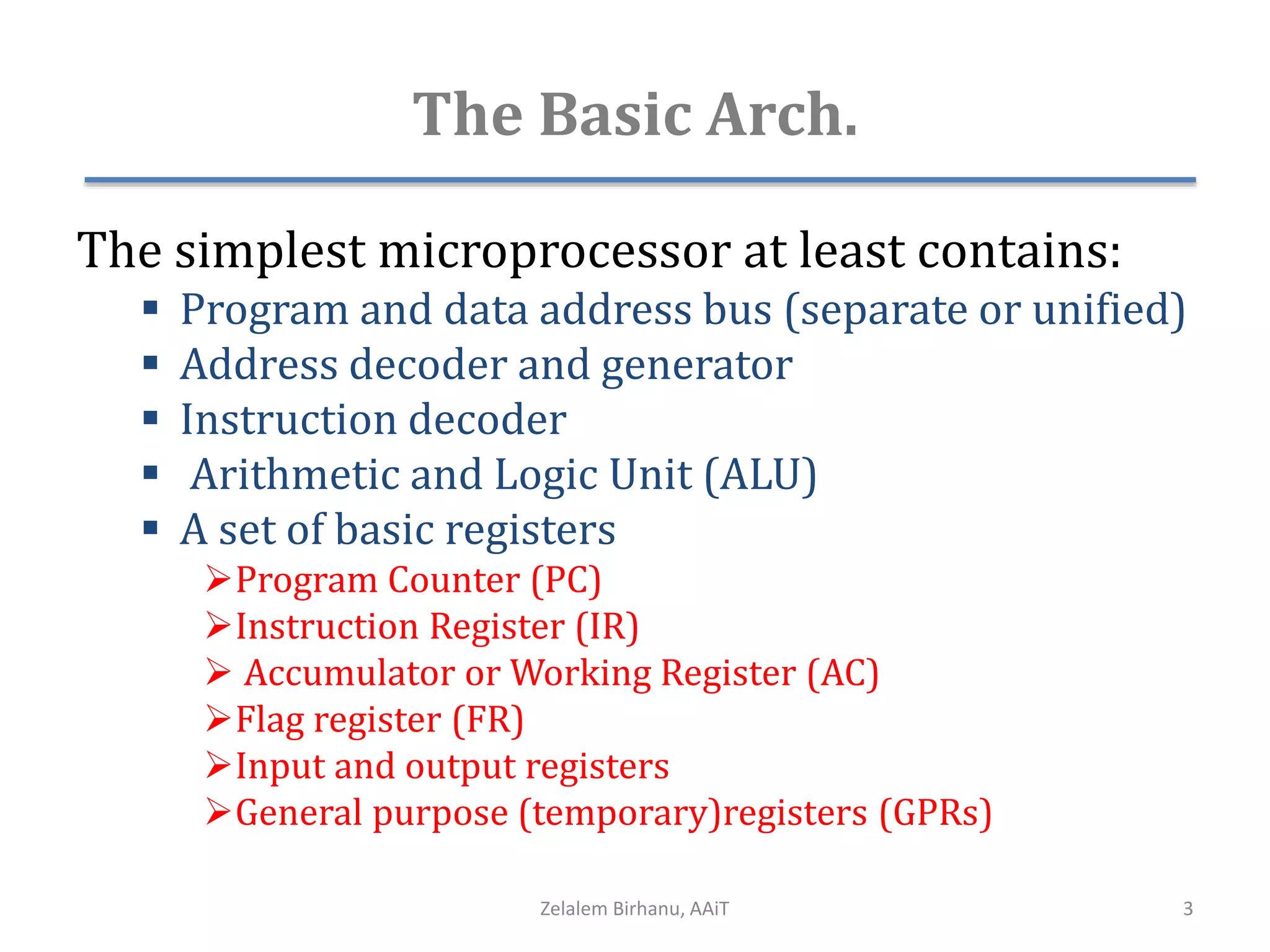
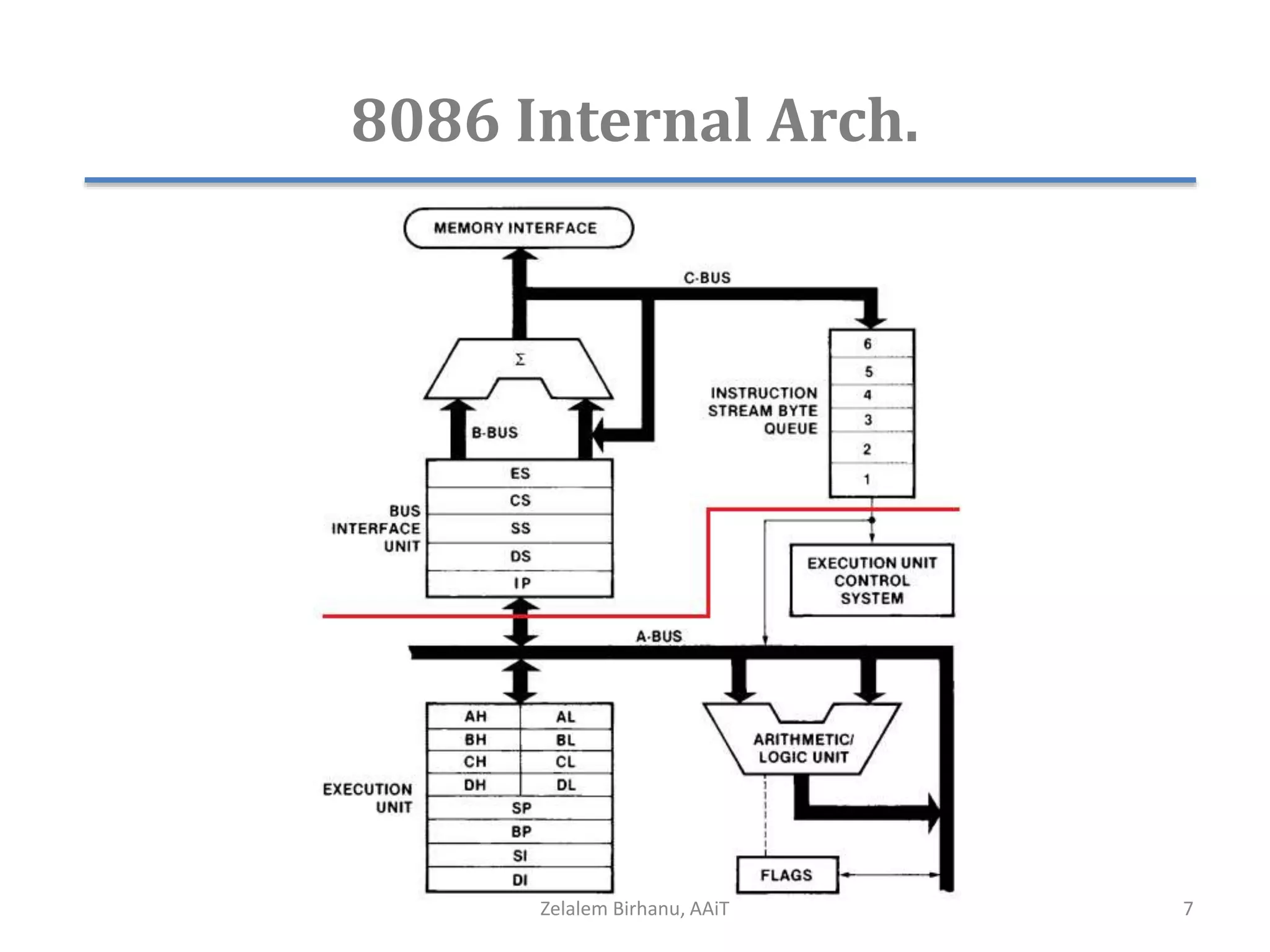
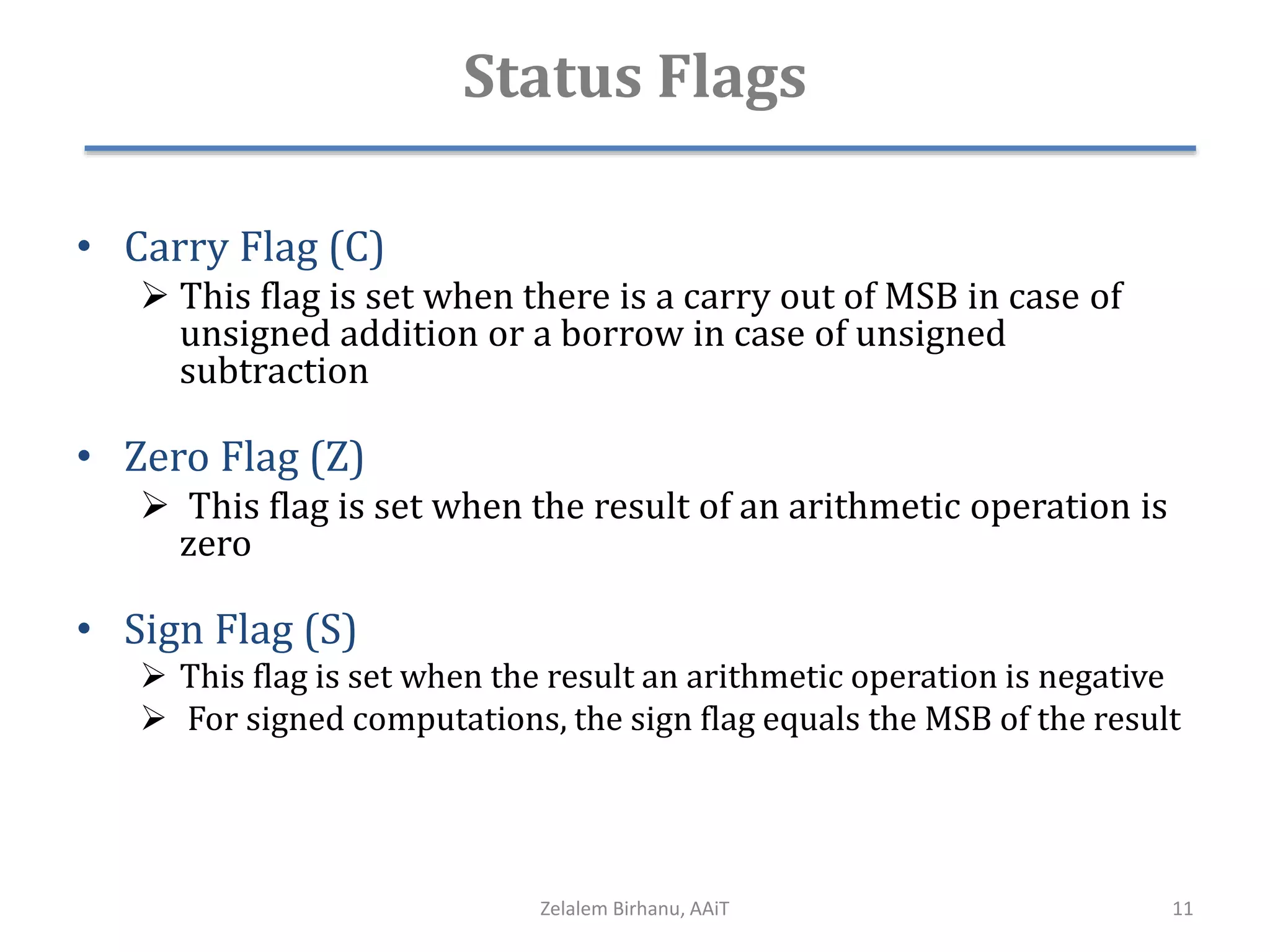
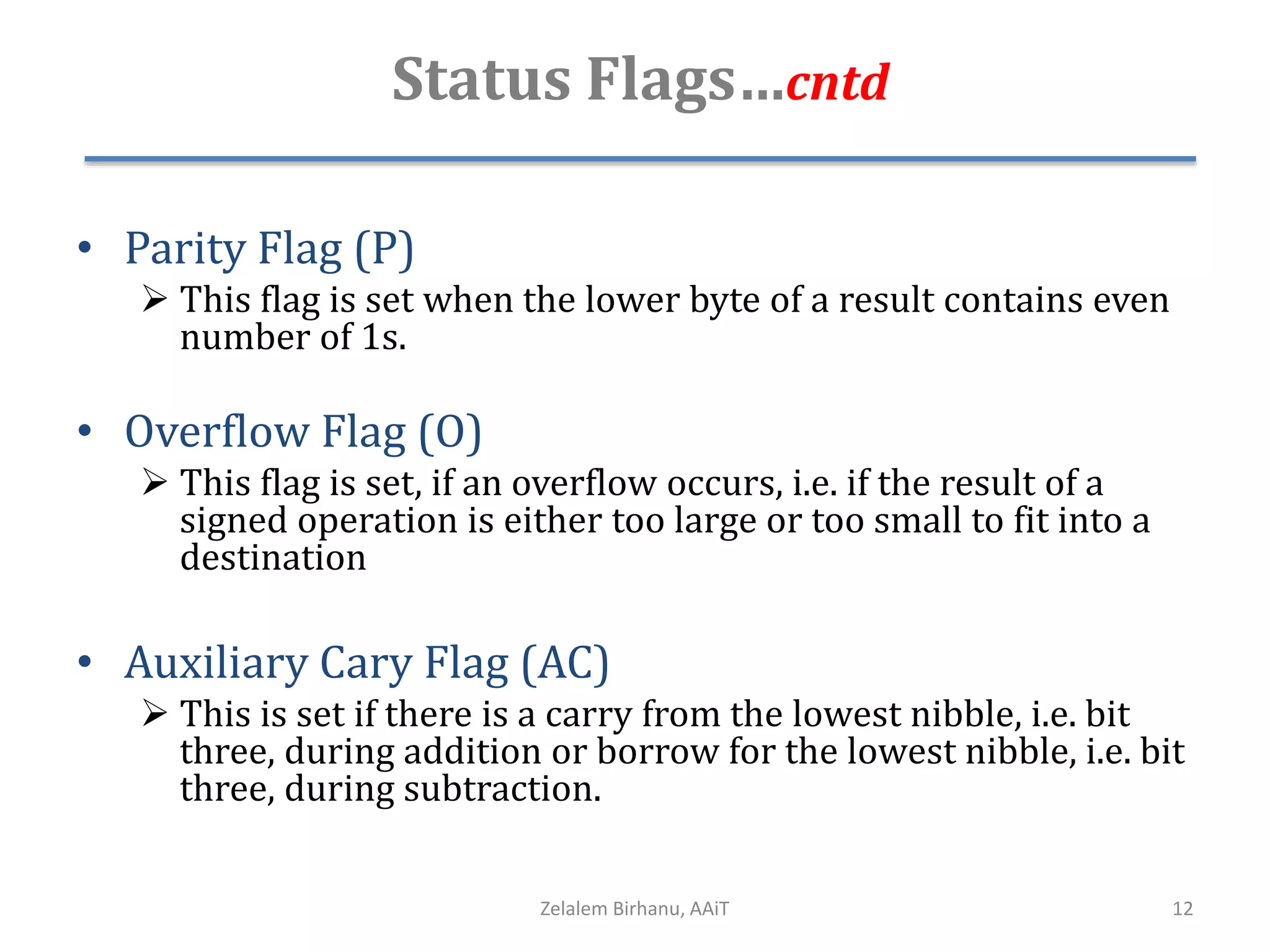
