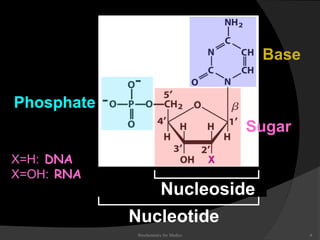
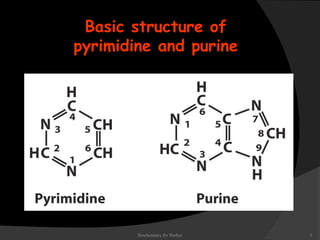
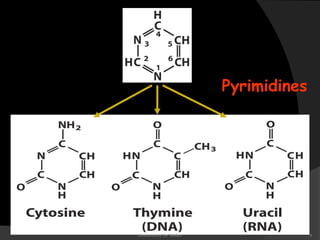
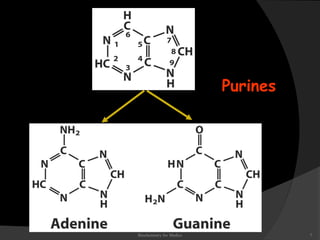
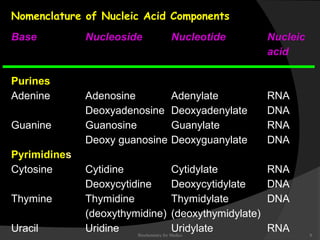
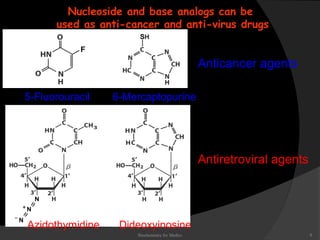
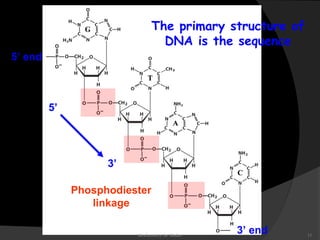
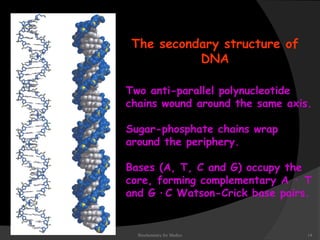
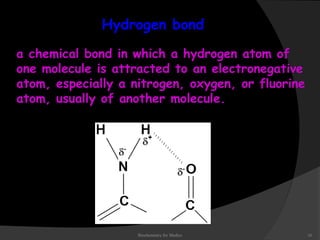
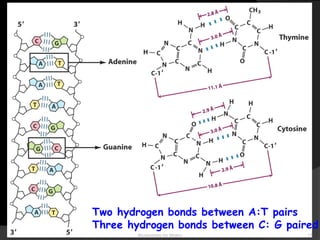
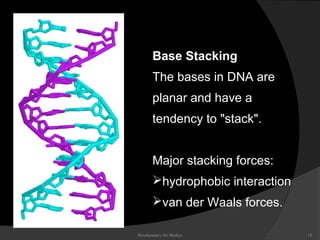
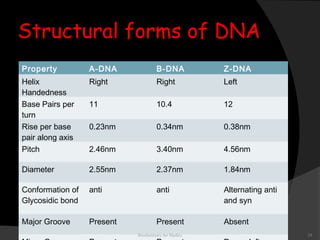
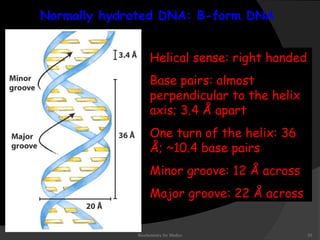
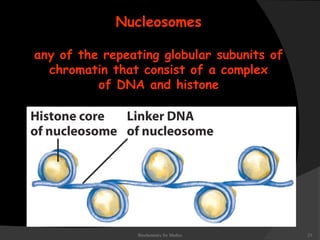
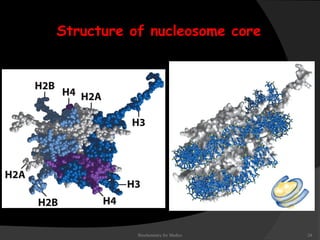
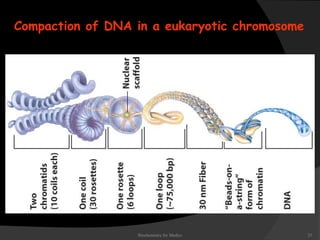
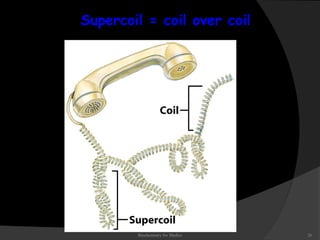
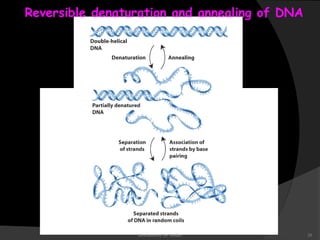
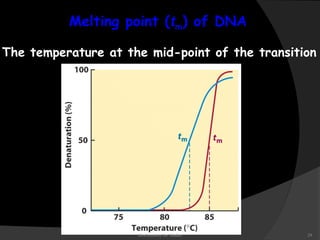
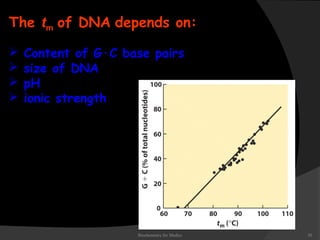
This document discusses the structure, properties, and functions of DNA. It describes DNA as a polymer composed of deoxyribonucleotides that carries the genetic information found in chromosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. The basic structure of DNA involves two anti-parallel strands coiled around each other to form the familiar double helix structure, held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide base pairs and base stacking interactions. DNA exists in various structural forms and undergoes compaction in the cell, ultimately forming chromatin through association with histone proteins. The primary function of DNA is to serve as the template for its own replication and transcription into RNA to direct protein synthesis.