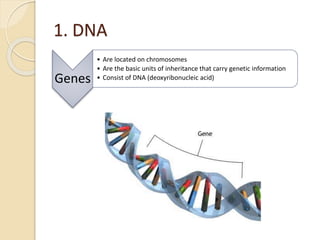
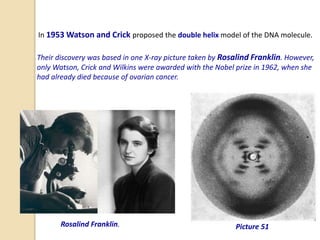
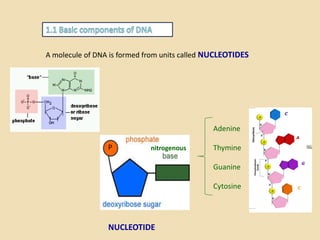
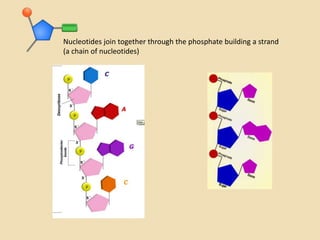
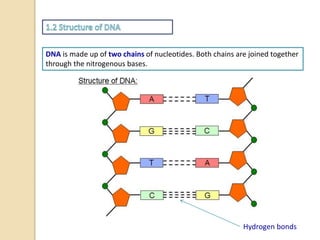
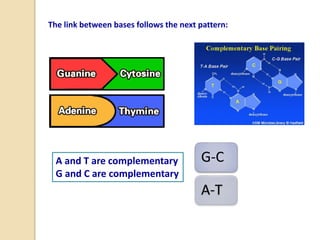
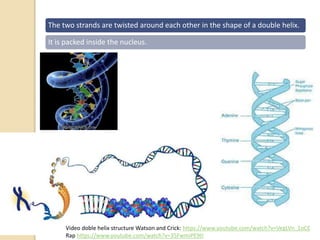
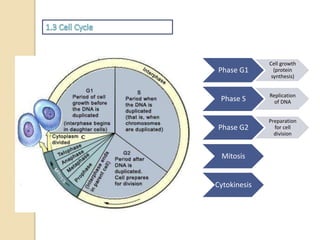
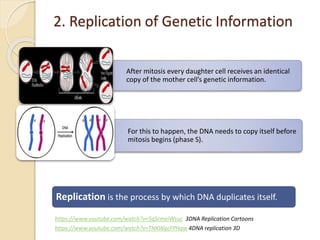
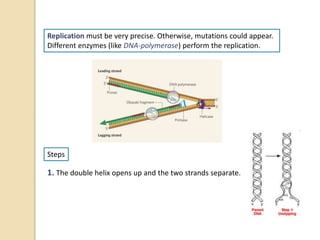
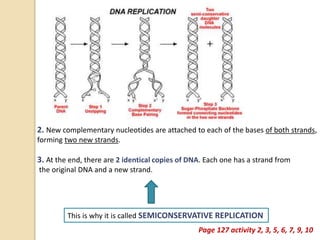
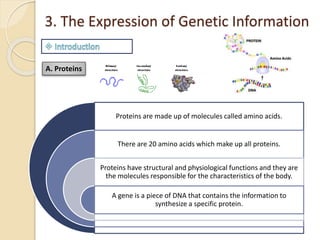
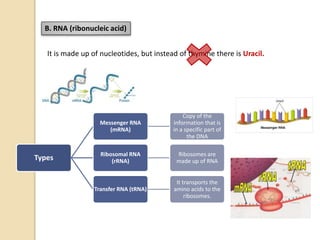
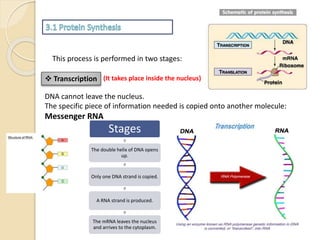
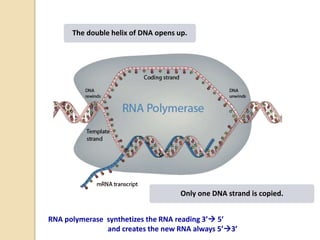
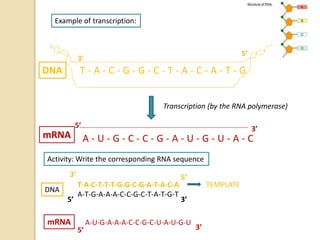
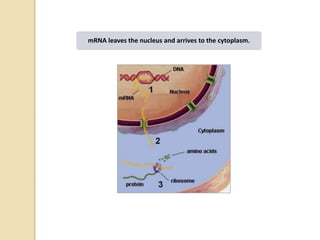
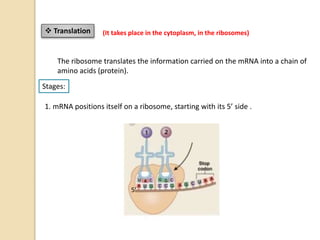
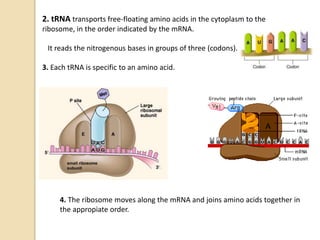
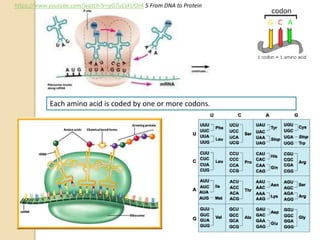
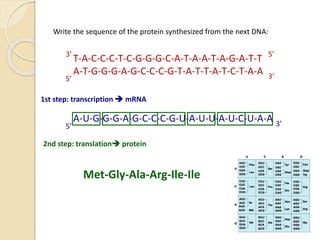
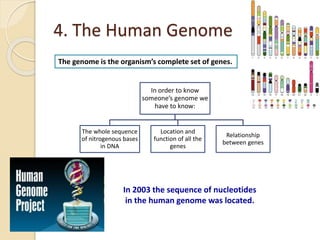
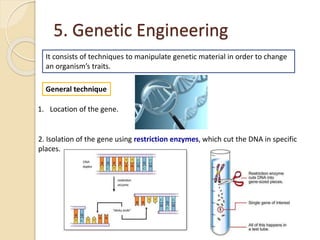
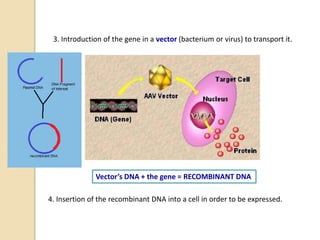