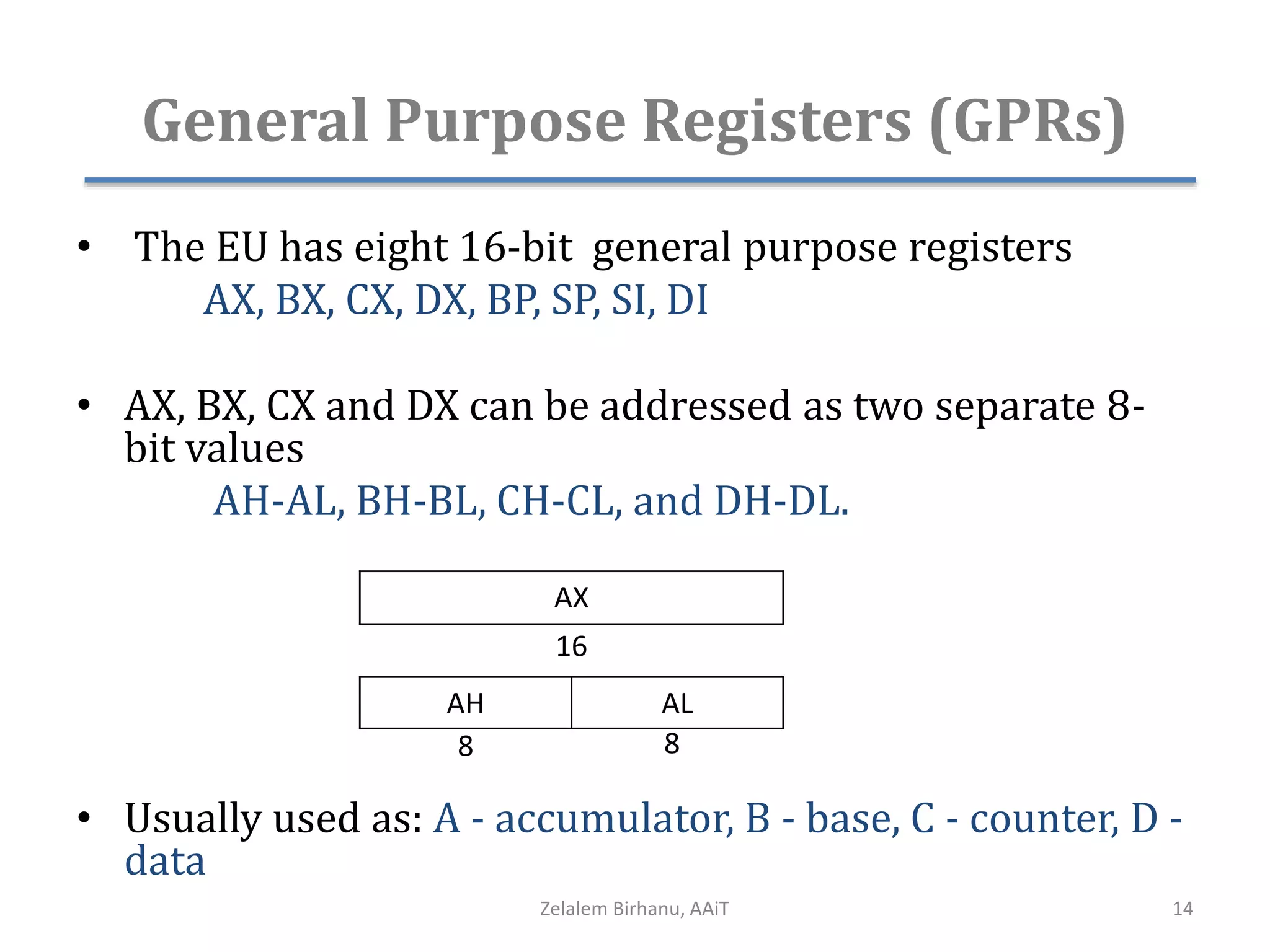
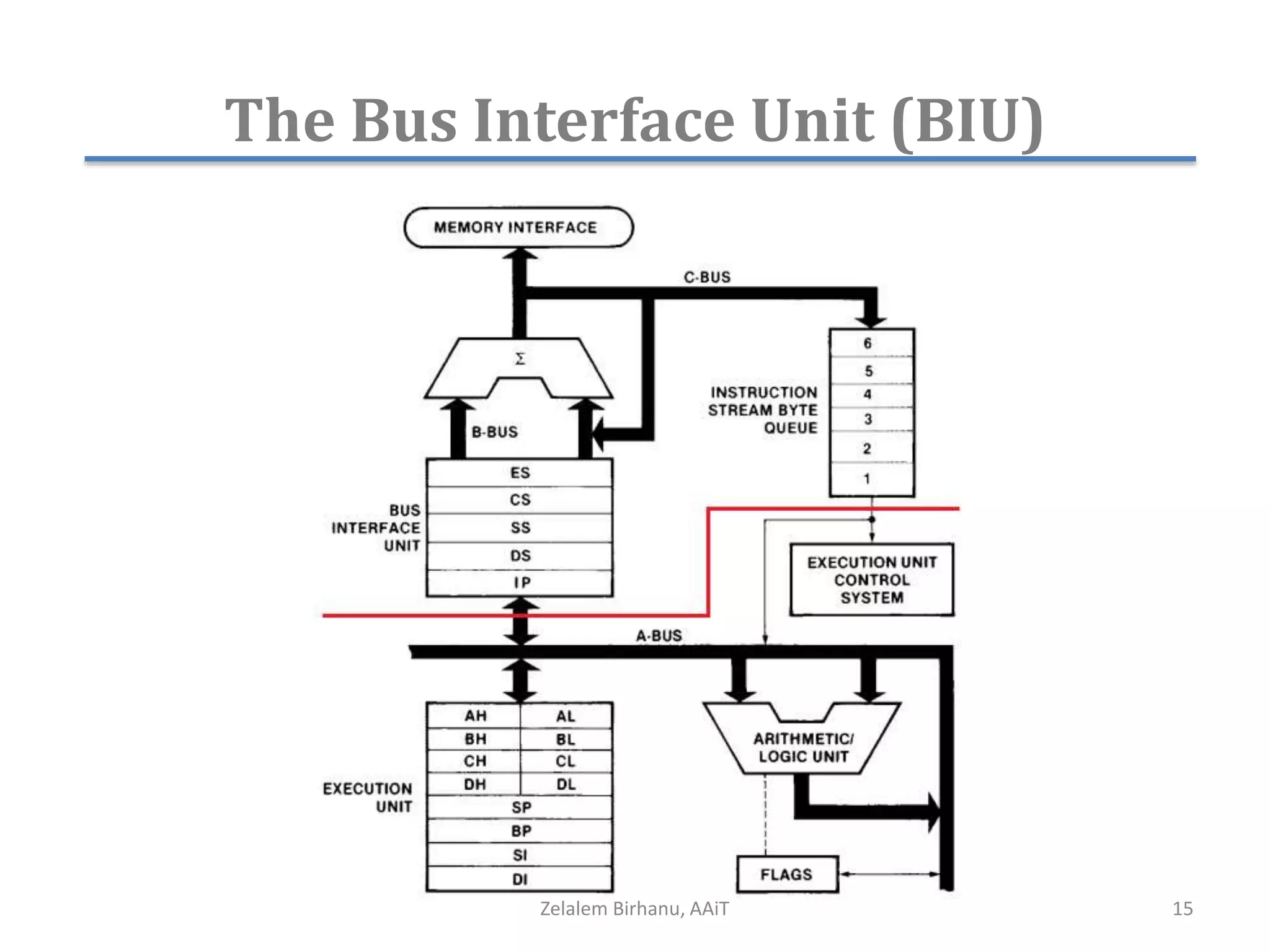
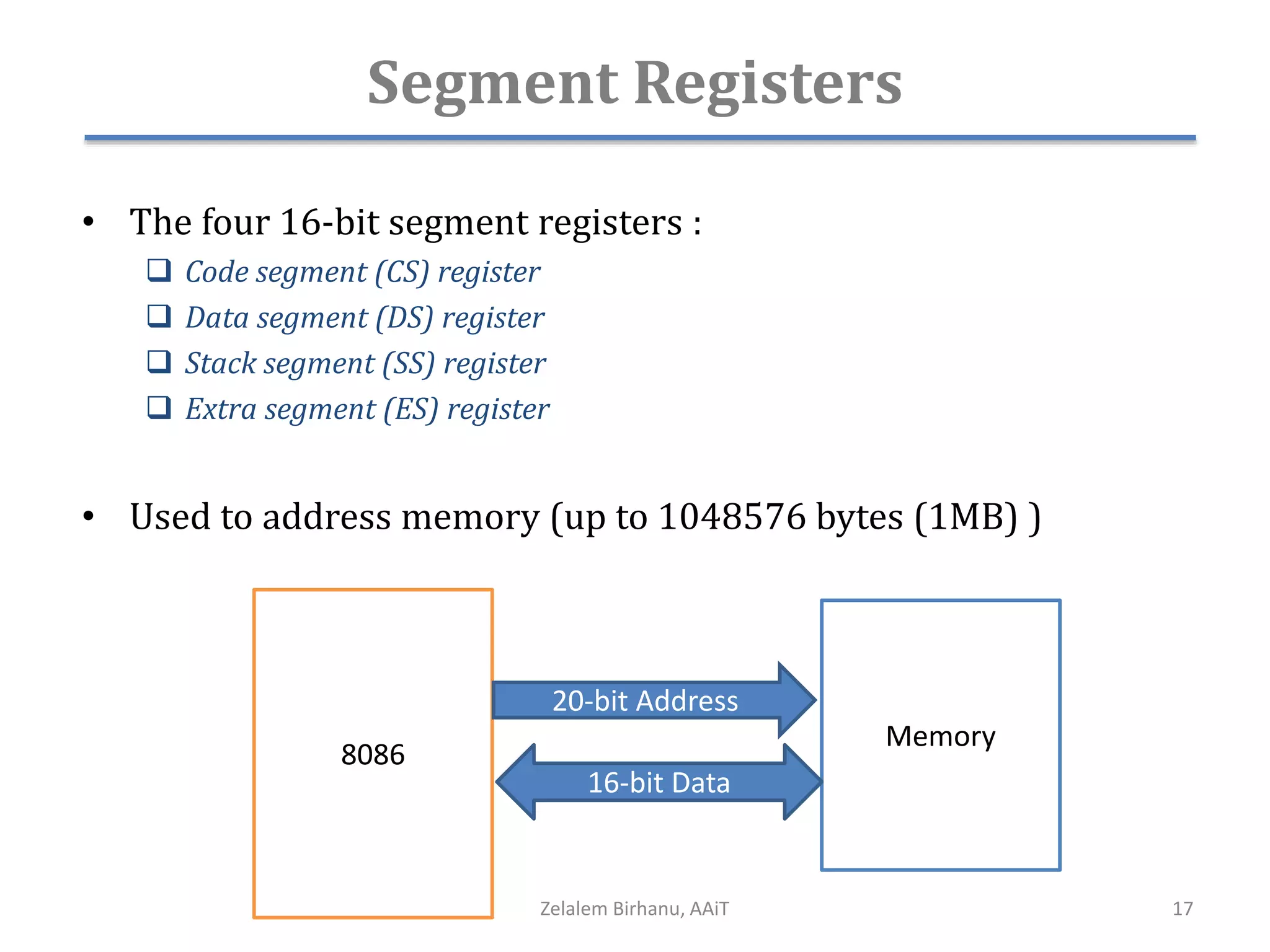
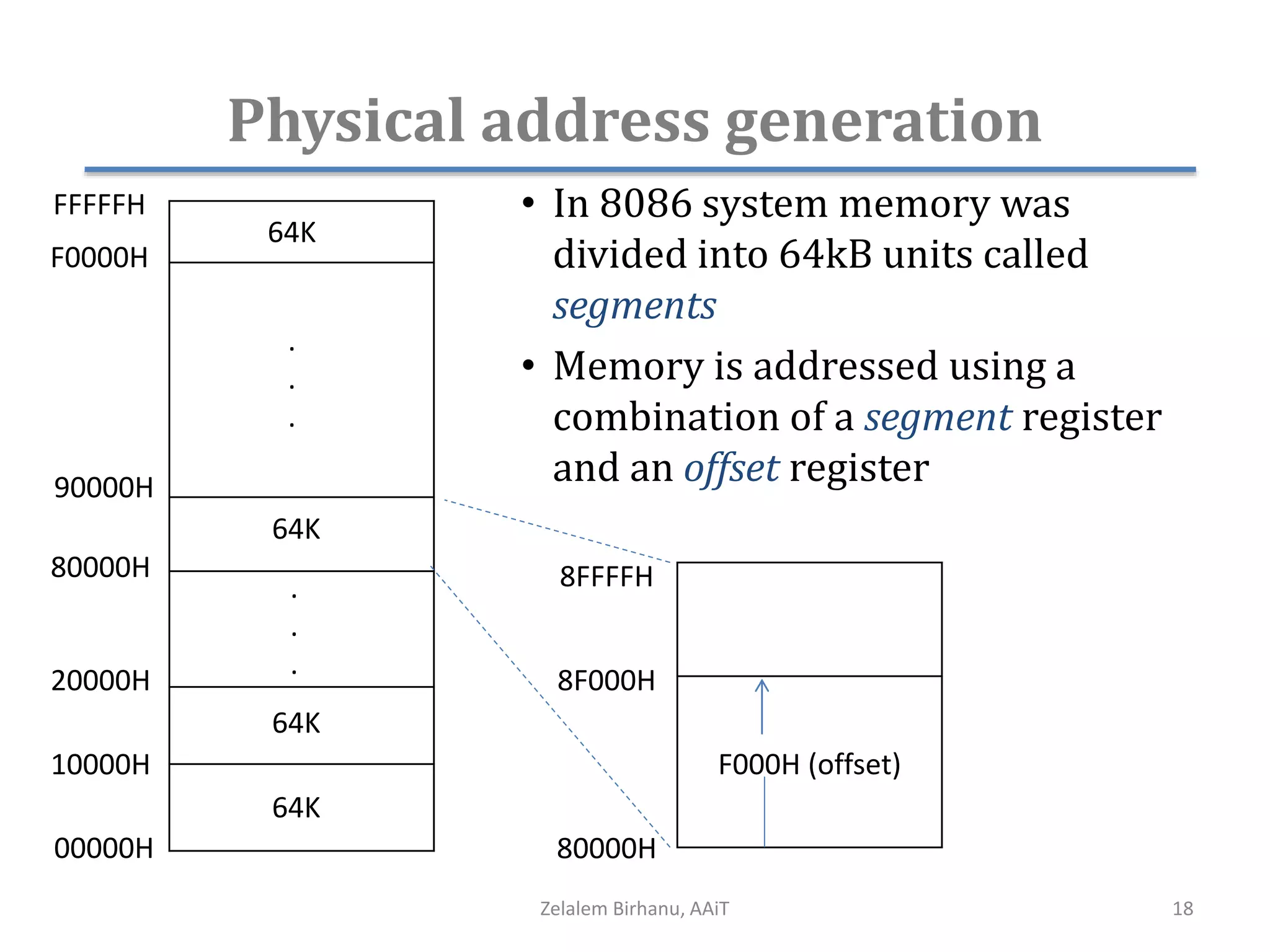
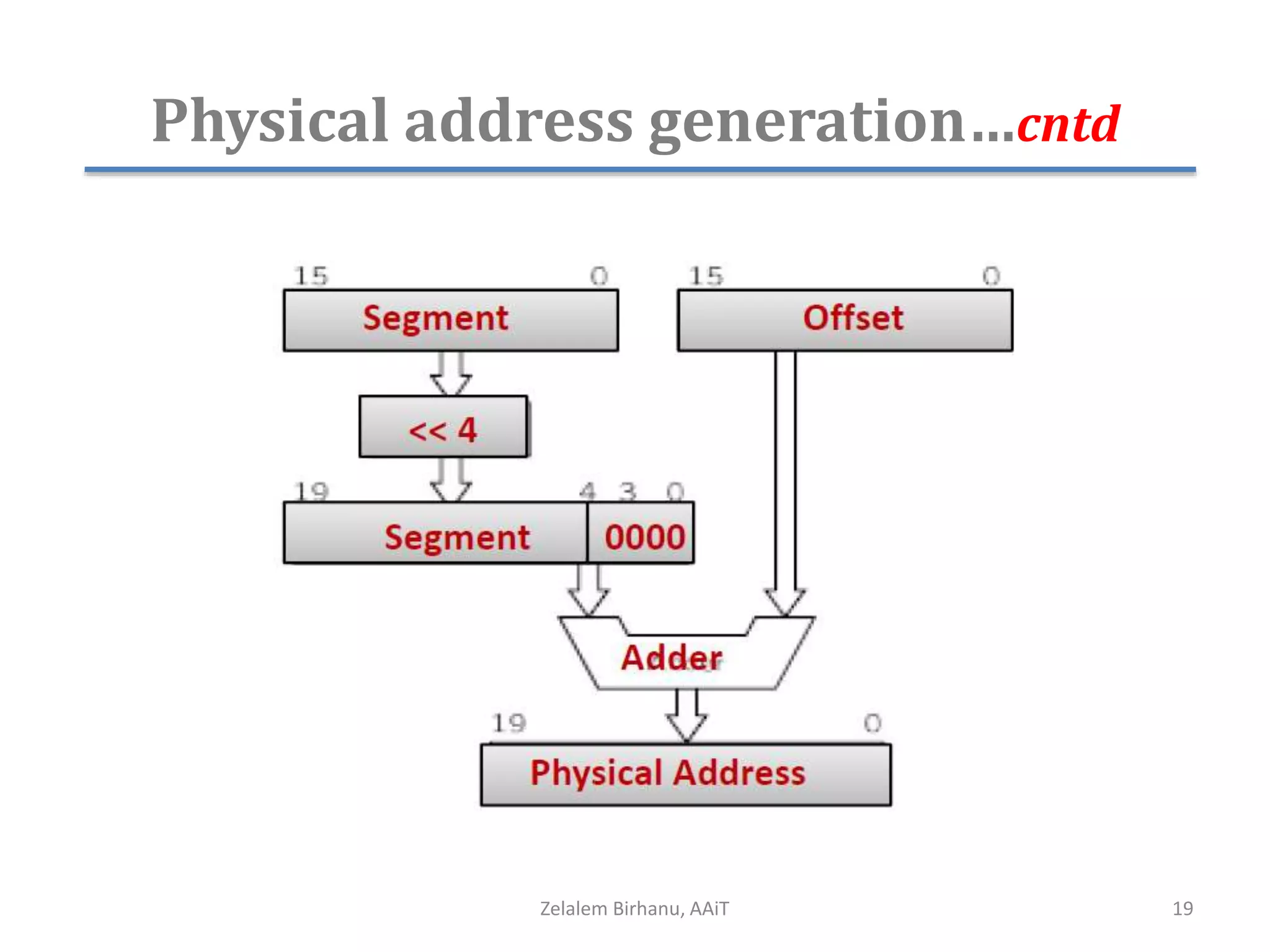
