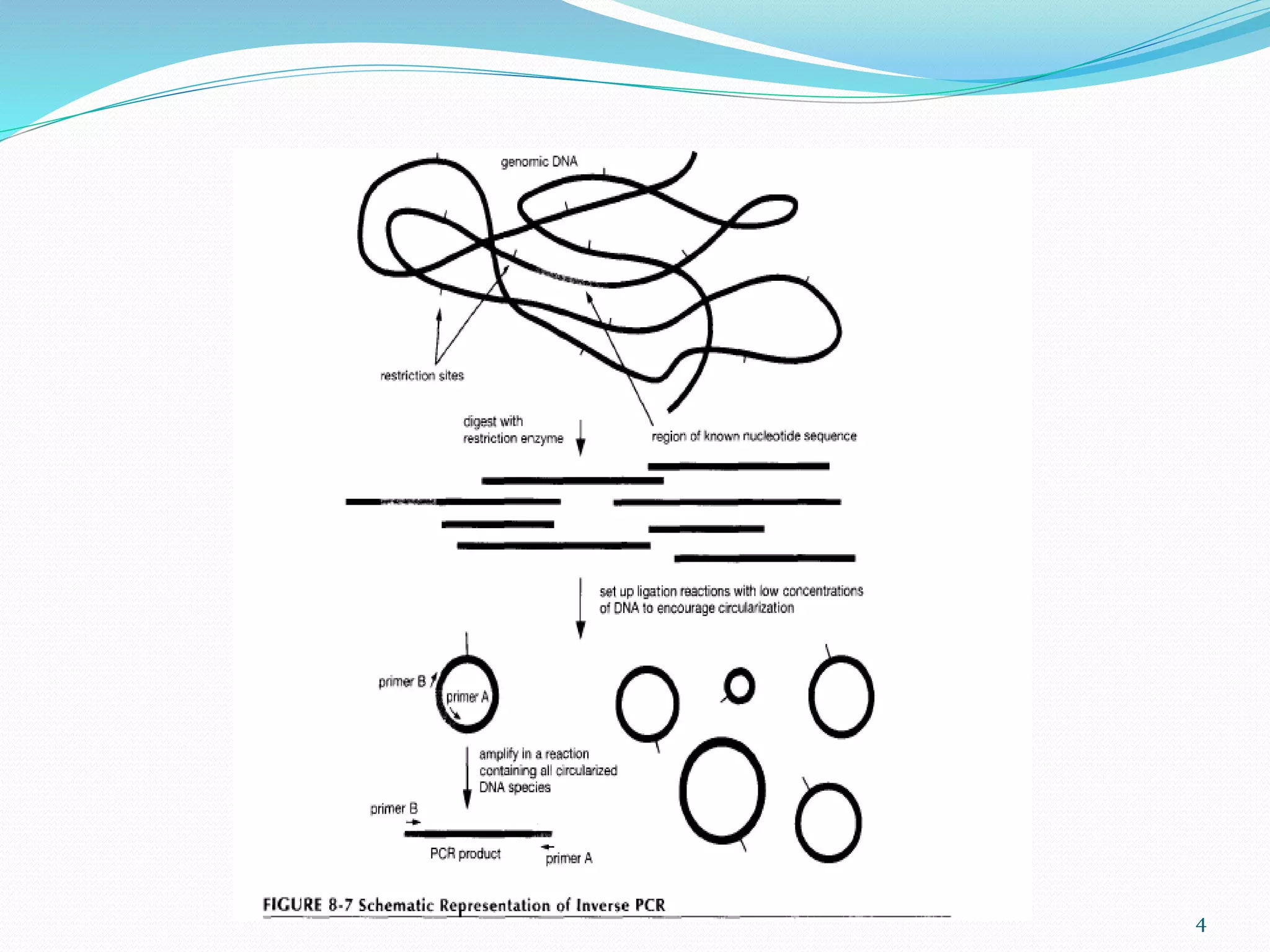
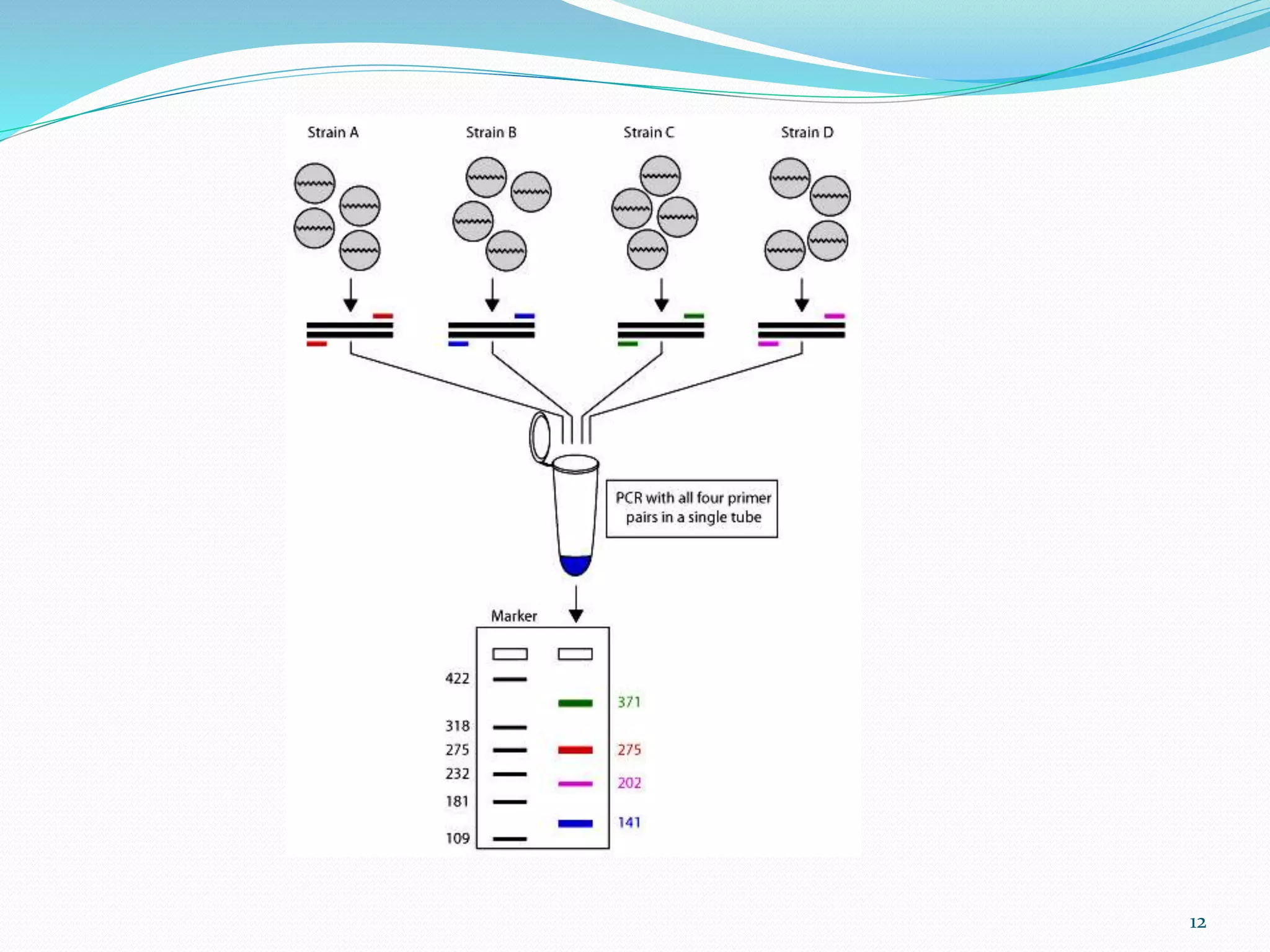
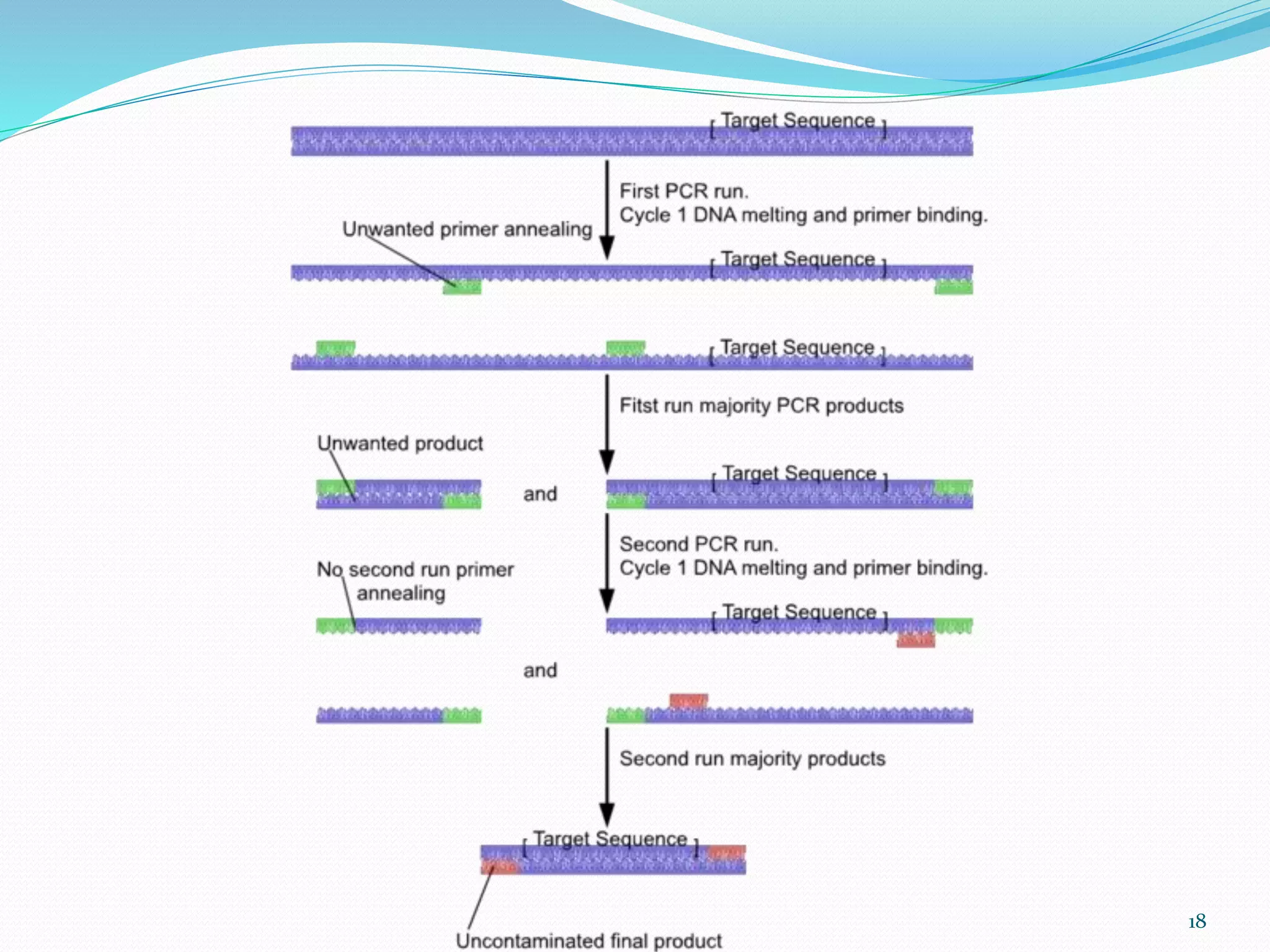
This document describes various types of PCR including inverse PCR, colony PCR, hot start PCR, multiplex PCR, in situ PCR, long PCR, nested PCR, touchdown PCR and their applications. Inverse PCR is used to amplify unknown flanking sequences. Colony PCR screens bacterial colonies without isolating DNA. Hot start PCR prevents nonspecific amplification. Multiplex PCR amplifies multiple targets simultaneously. Nested PCR increases specificity with two primer sets. Touchdown PCR optimizes annealing temperatures.