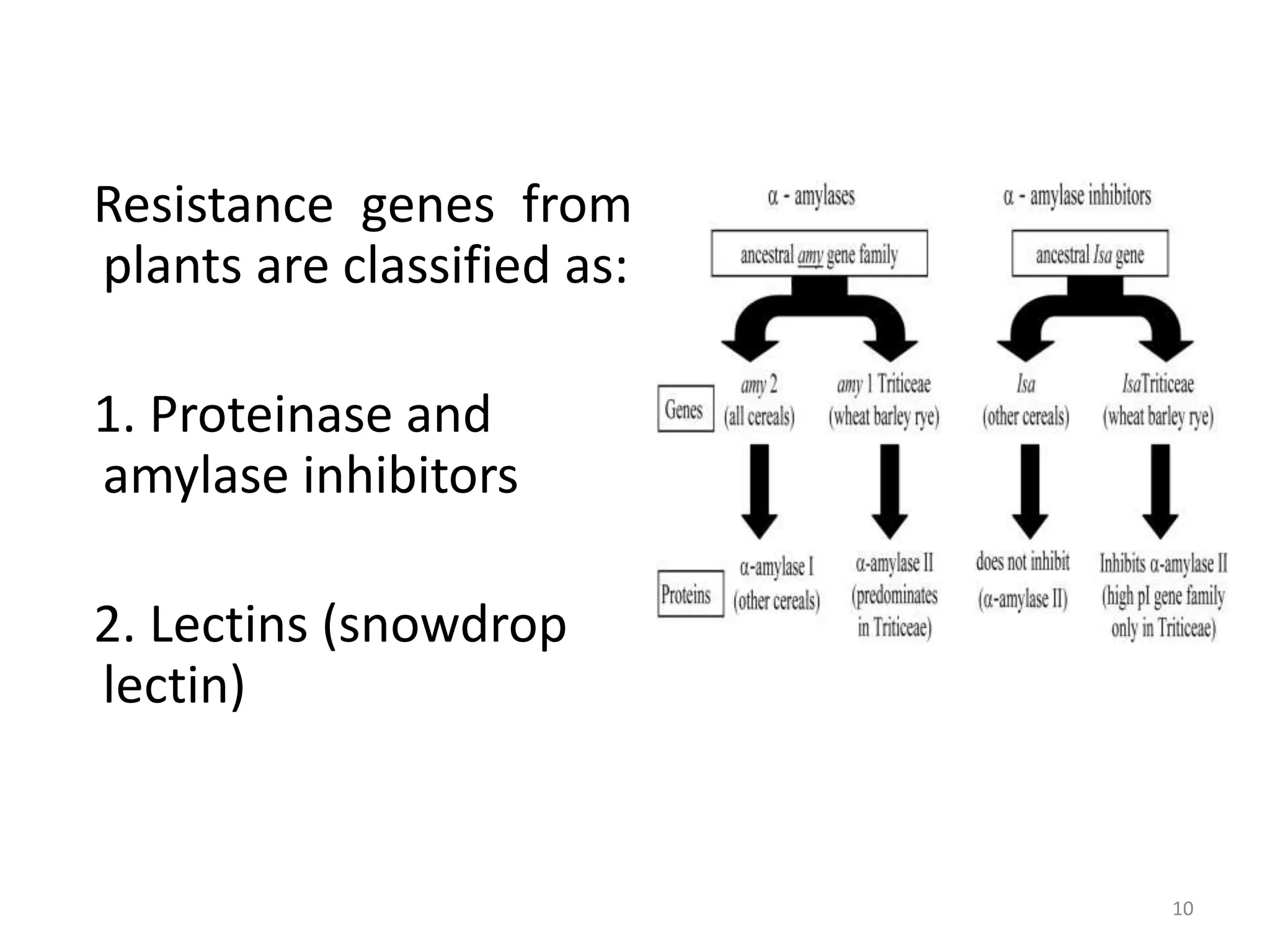
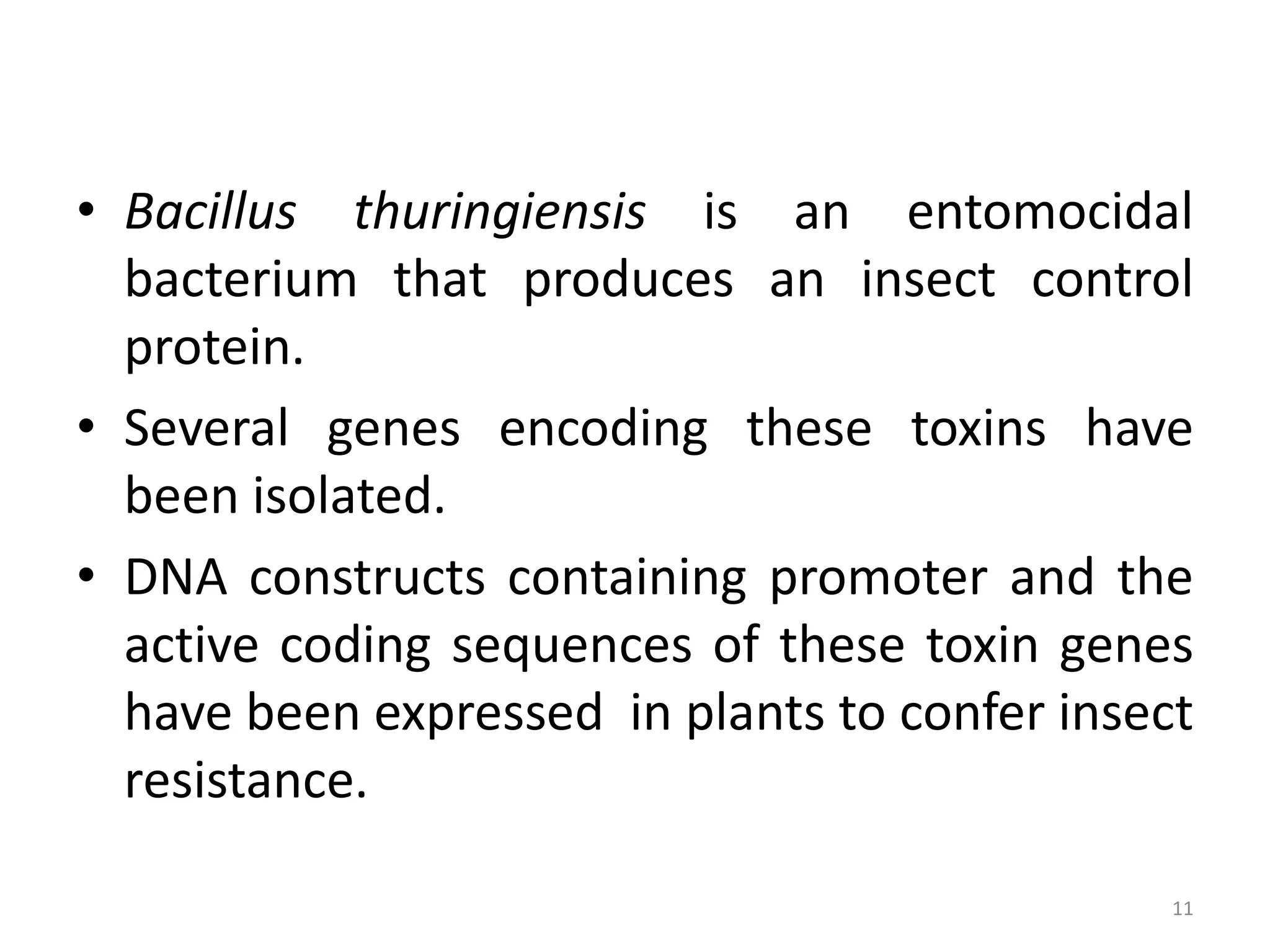
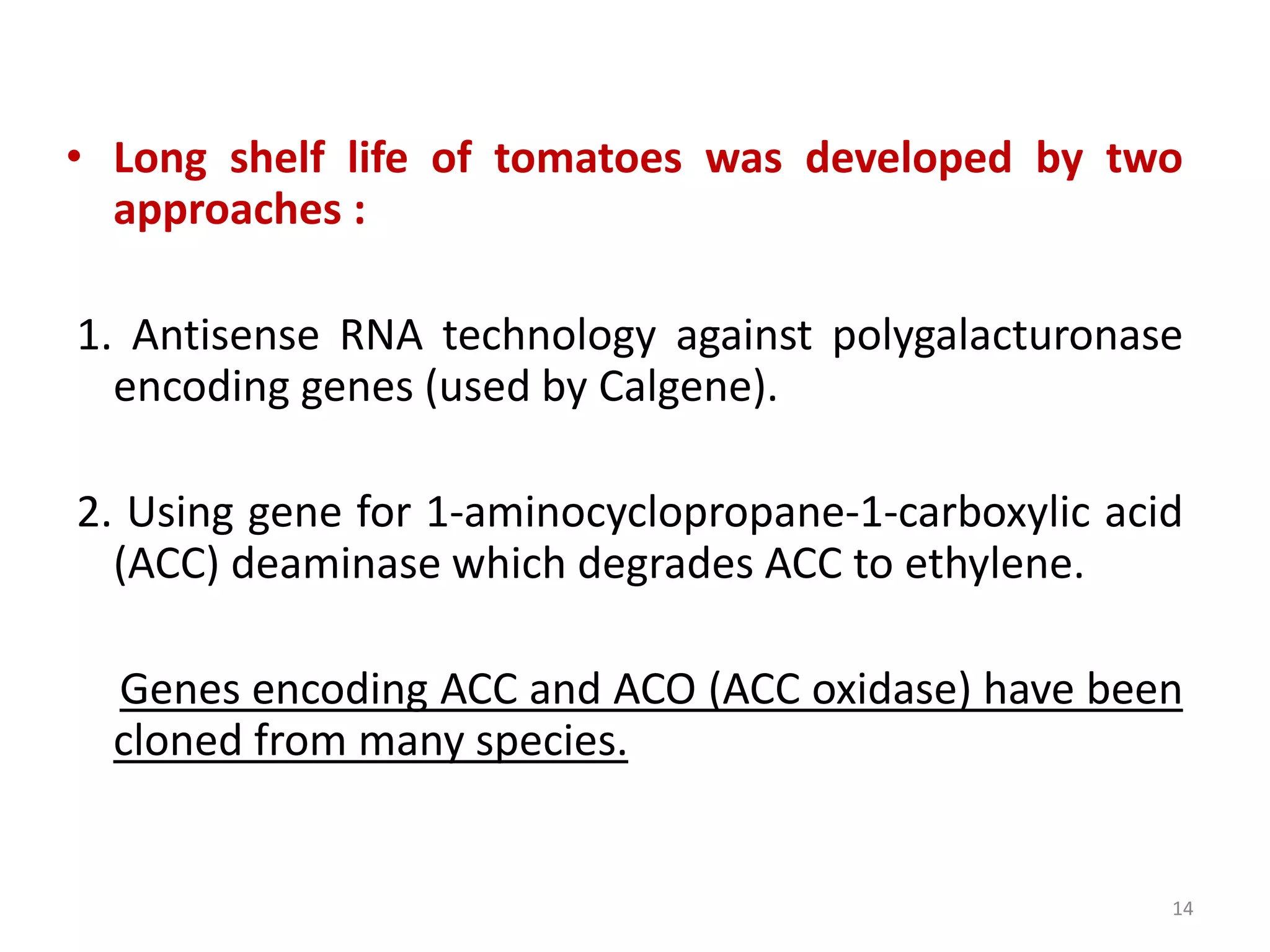
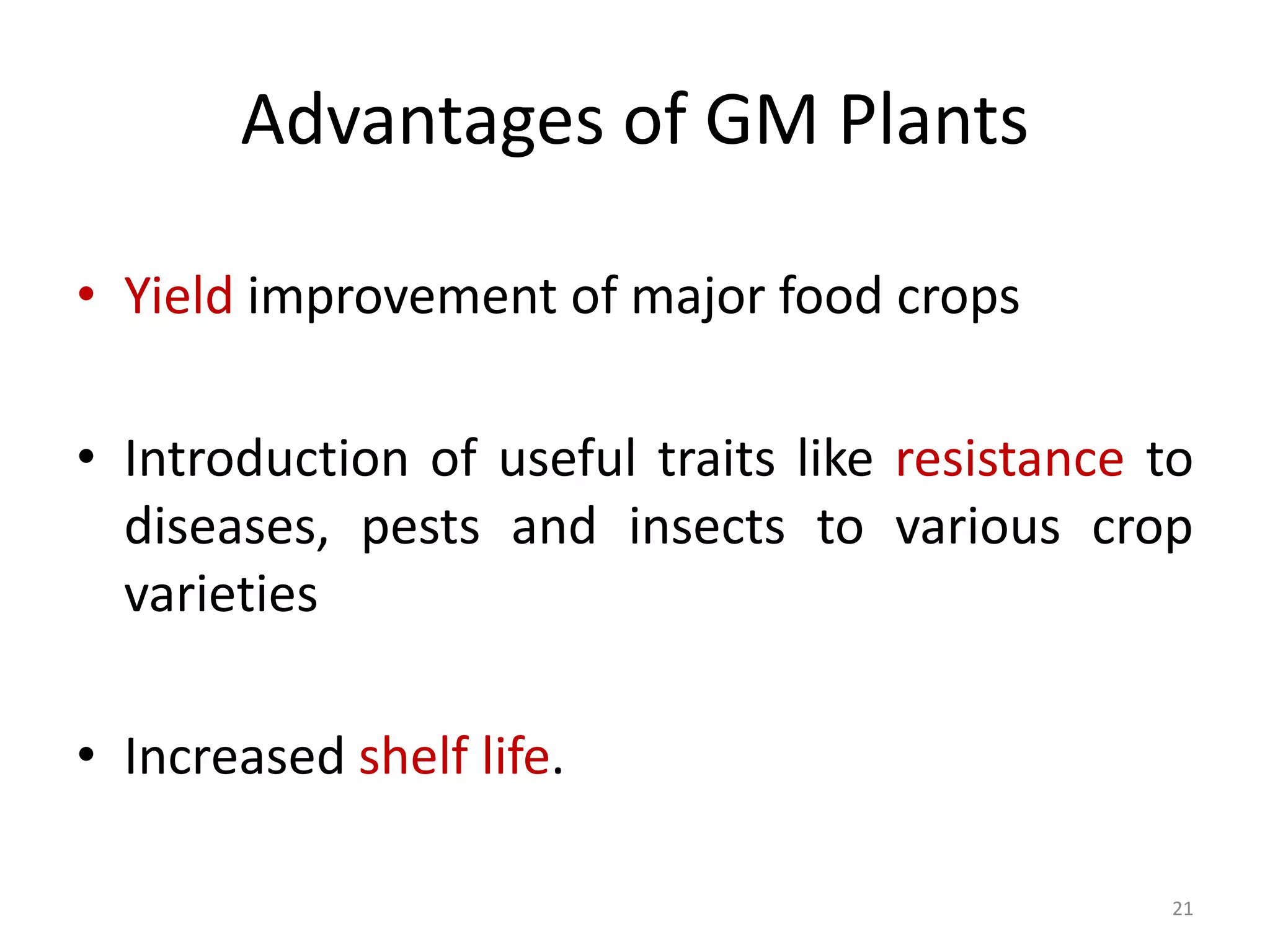
Genetically modified organisms are defined as organisms that have had their DNA altered in a way that does not occur naturally, such as by transferring genes between non-related species. The first GM plants and animals were created in the 1970s-1980s and included E. coli bacteria containing human genes and transgenic mice. Since then, many other GM crops have been developed including Bt cotton in 1996, which resisted lepidopteran insects without the need for pesticides. More recent developments include safflower plants producing human insulin in 2008 and poplar trees with altered cellulose and lignin levels in 2009. Overall, GM technology has allowed for the introduction of useful traits like increased yield, herbicide and pest resistance, and nutritional enhancements