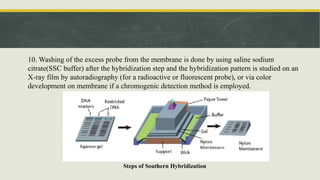
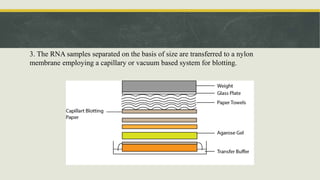
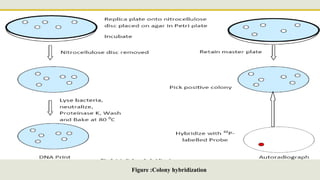
Nucleic acid hybridization is a technique used to identify specific DNA sequences. It involves denaturing DNA or RNA samples and probes, followed by annealing of the probes to complementary sequences. There are two main types: Southern blotting separates DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis before hybridization with probes, while Northern blotting separates RNA this way. Both techniques allow detection of specific sequences through the use of labeled probes.