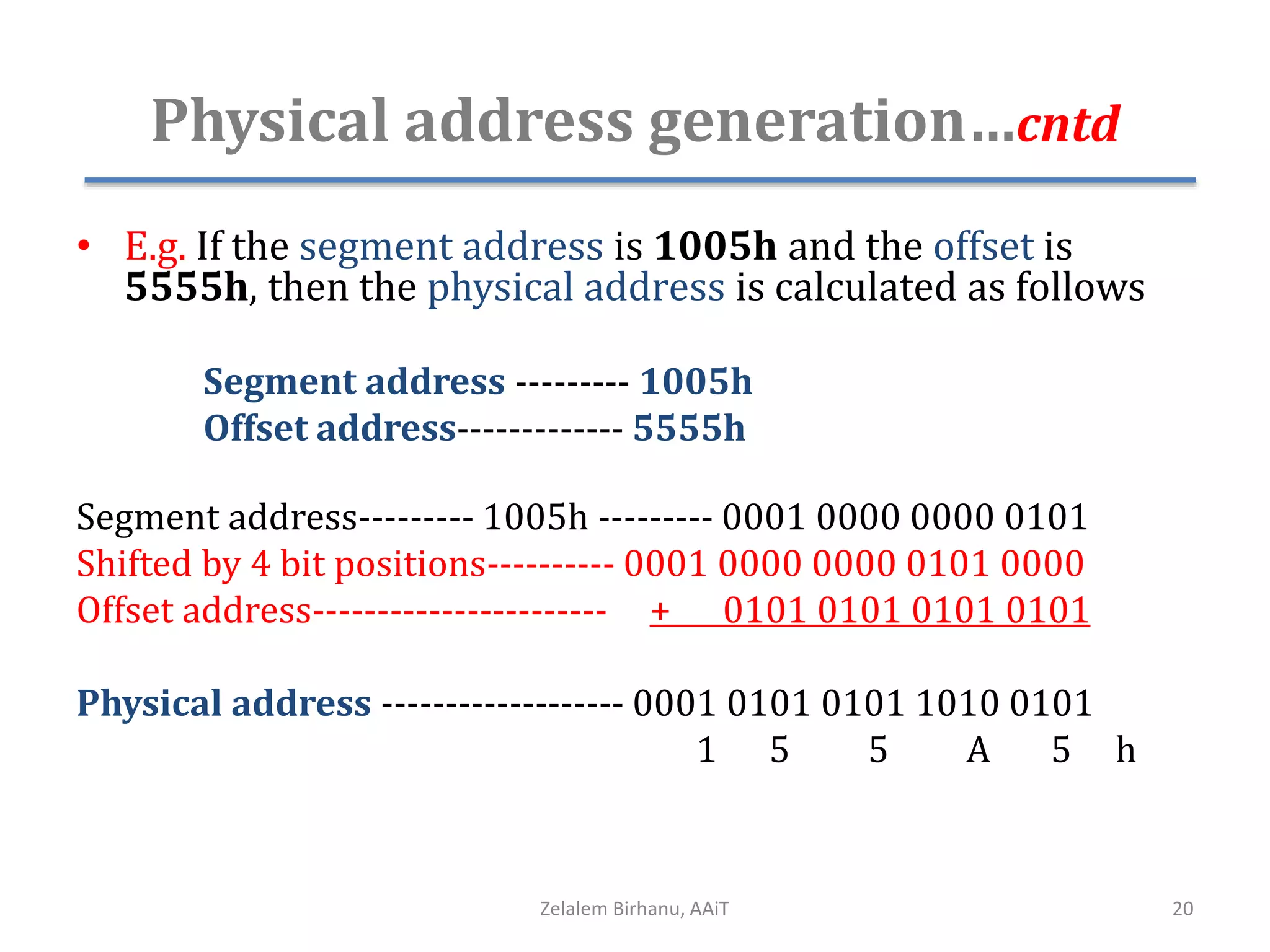
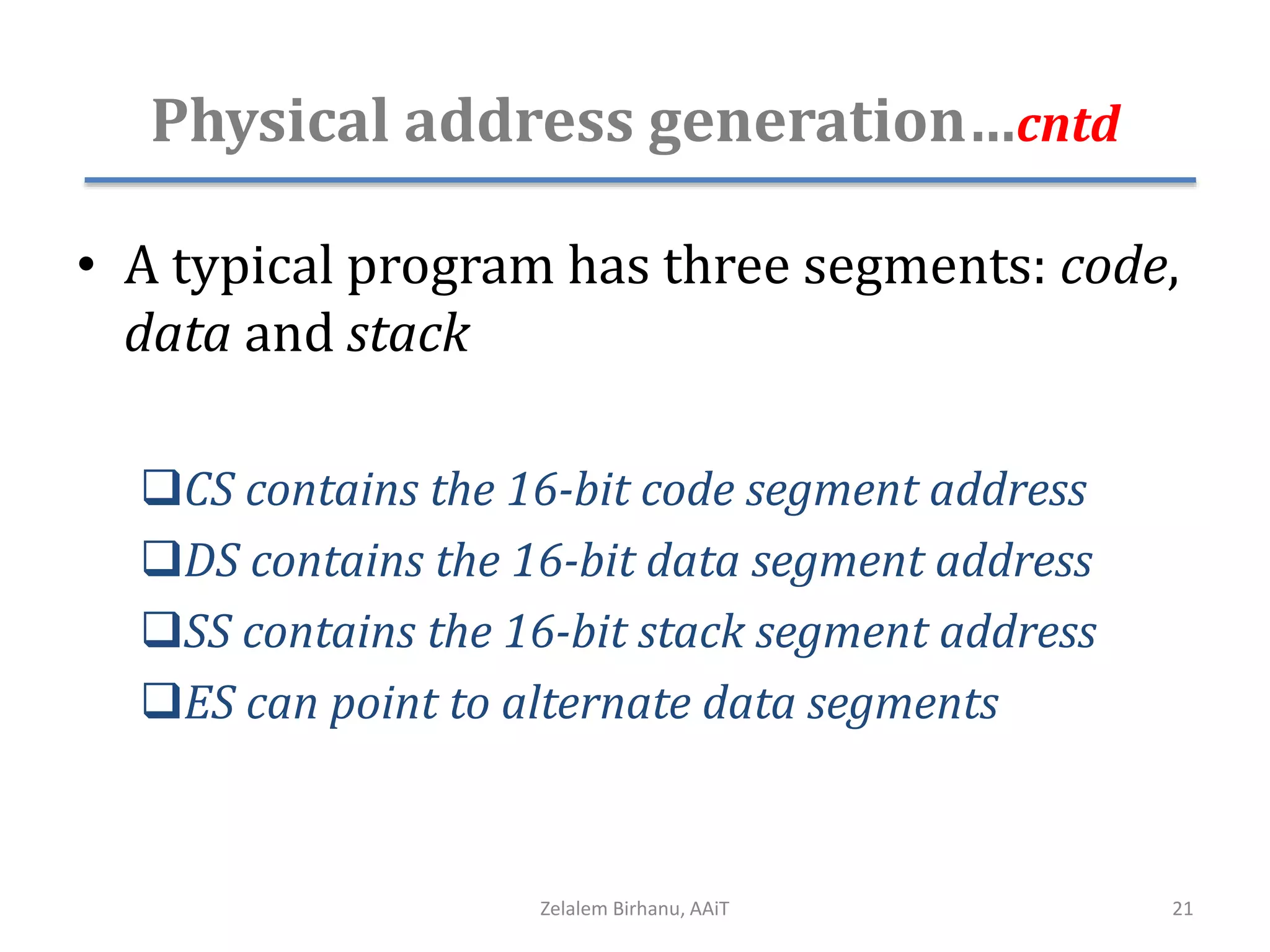
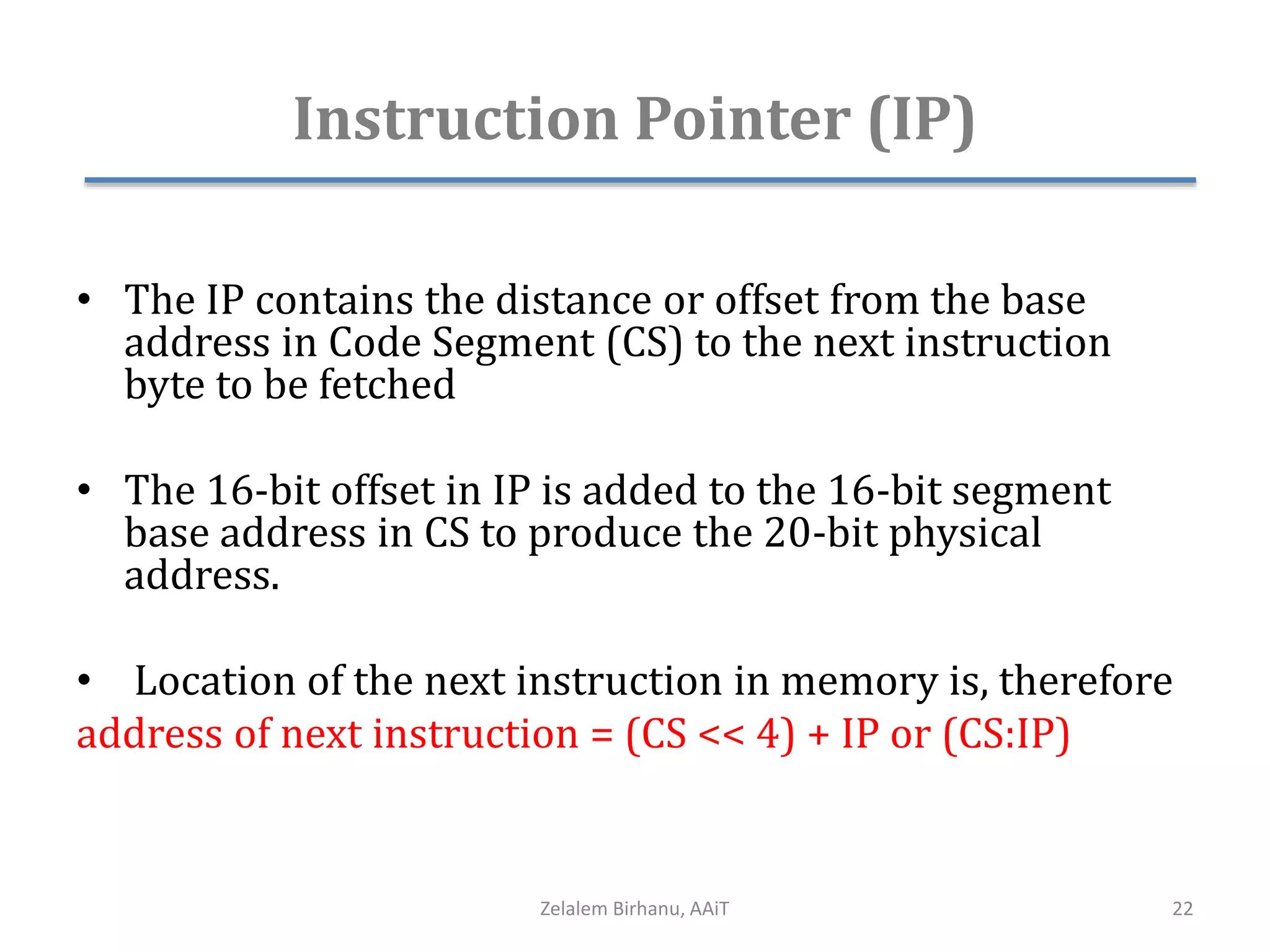
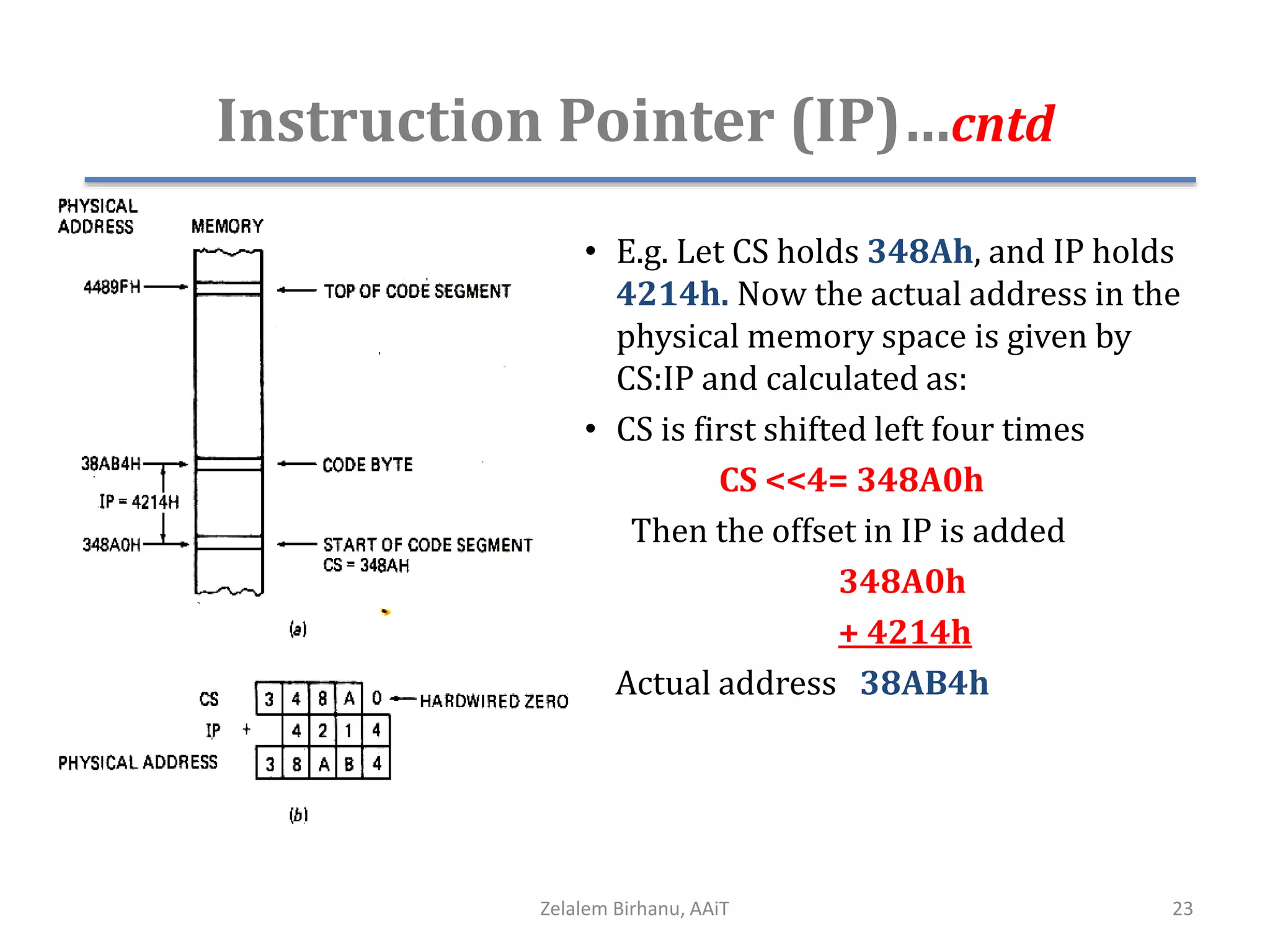
