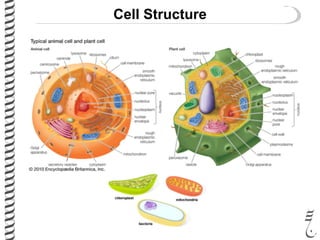
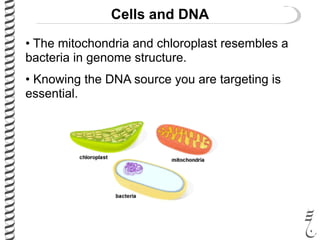
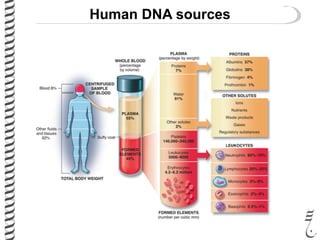
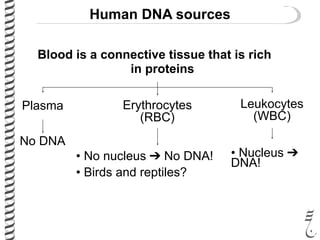
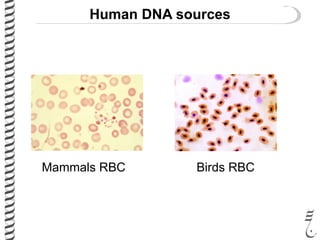
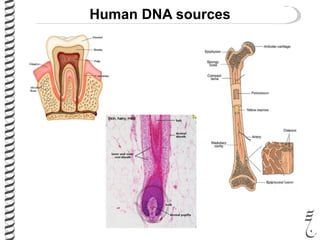
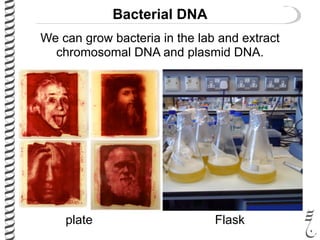
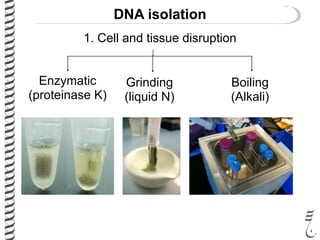
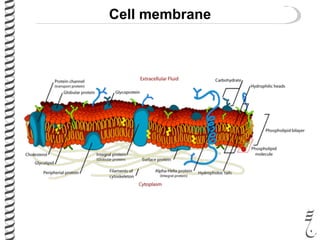
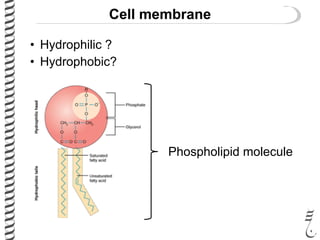
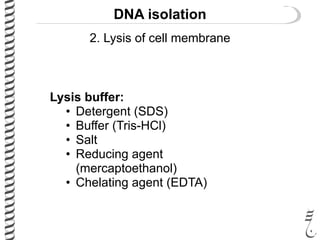
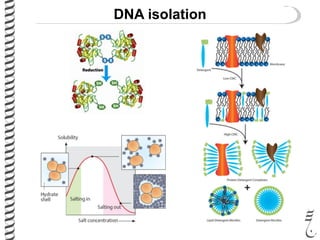
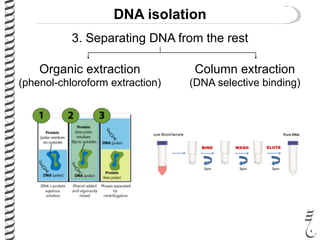
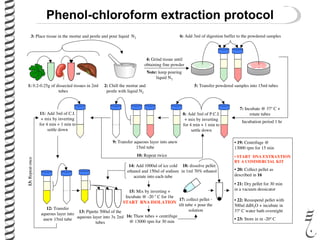
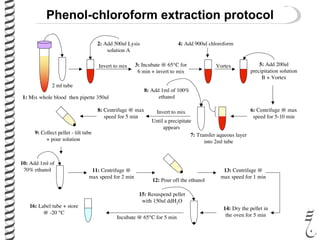
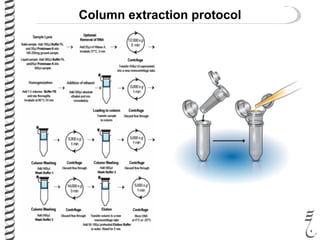
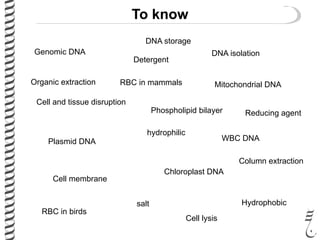
The document discusses DNA extraction from various organisms. It describes that DNA can be found in the nucleus and mitochondria of animal cells, the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts of plant cells, and the bacterial chromosome and plasmids of bacteria. The document outlines the steps of DNA extraction, including disrupting the cell, lysing the cell membrane using detergents and buffers, and separating the DNA from other cell contents using organic extraction or column extraction. It also discusses sources of human DNA, such as white blood cells, and storage of extracted DNA in TE buffer or freezing.