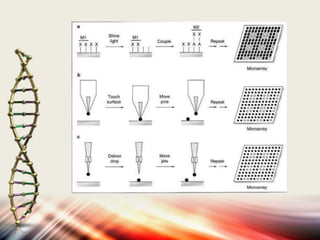
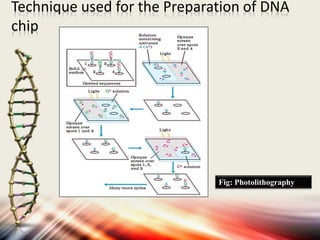
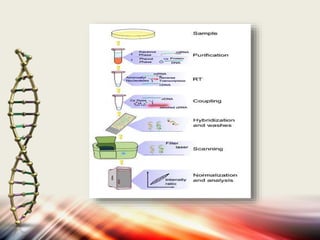
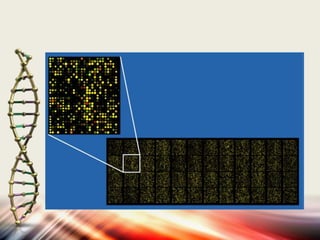
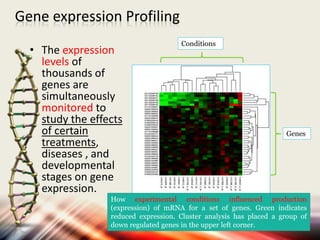
Microarrays allow researchers to analyze gene expression levels across thousands of genes simultaneously. DNA microarrays work by hybridizing fluorescently-labeled cDNA or cRNA to complementary DNA probes attached to a solid surface. This technology has applications in gene expression profiling, disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and toxicology research. While microarrays provide high-throughput analysis, their limitations include not reflecting true protein levels, complex data analysis, expense, and short shelf life of DNA chips.