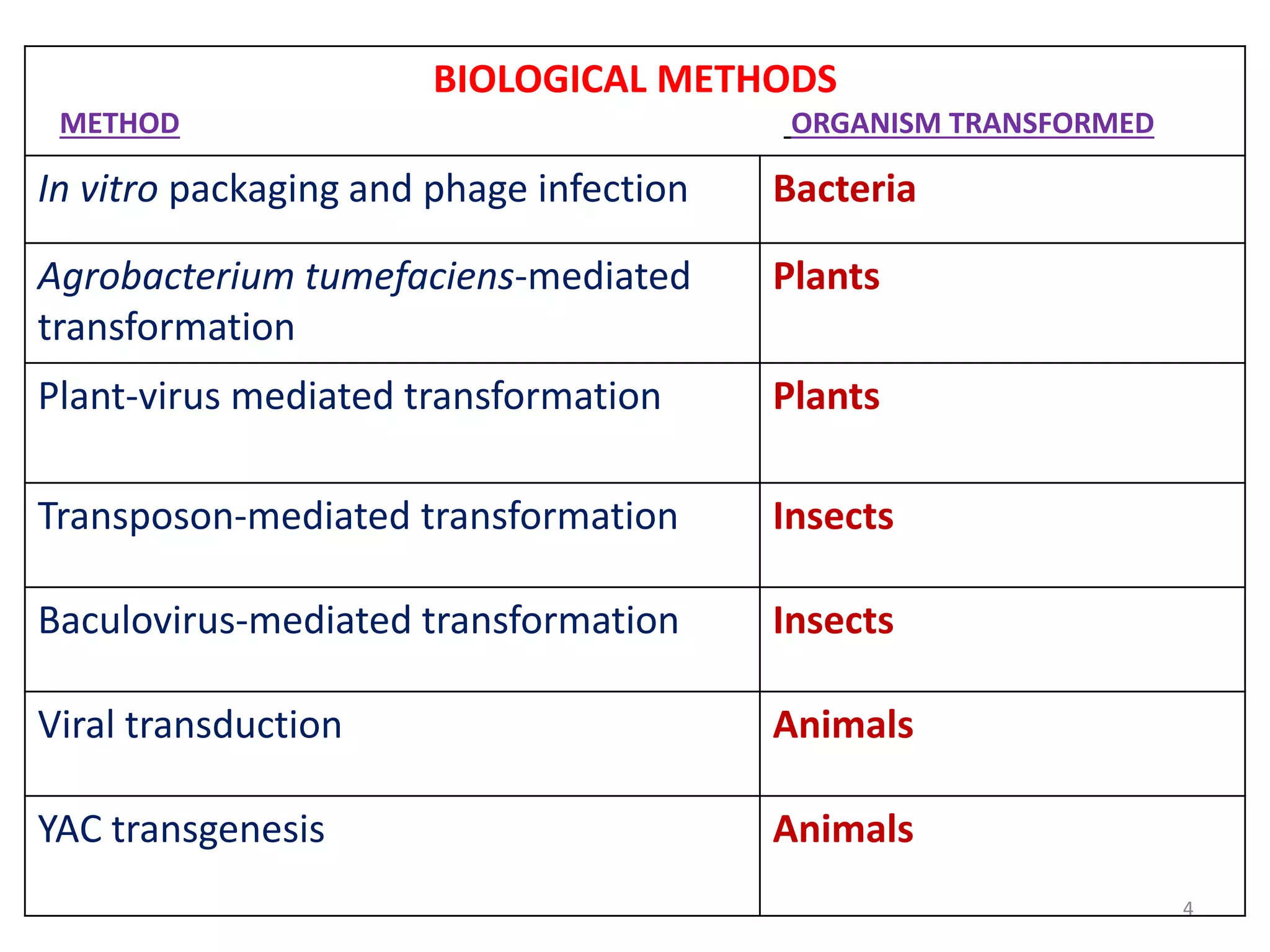
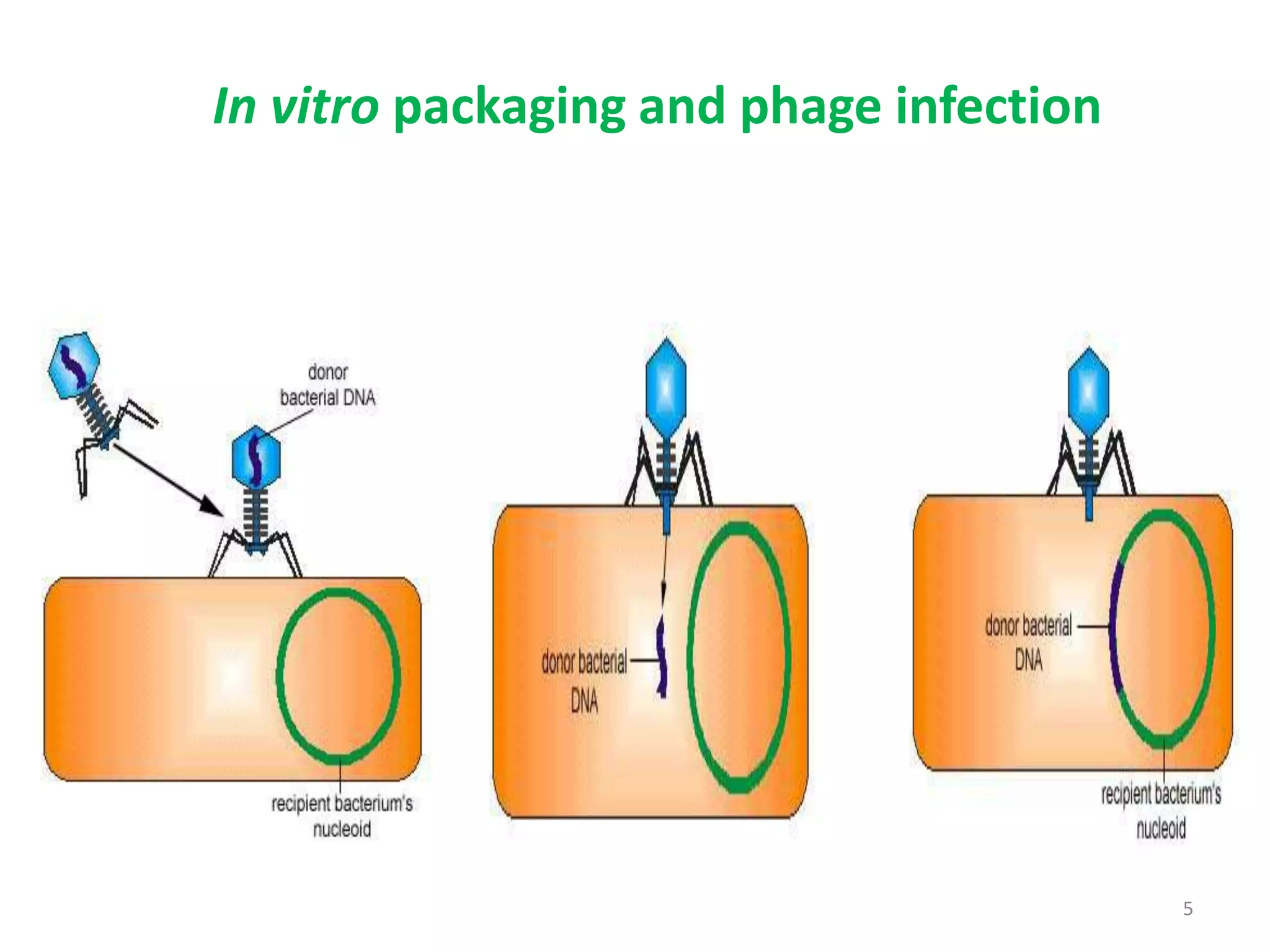
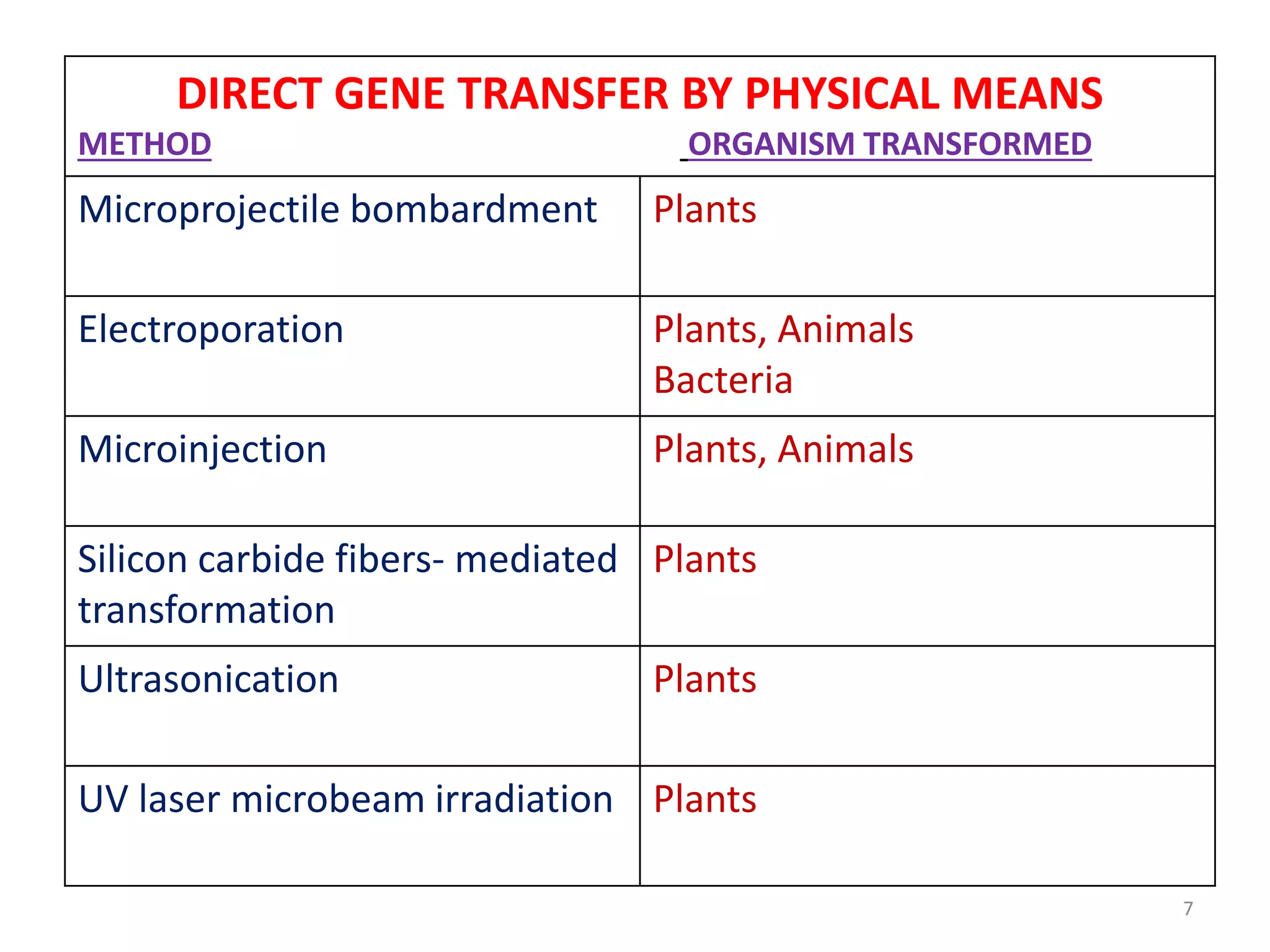