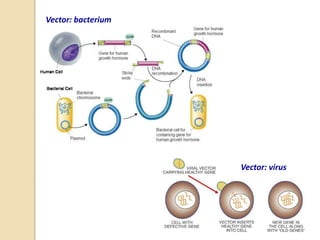
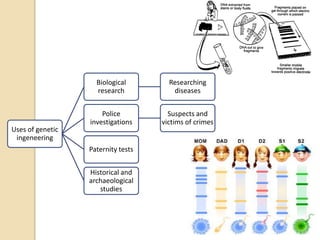
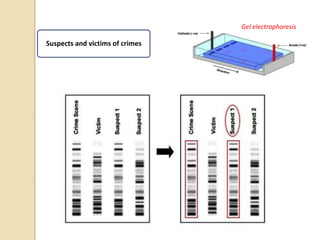
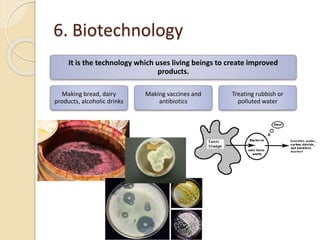
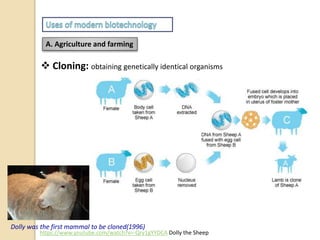
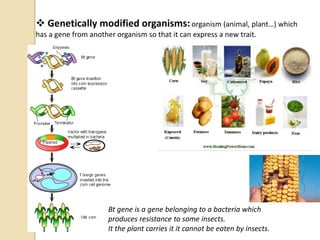
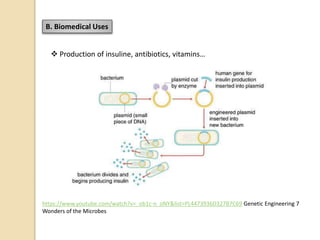
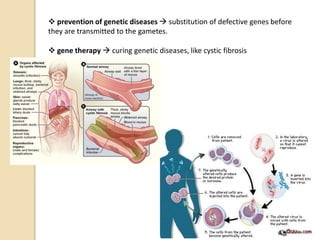
This document provides an overview of molecular genetics and biotechnology. It discusses the structure of DNA and the DNA double helix model. It explains DNA replication, which is essential for cells to copy genetic material before cell division. Gene expression through transcription and translation is summarized, including how DNA is copied into mRNA and then translated into proteins. The sequencing of the human genome is mentioned, along with applications like disease diagnosis. Genetic engineering techniques like isolating, inserting, and recombining genes are outlined. Uses of biotechnology in agriculture, farming, and medicine are also reviewed.