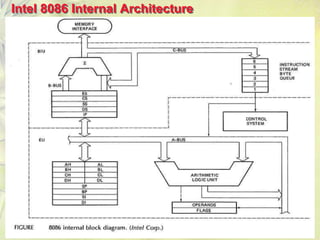
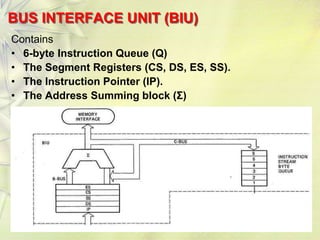
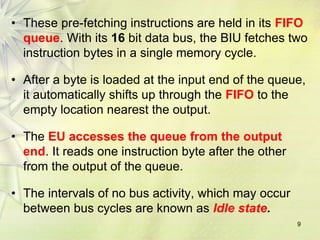
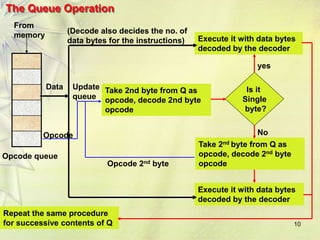
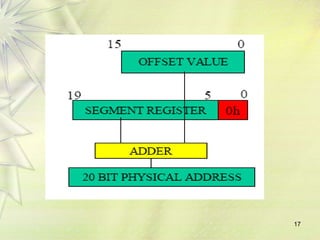
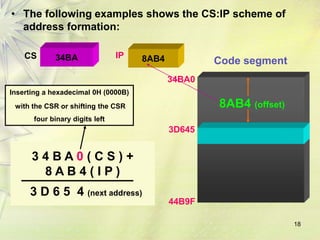
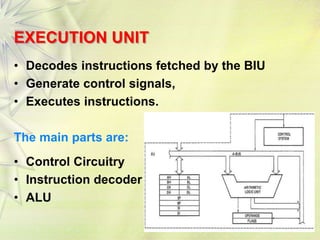
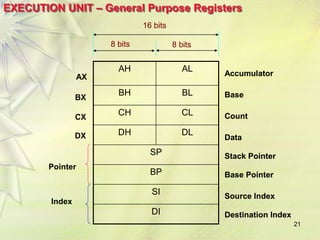
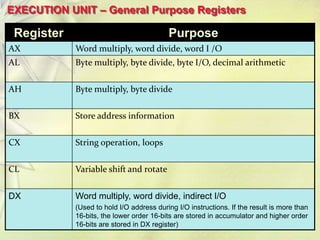
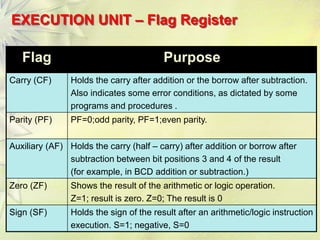
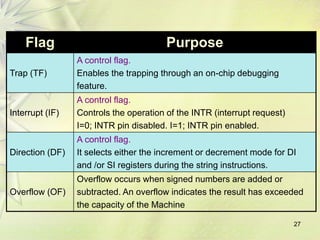
The 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor that can access up to 1MB of memory. It has an internal architecture with two main units - the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and Execution Unit (EU). The BIU handles fetching instructions from memory and passing them to the EU via an instruction queue. The EU then decodes and executes the instructions. The 8086 supports segmented memory addressing using segment registers and offsets. It has general purpose registers like the accumulator, flags to indicate arithmetic results, and pointer/index registers used for memory addressing.