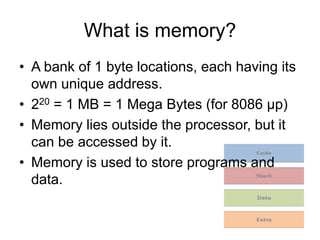
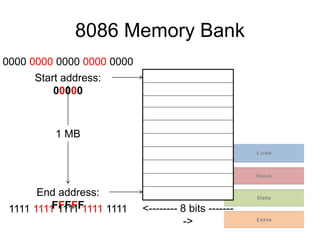
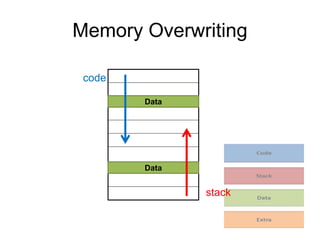
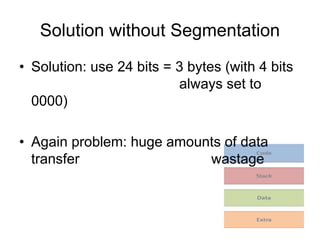
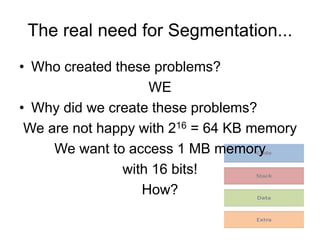
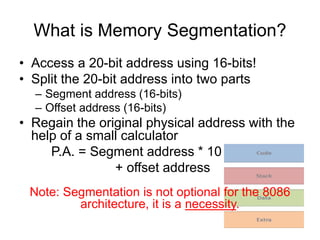
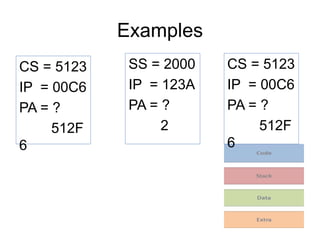
Memory segmentation allows the 8086 processor to access 1 MB of memory using 16-bit registers by splitting the 20-bit physical address into a 16-bit segment address and 16-bit offset address. This organizes memory into segments of minimum 16 bytes and maximum 64 KB in size. The segment registers store the starting address of each segment, and the physical address is regained by multiplying the segment address by 16 and adding the offset. This prevents issues like overwriting memory and allows efficient management of the limited 16-bit addressing scheme.