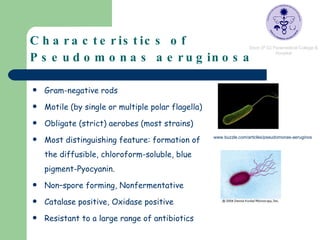
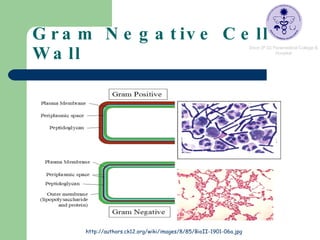
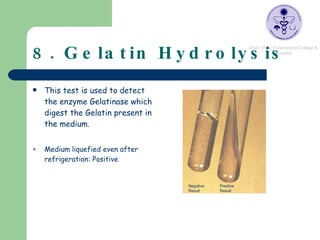
Pseudomonas are ubiquitous bacteria found in soil, water, and other moist environments. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in particular is an opportunistic pathogen capable of infecting susceptible hosts. It is a gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that produces several pigments and is resistant to many antibiotics. Biochemical tests were performed on soil isolates to identify them as P. aeruginosa, including positive results for oxidase, catalase, citrate, and gelatin hydrolysis tests, along with glucose respiration.