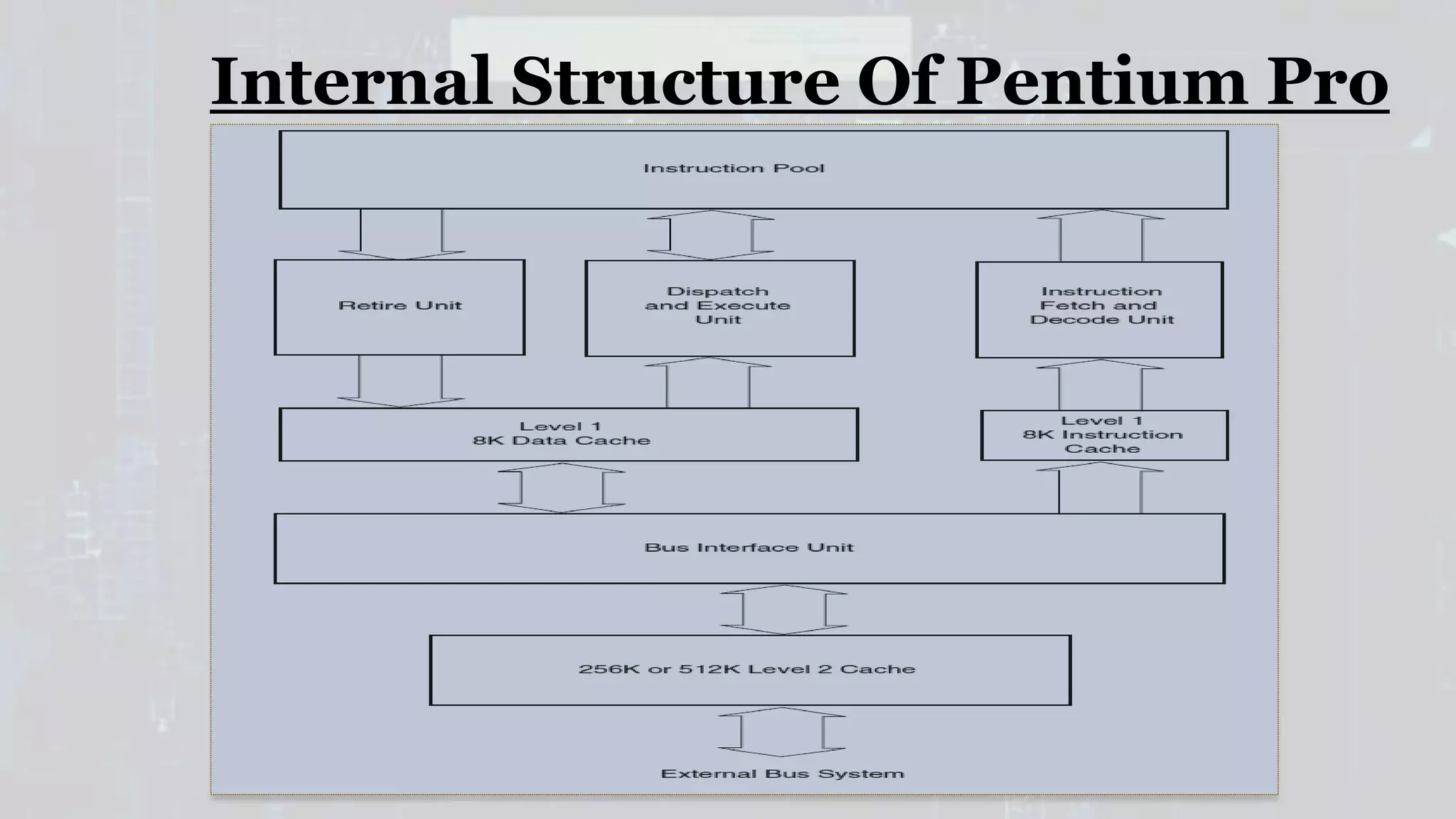
The Intel Pentium Pro is a sixth generation x86 microprocessor introduced in 1995, offering capabilities for dual and quad-processor configurations and supporting up to 64GB of memory through a 36-bit address bus. It features integrated L2 cache, dynamic execution, and an error correction circuitry, which differentiates it from its predecessor, the Intel Pentium. Key drawbacks include performance hits from converting CISC to RISC instructions and issues with executing 16-bit code efficiently.