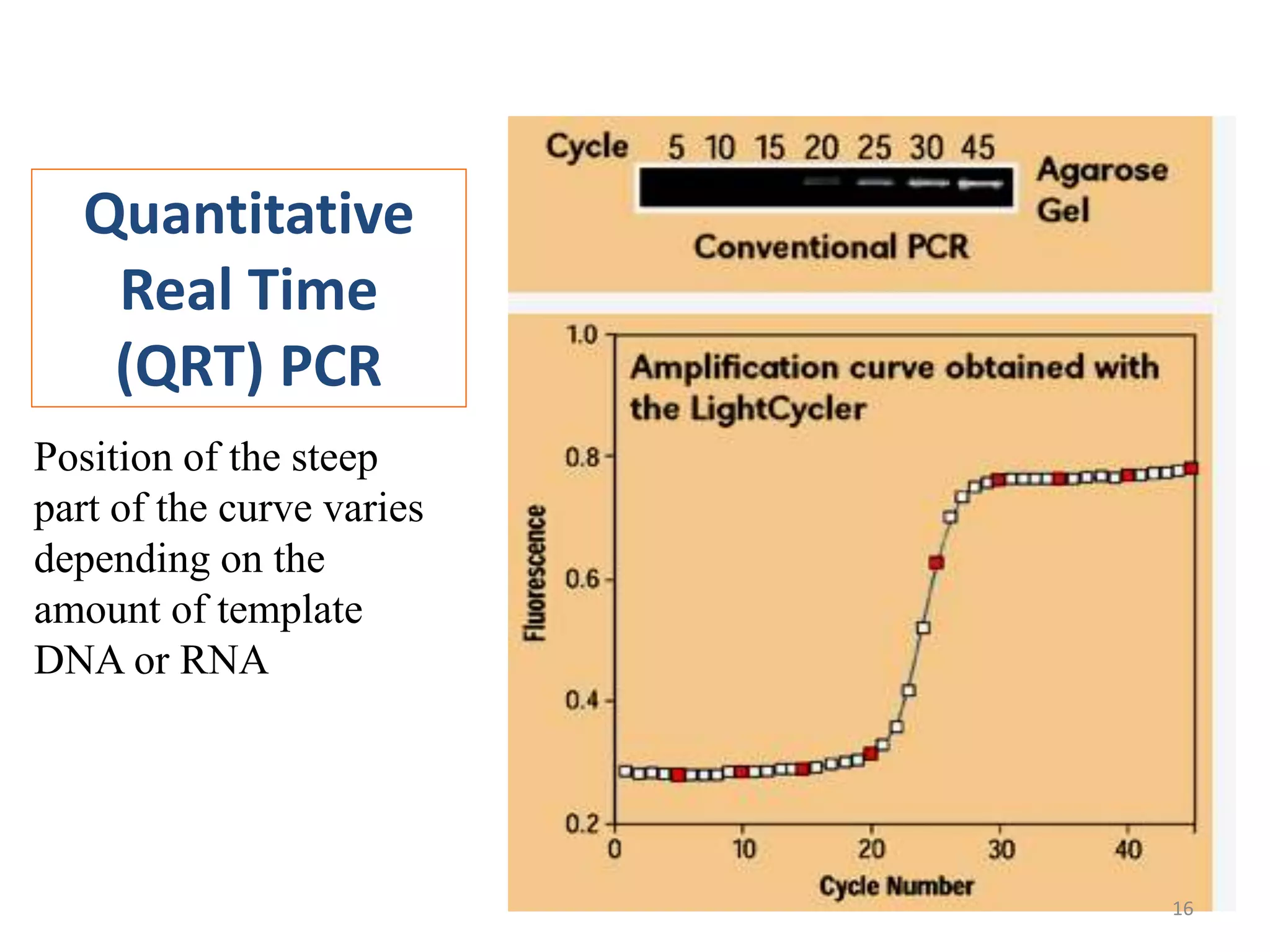
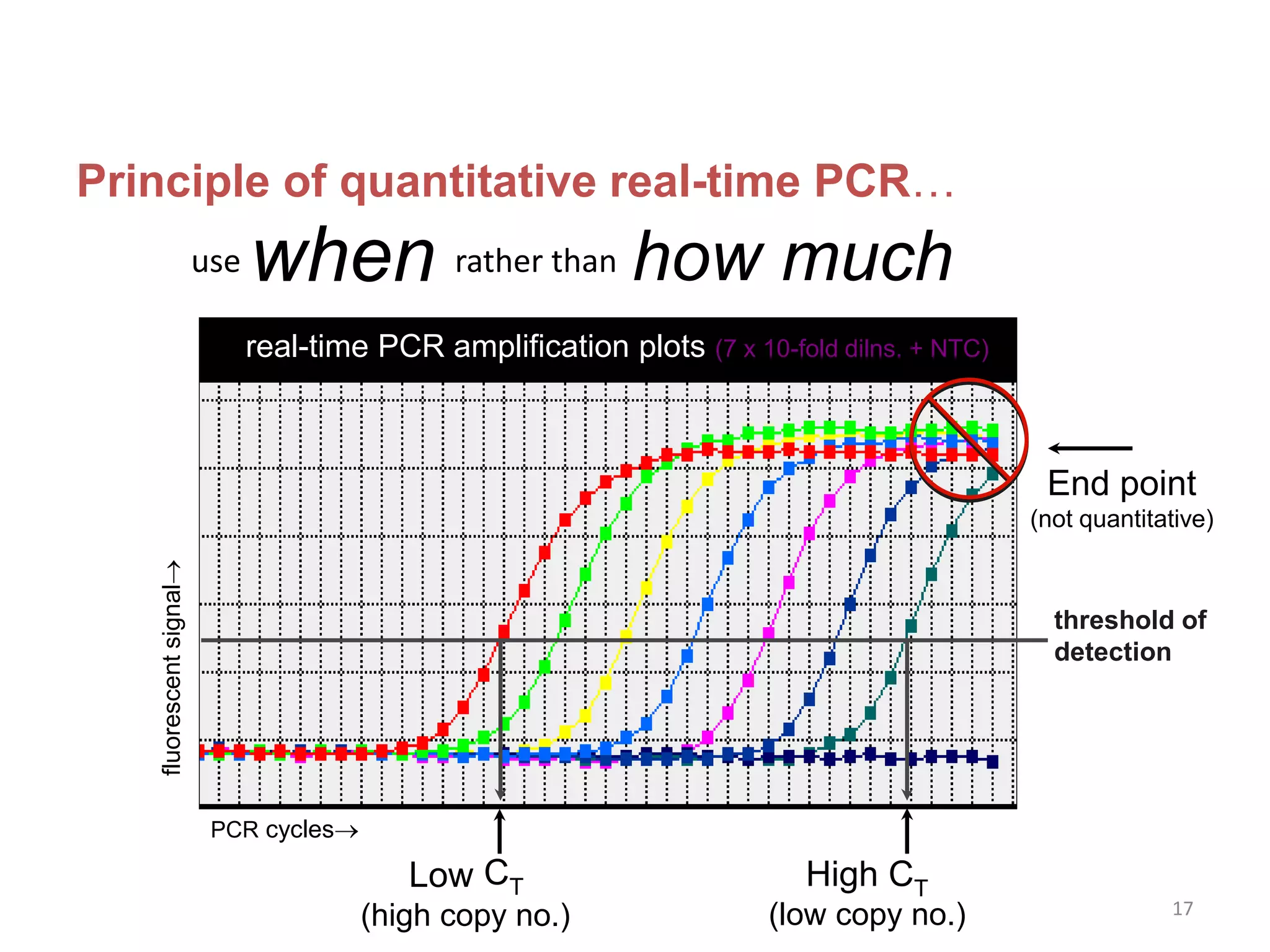
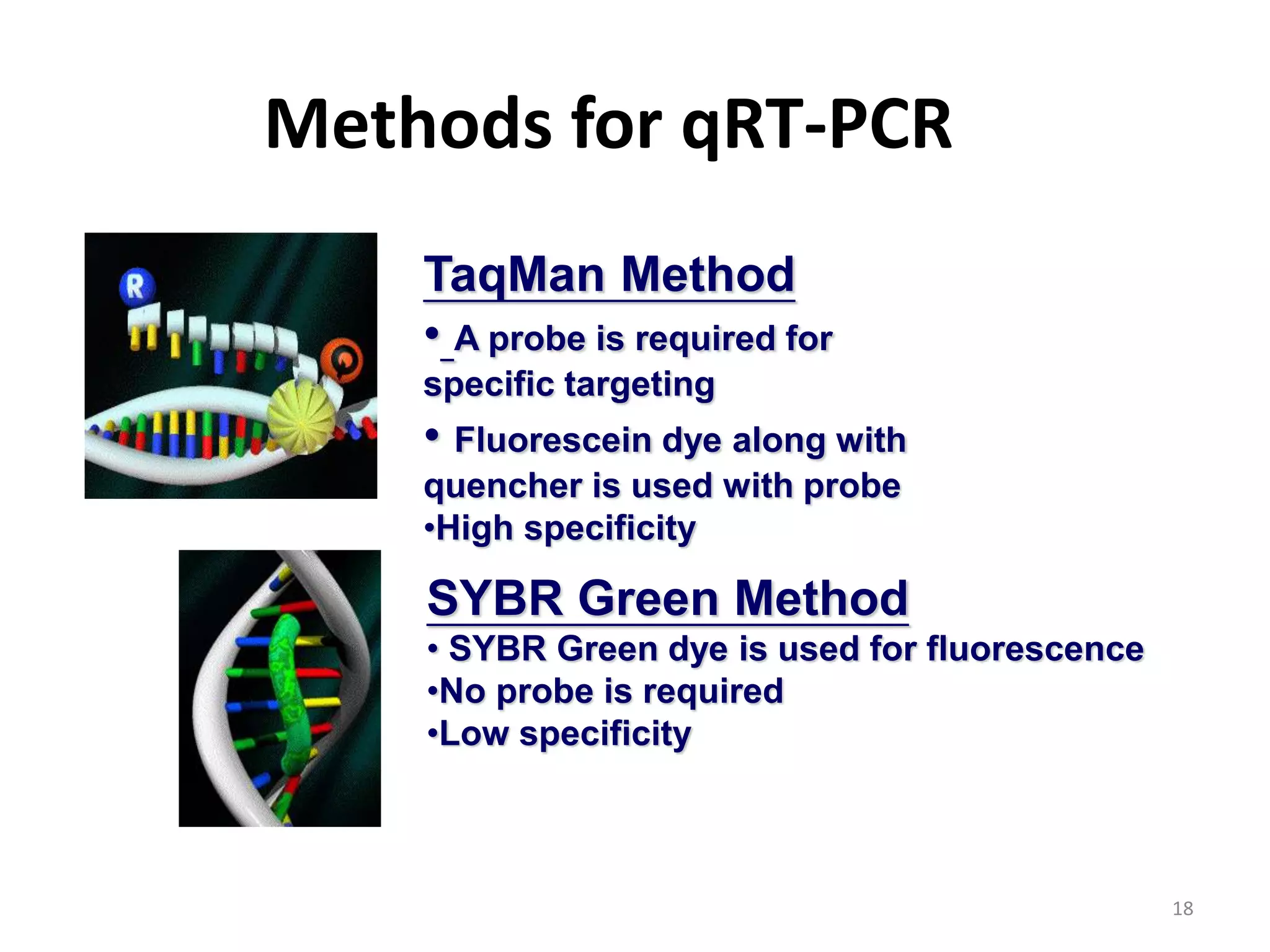