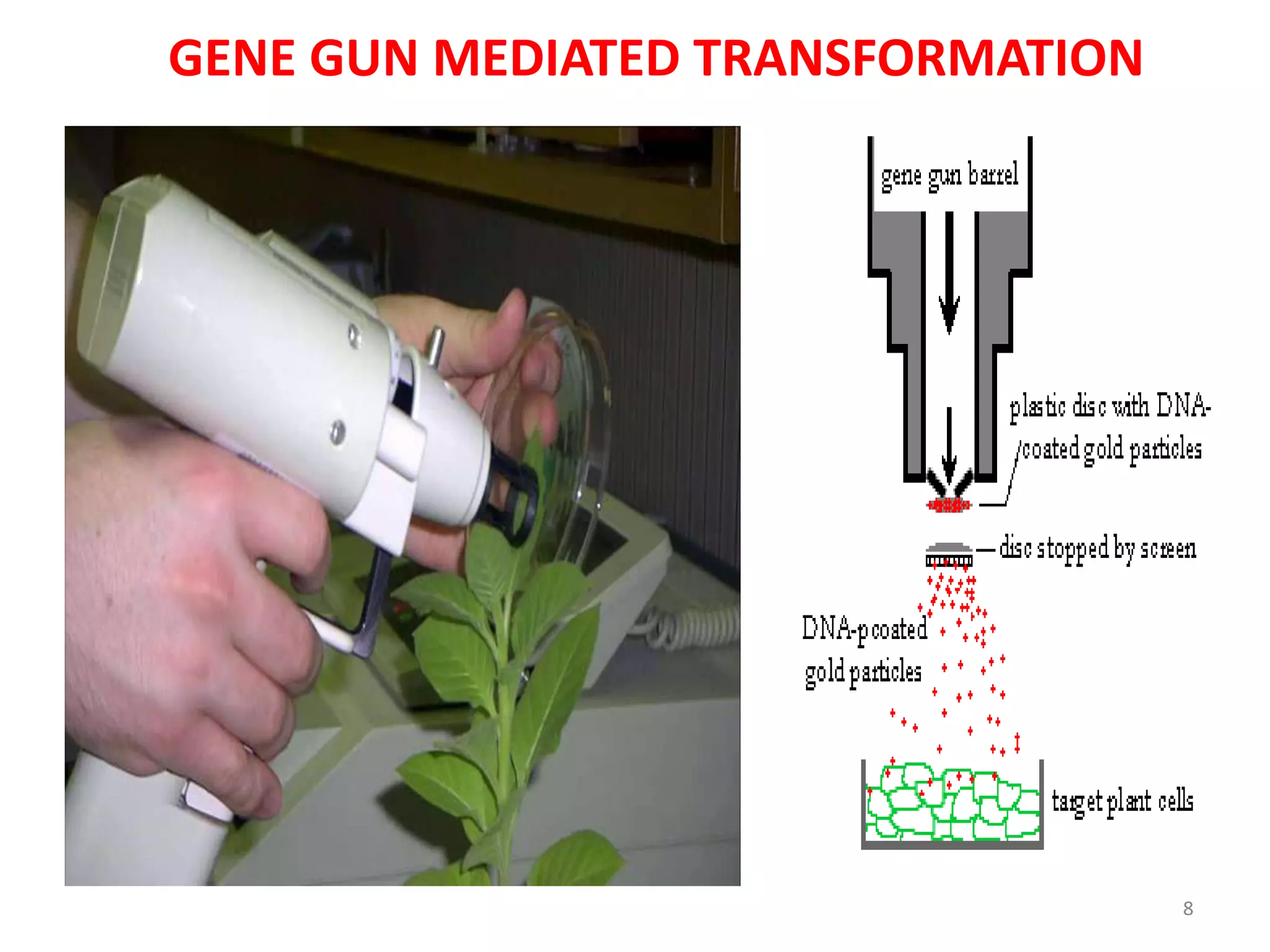
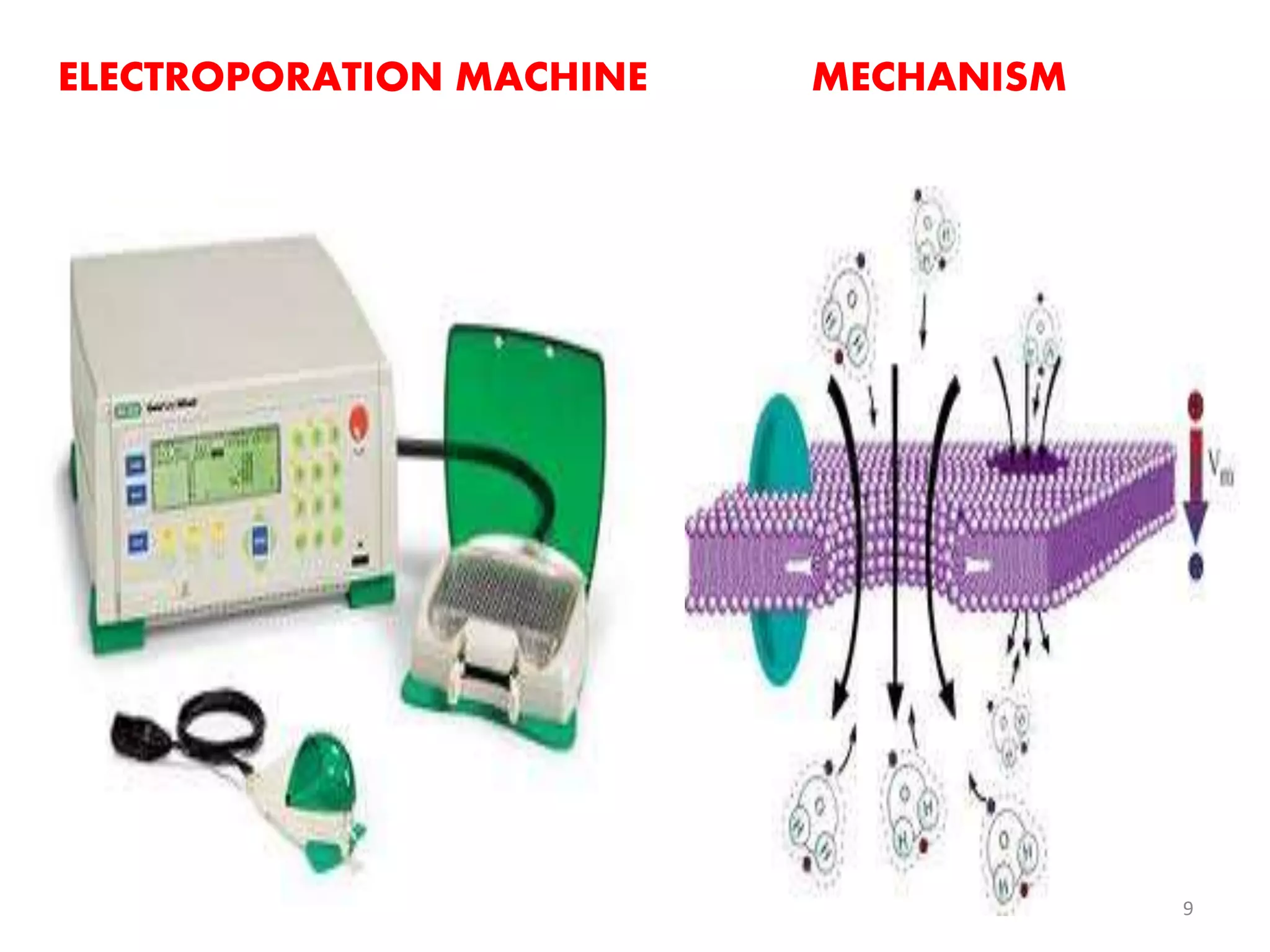
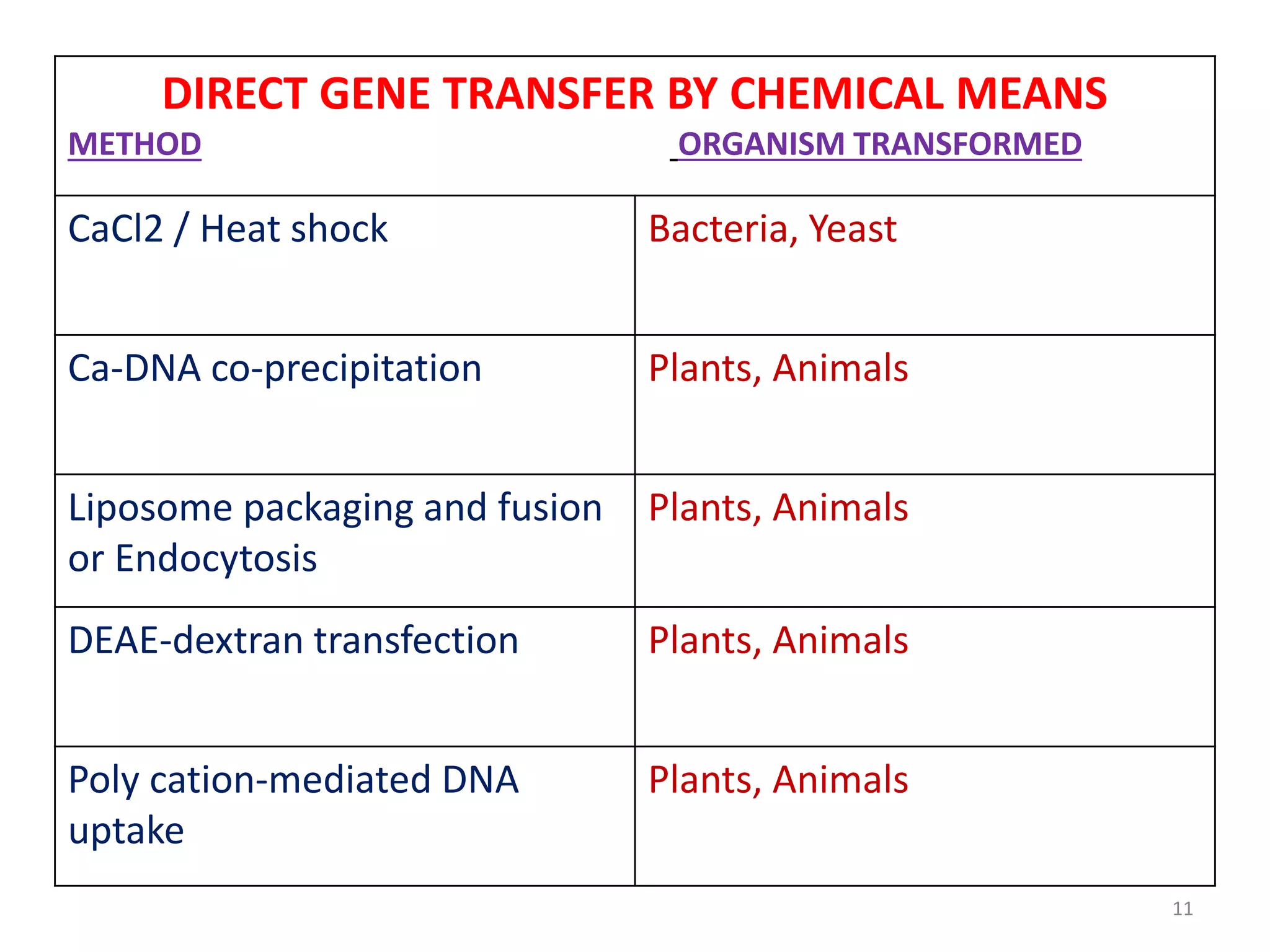
