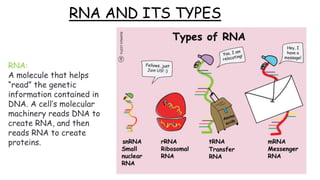
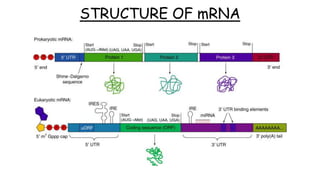
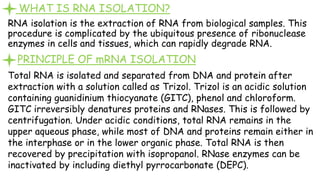
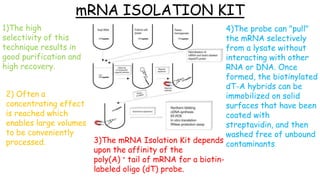
1. mRNA isolation is the process of extracting messenger RNA from biological samples. It is important for research and industry applications as mRNA provides insight into which genes are being expressed and translated into proteins.
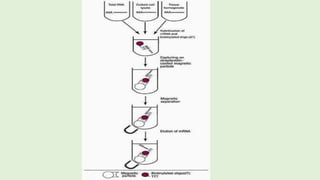
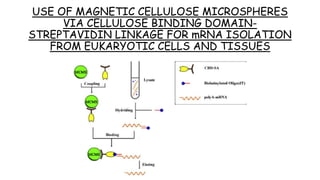
2. Total RNA is first extracted using Trizol, which separates RNA, DNA and proteins. mRNA is then isolated from total RNA using biotin-labeled oligo dT probes that selectively bind to the poly-A tail of mRNA molecules.
3. The mRNA-probe complexes are immobilized on magnetic beads coated with streptavidin. This allows the mRNA to be separated and purified from other RNAs through magnetic separation washes. The purified mRNA can then be used in applications like RT-PCR and protein