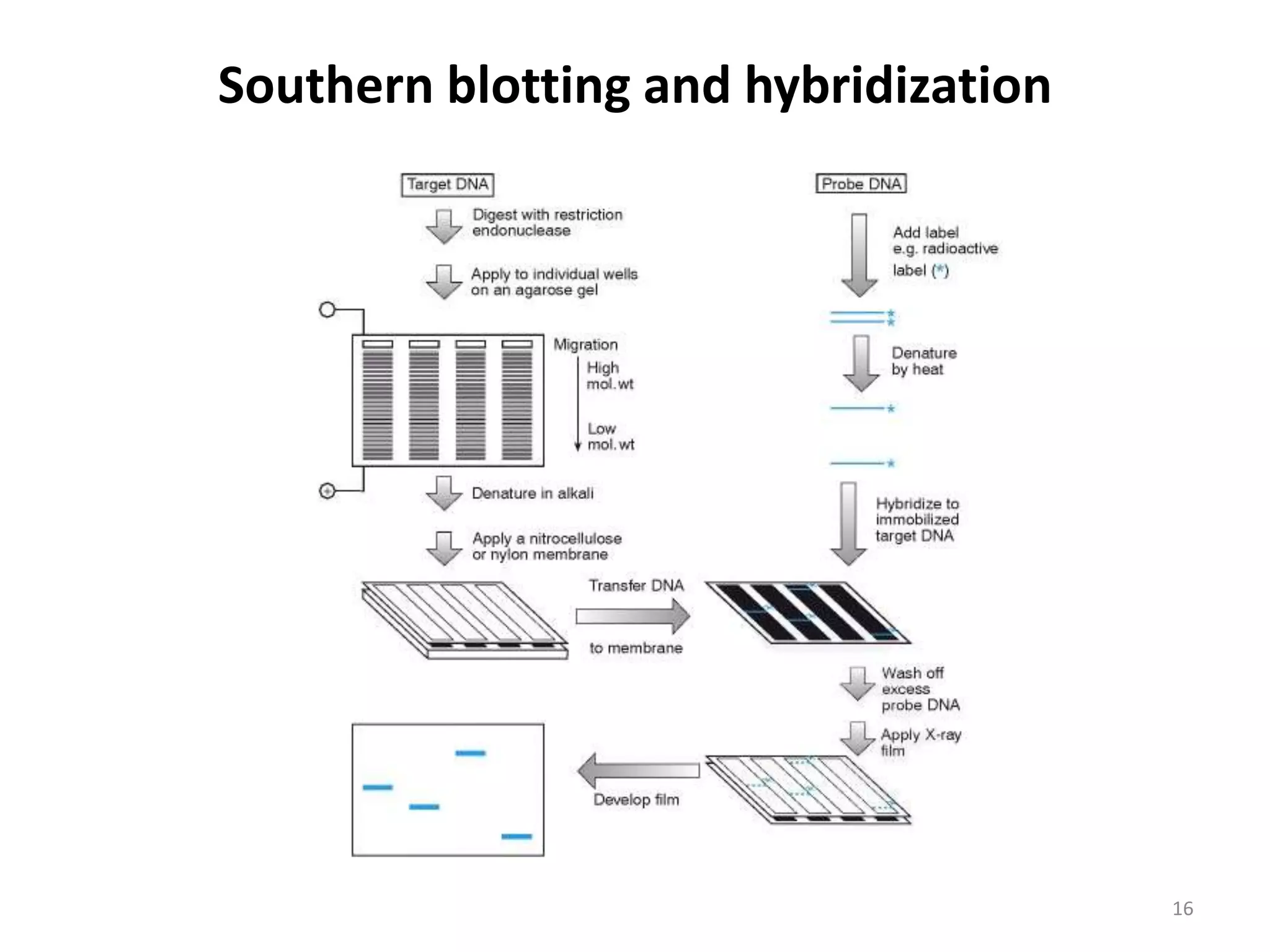
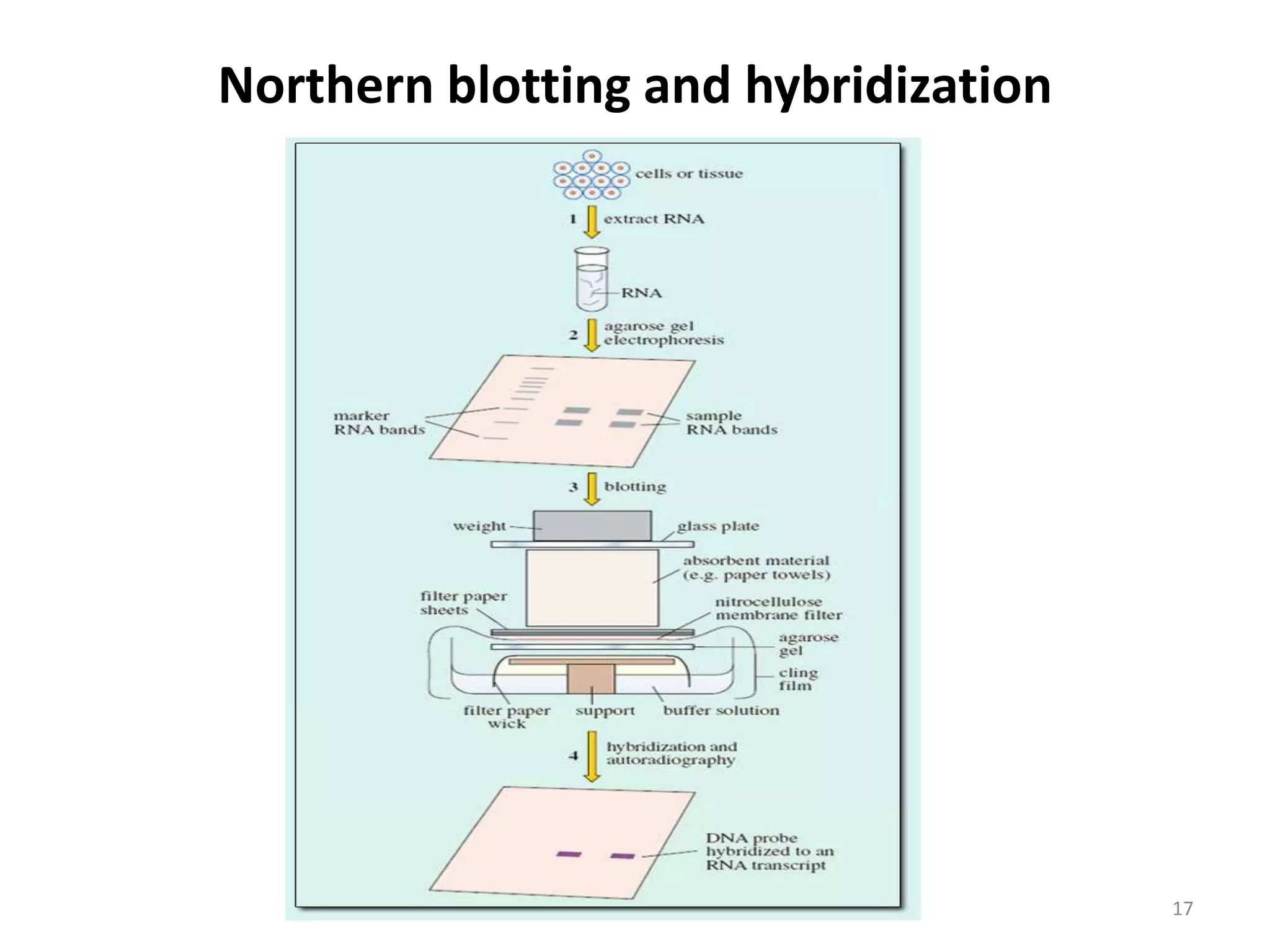
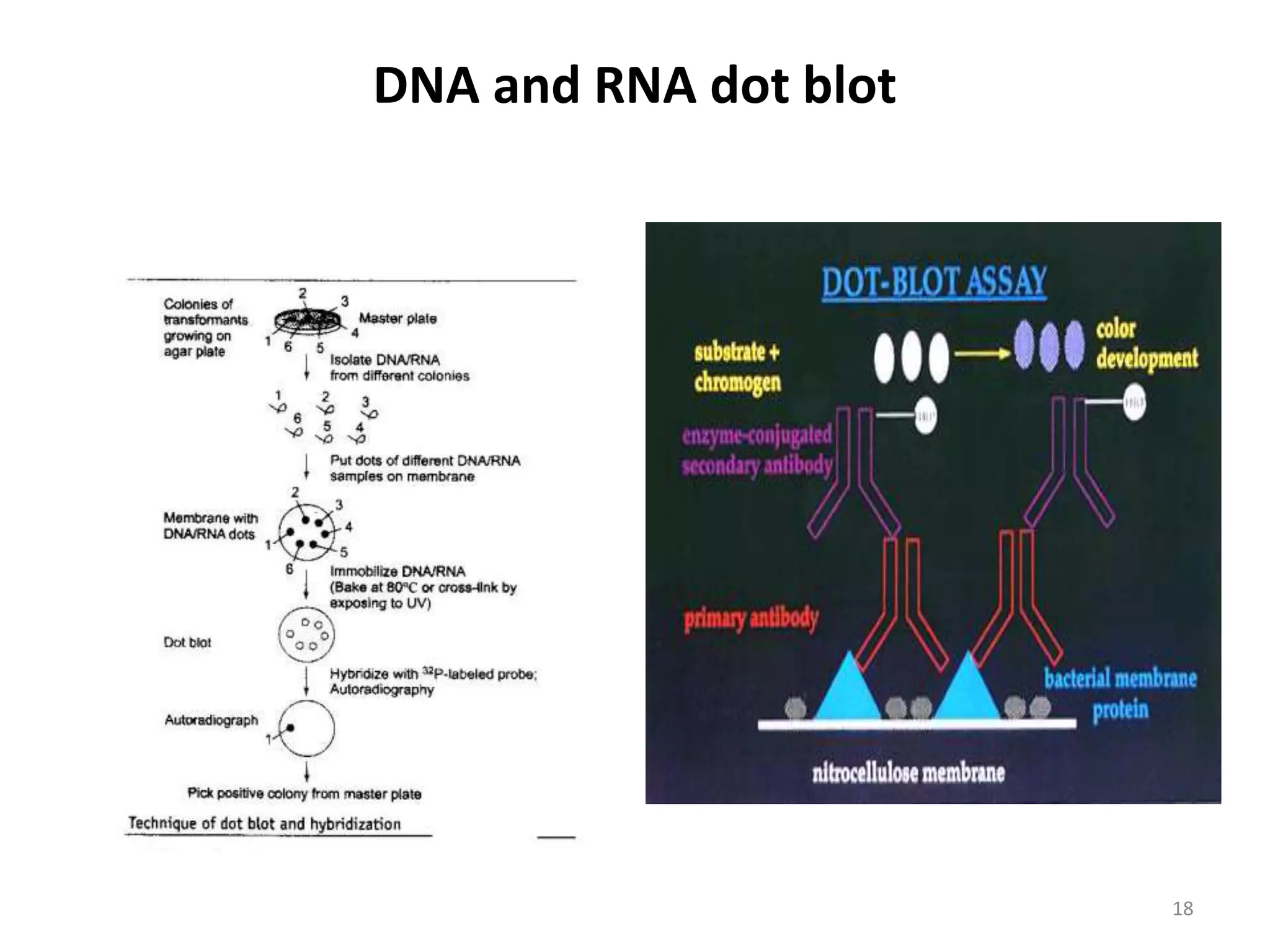