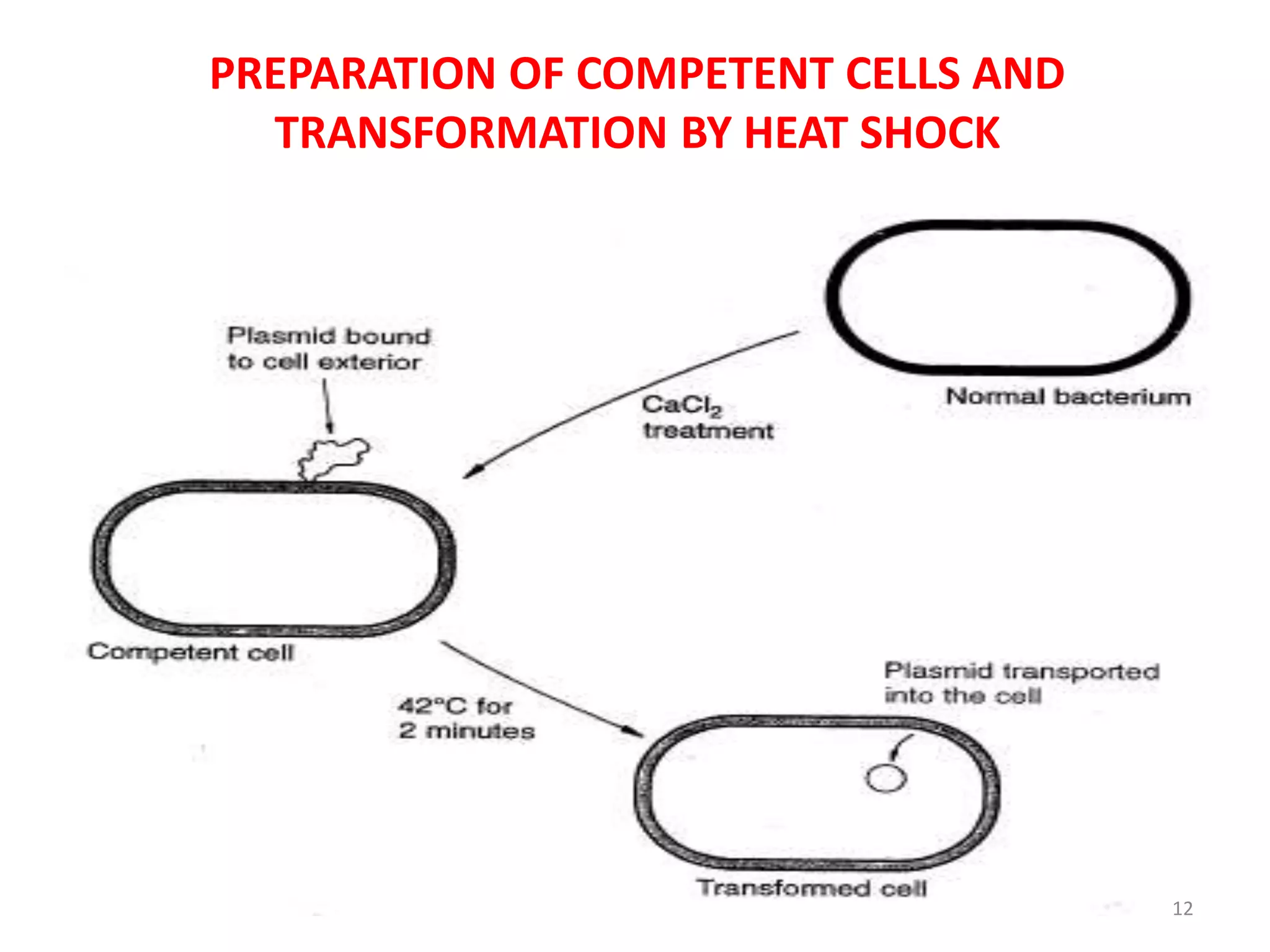
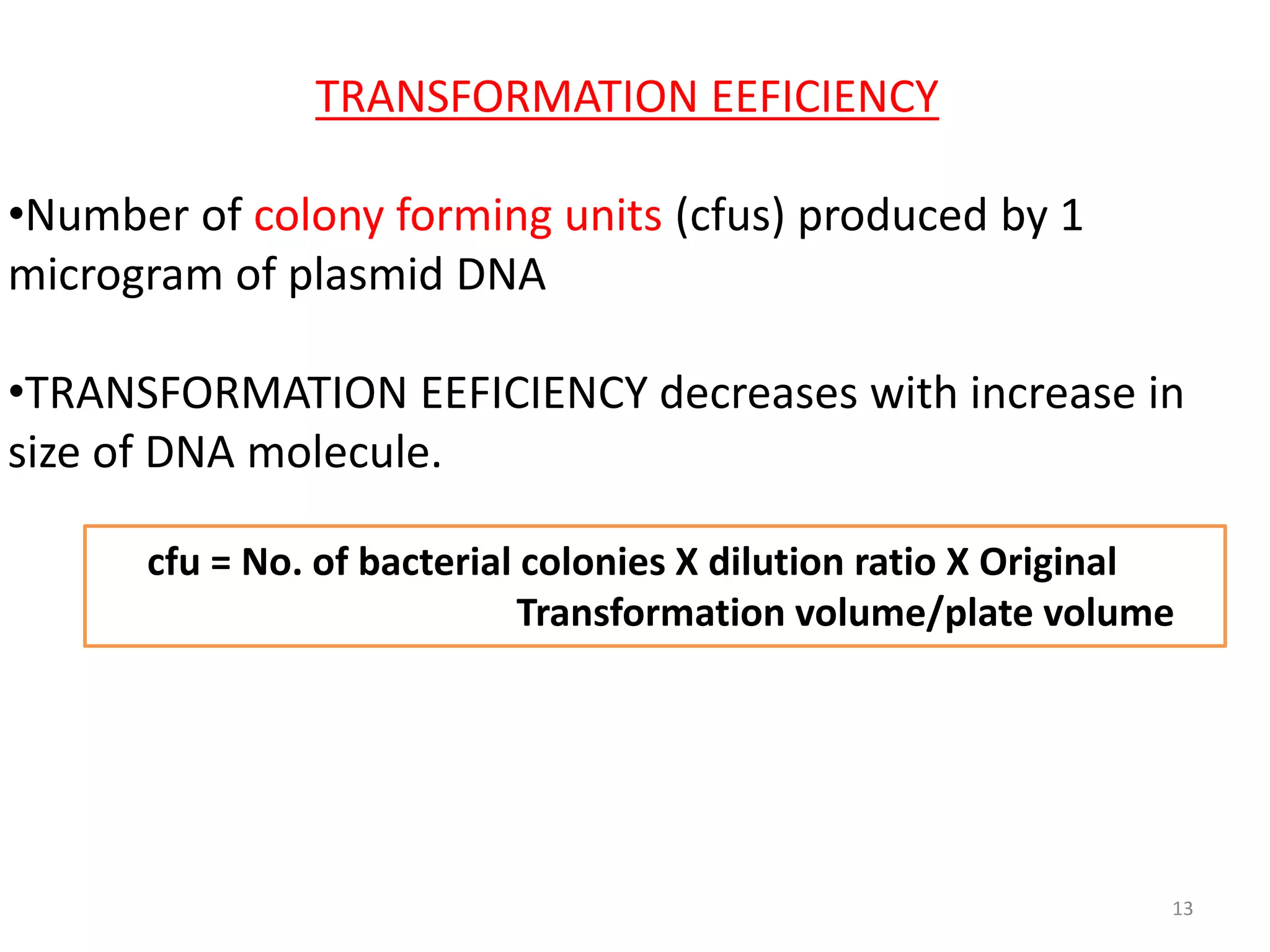
This document discusses various methods for introducing DNA into host cells, which is an important step in genetic engineering. It describes transformation, which is introducing DNA into living cells, and transfection, which is introducing viral DNA into living cells. The document then outlines several biological, chemical, and physical methods for transformation and transfection in bacteria, plants, insects, and animal cells. These include techniques like bacterial infection with bacteriophage, Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation, microprojectile bombardment, electroporation, microinjection, and calcium phosphate transfection. It also discusses factors that affect transformation efficiency.