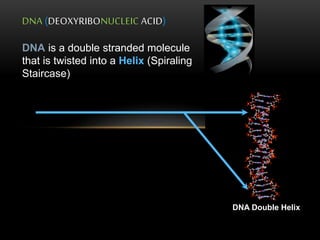
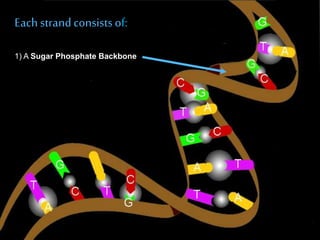
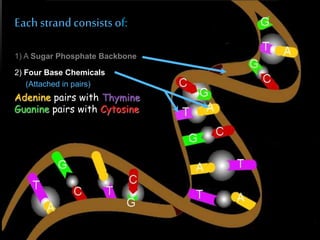
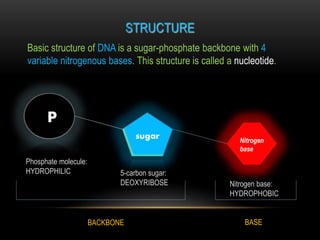
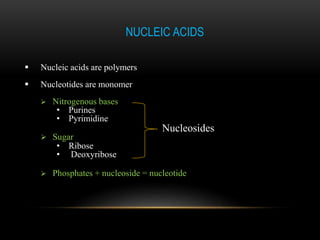
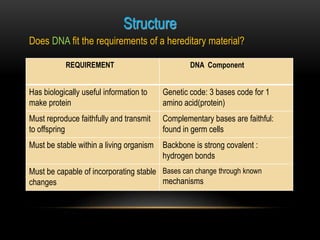
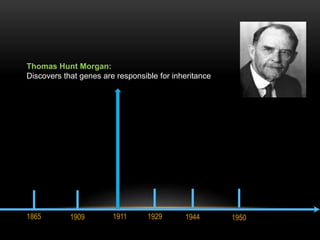
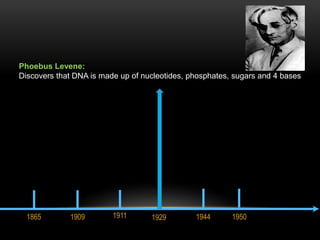
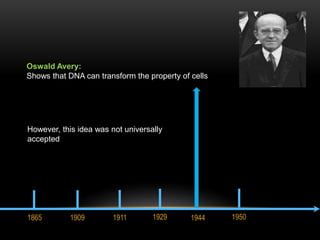
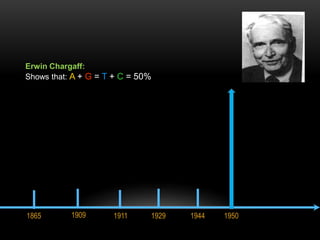
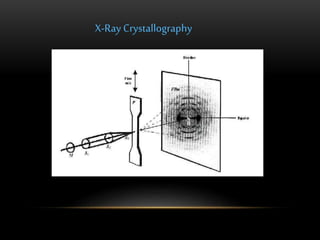
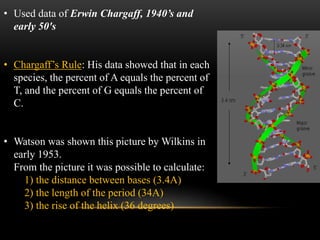
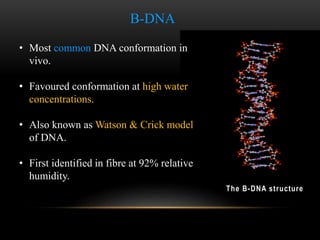
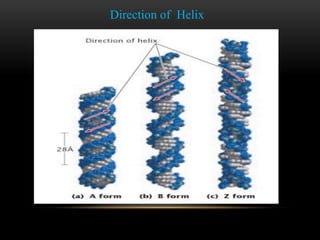
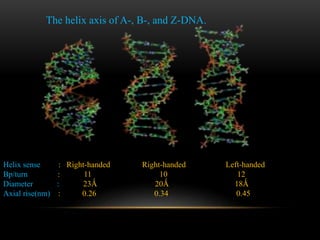
The discovery of the DNA double helix structure in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick was one of the greatest scientific achievements of the 20th century. They were able to determine that DNA consists of two strands coiled around each other to form a double helix. Each strand is made up of a backbone of alternating sugar and phosphate groups with nitrogenous bases protruding from the sugars. The bases on one strand form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases on the other strand. Watson and Crick's double helix model explained how DNA could replicate itself and be stable within organisms. Their discovery fundamentally changed our understanding of genetics and laid the foundation for modern molecular biology and genetic engineering.