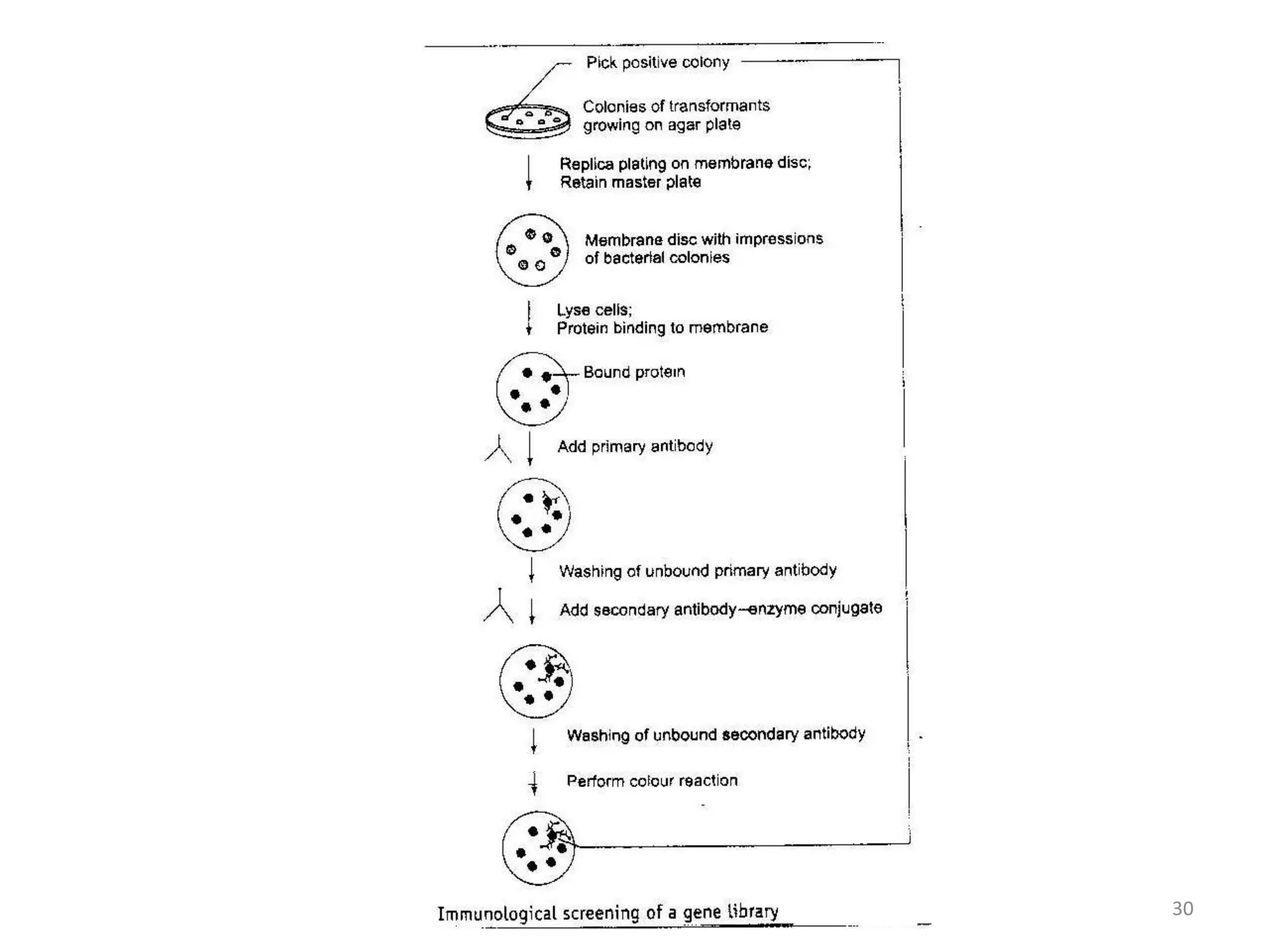
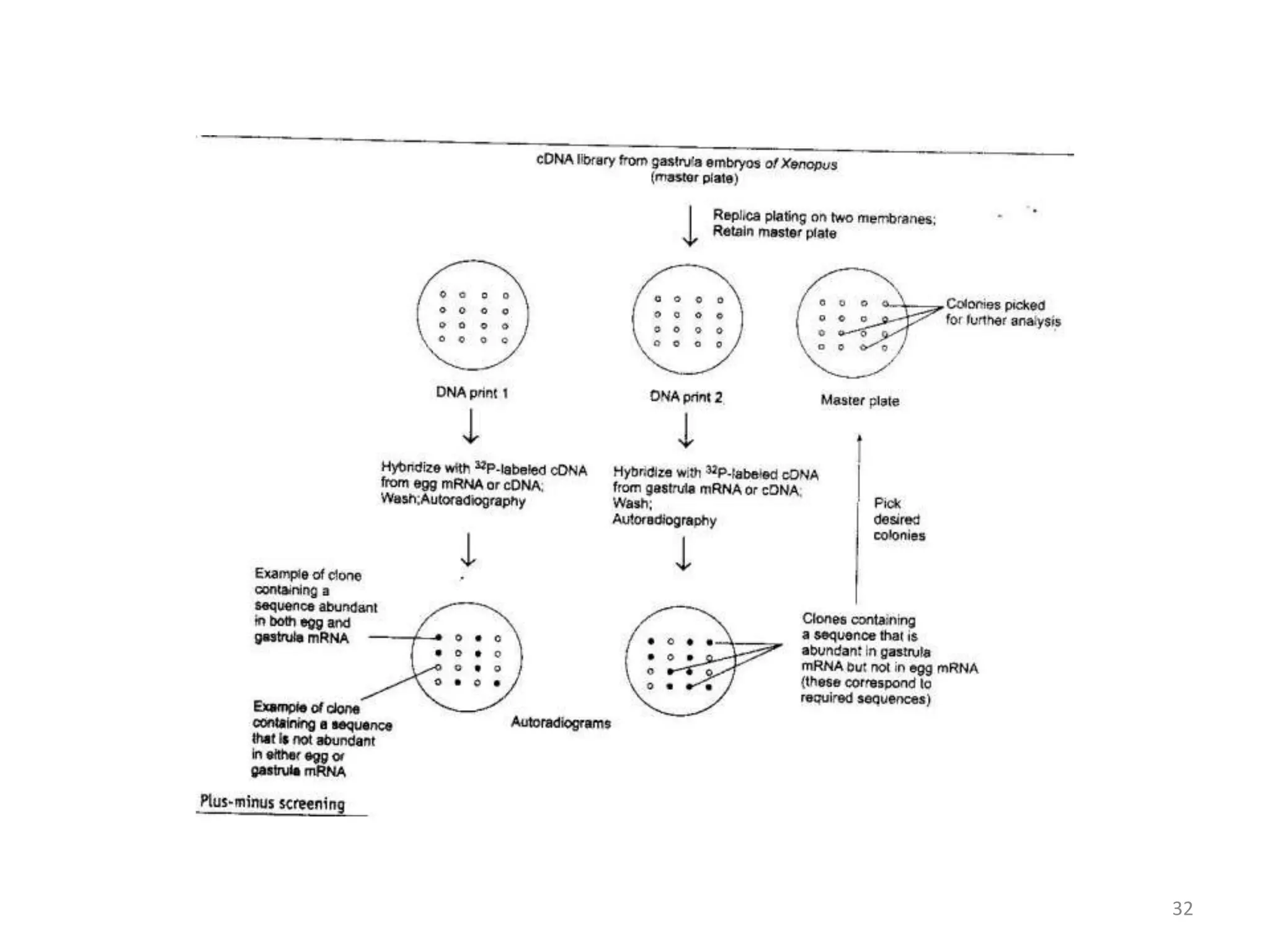
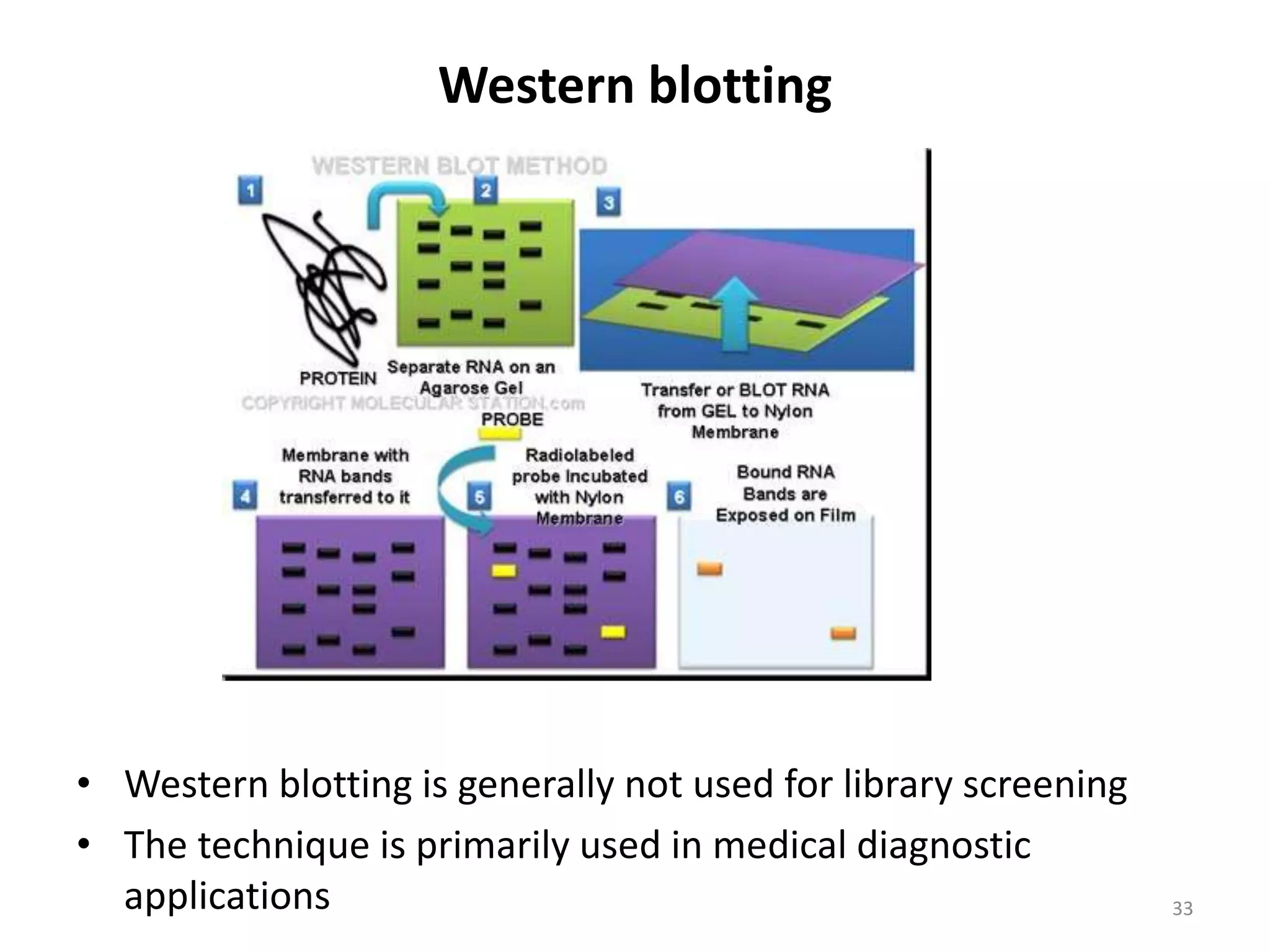
Hybridization techniques involve immobilizing target DNA/RNA on a membrane and probing it with a labeled DNA/RNA probe. The key steps are immobilizing the target nucleic acid, preparing a labeled probe with complementary sequence, hybridizing the probe to the target, and detecting the hybridized probe. Membrane hybridization does not proceed to completion as some nucleic acids are embedded in the membrane and inaccessible to the probe. Pre-hybridization and hybridization buffers contain components like rate enhancers and blocking agents to promote hybridization while preventing non-specific binding.