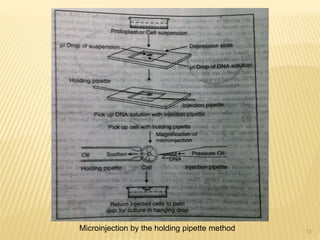
Genetic transformation involves introducing naked DNA into living cells. The first successful genetic transformation was achieved in 1972 by Stanley Cohen and coworkers using E. coli cells and plasmid DNA. Various methods were subsequently developed for transforming other organisms and cell types, including stimulation with chemicals, encapsulation in liposomes, electroporation, microprojectile bombardment, microinjection, and cell perforation using silicon carbide whiskers. These genetic transformation methods allow foreign DNA to enter cells and become integrated into the host genome.