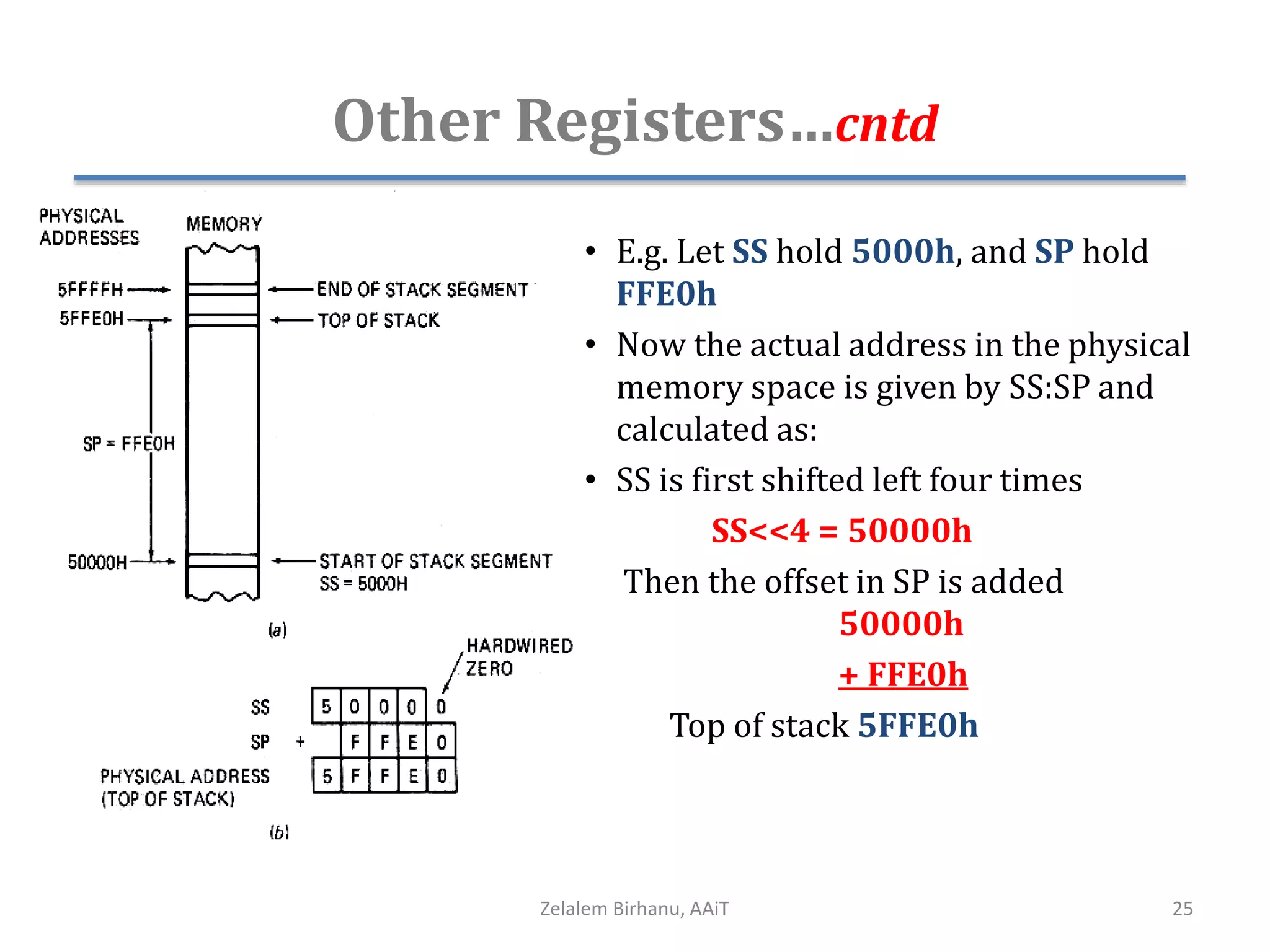
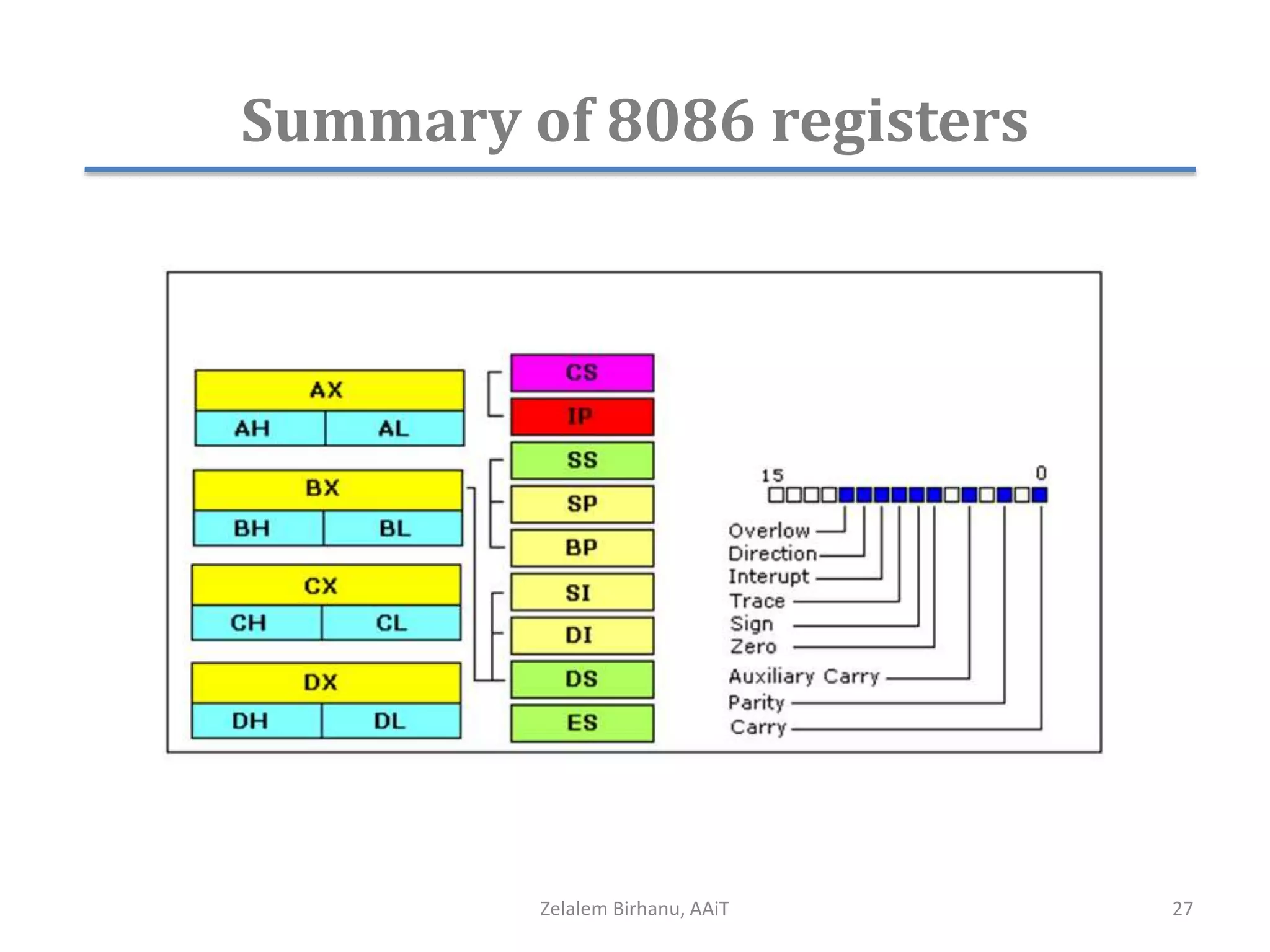
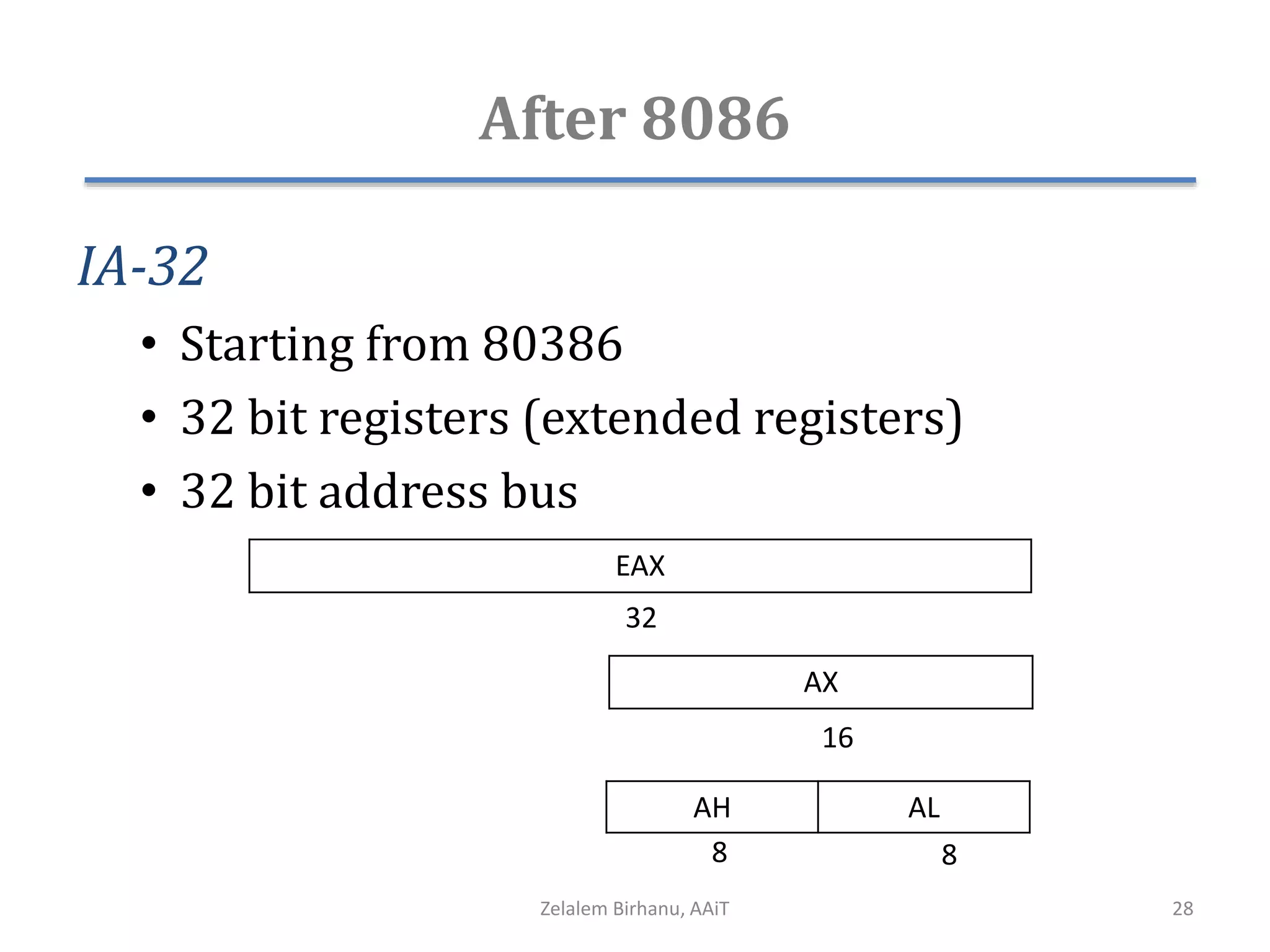
The document discusses the architecture of the 8086 microprocessor. It describes the internal components including the execution unit containing the ALU, registers, and control circuitry, and the bus interface unit. The 8086 uses segment registers and offset registers to generate 20-bit physical addresses. It has general purpose registers including AX, BX, CX, DX and status flags in the flag register. The stack pointer register points to the top of the stack in memory. The 8086 was used in early IBM PCs and led to the development of 32-bit Intel architectures.
![Lecture 2
The 8086 Microprocessor
Architecture
[Register level organization]
Zelalem Birhanu, AAiT 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-141227125552-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture2-1-2048.jpg)