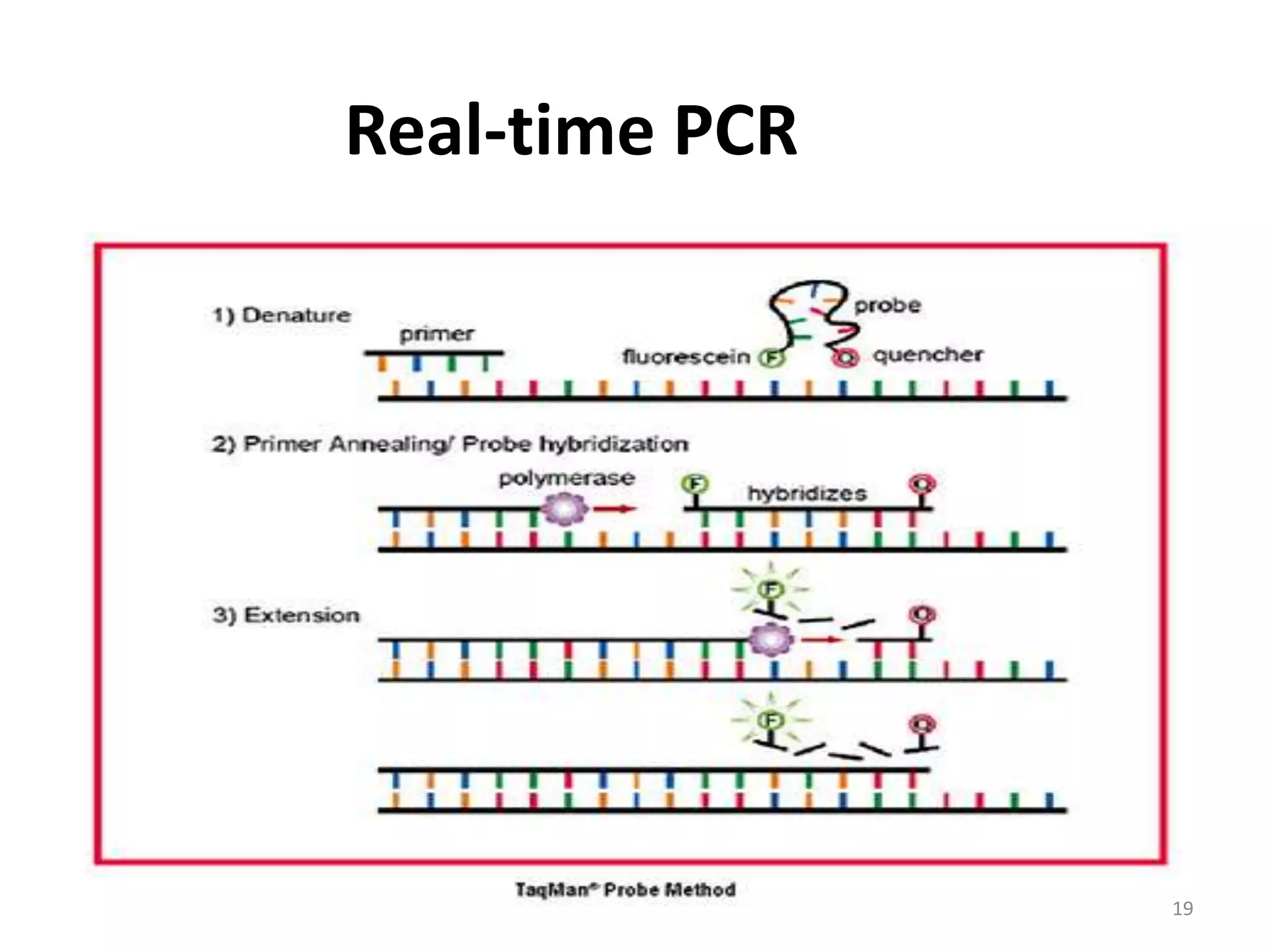
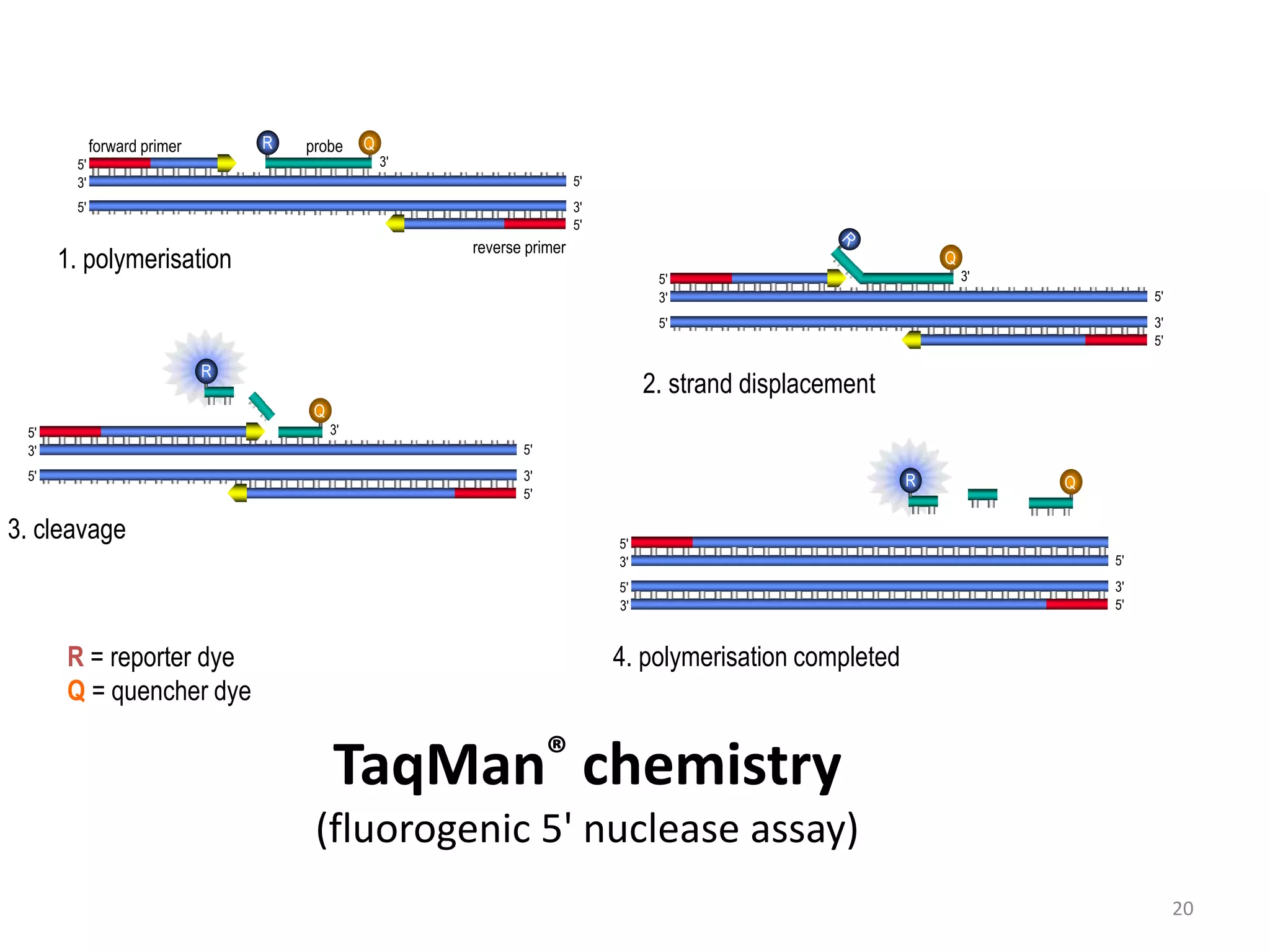
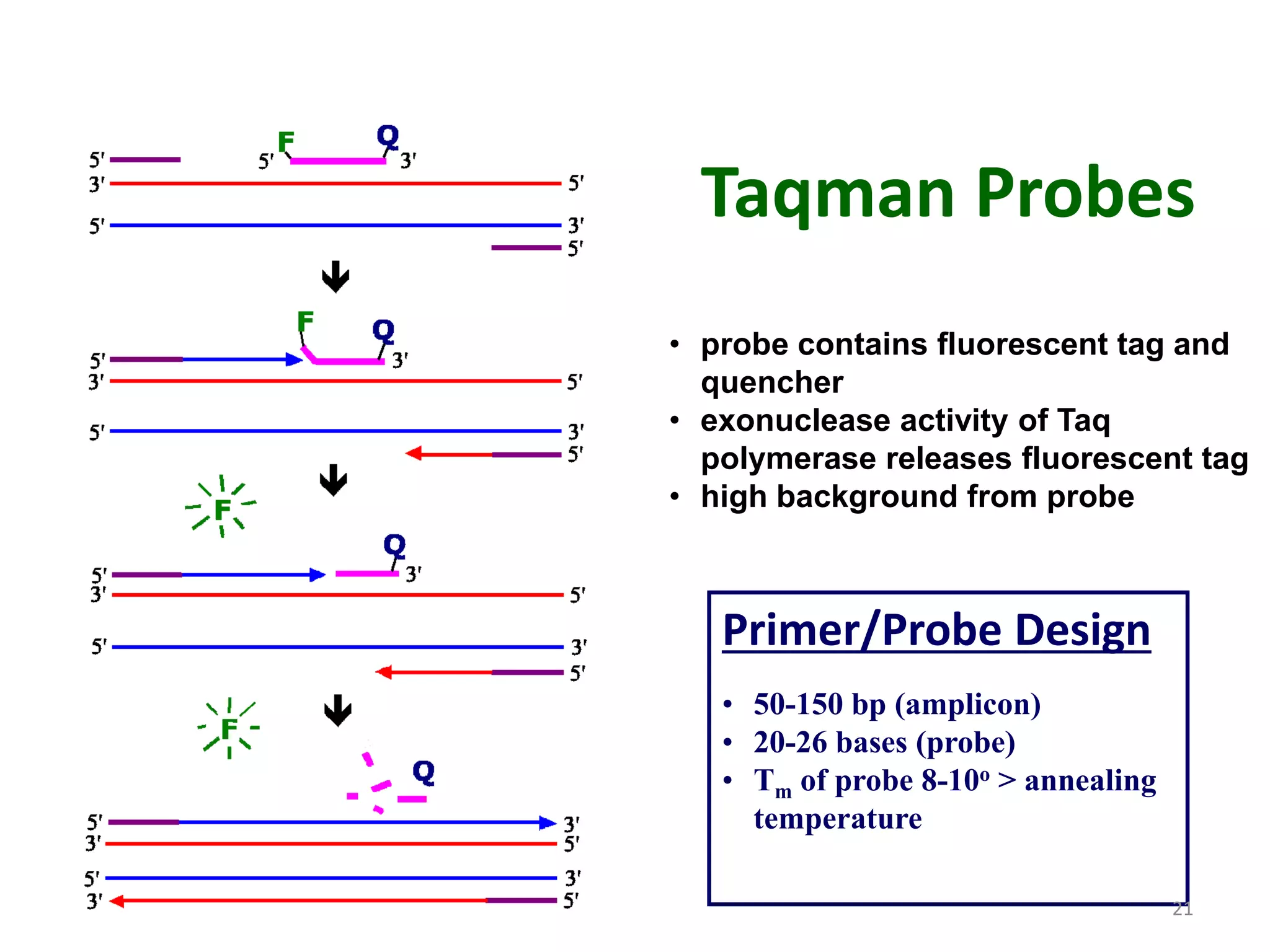
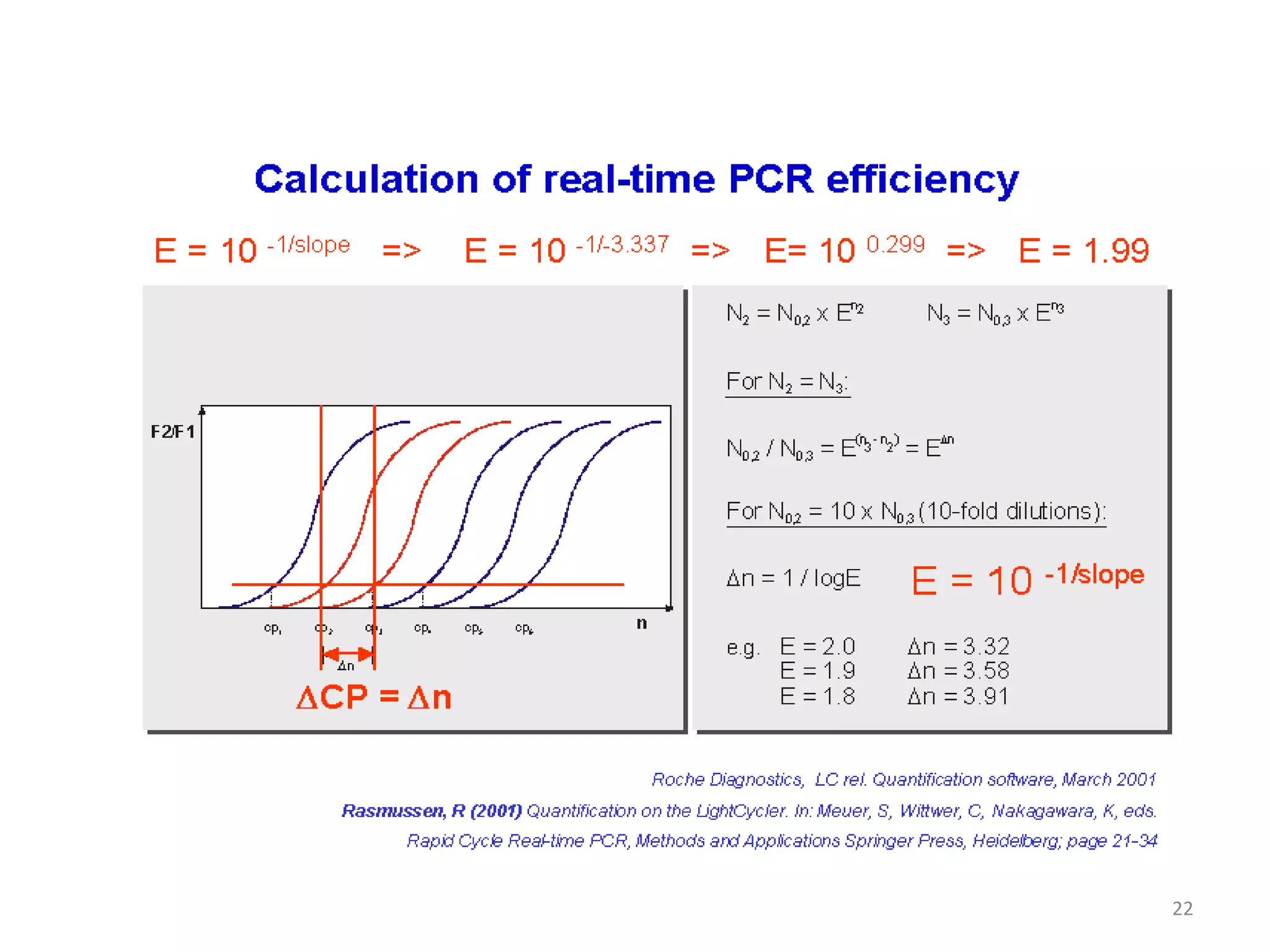
Reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) is used to amplify cDNA copies of RNA. It involves reverse transcribing RNA to cDNA then amplifying the cDNA with PCR. RT-PCR can be used to study gene expression and diagnose genetic diseases. Variations include band-stab PCR which reamplifies low yield fragments, degenerate PCR which uses mixed primers for related gene families, and anchored PCR which attaches a known sequence to amplify unknown 5' sequences. Real-time PCR monitors fluorescence during amplification to quantify templates in each cycle, allowing visualization of reactions in real-time. It is commonly used to measure changes in gene expression.