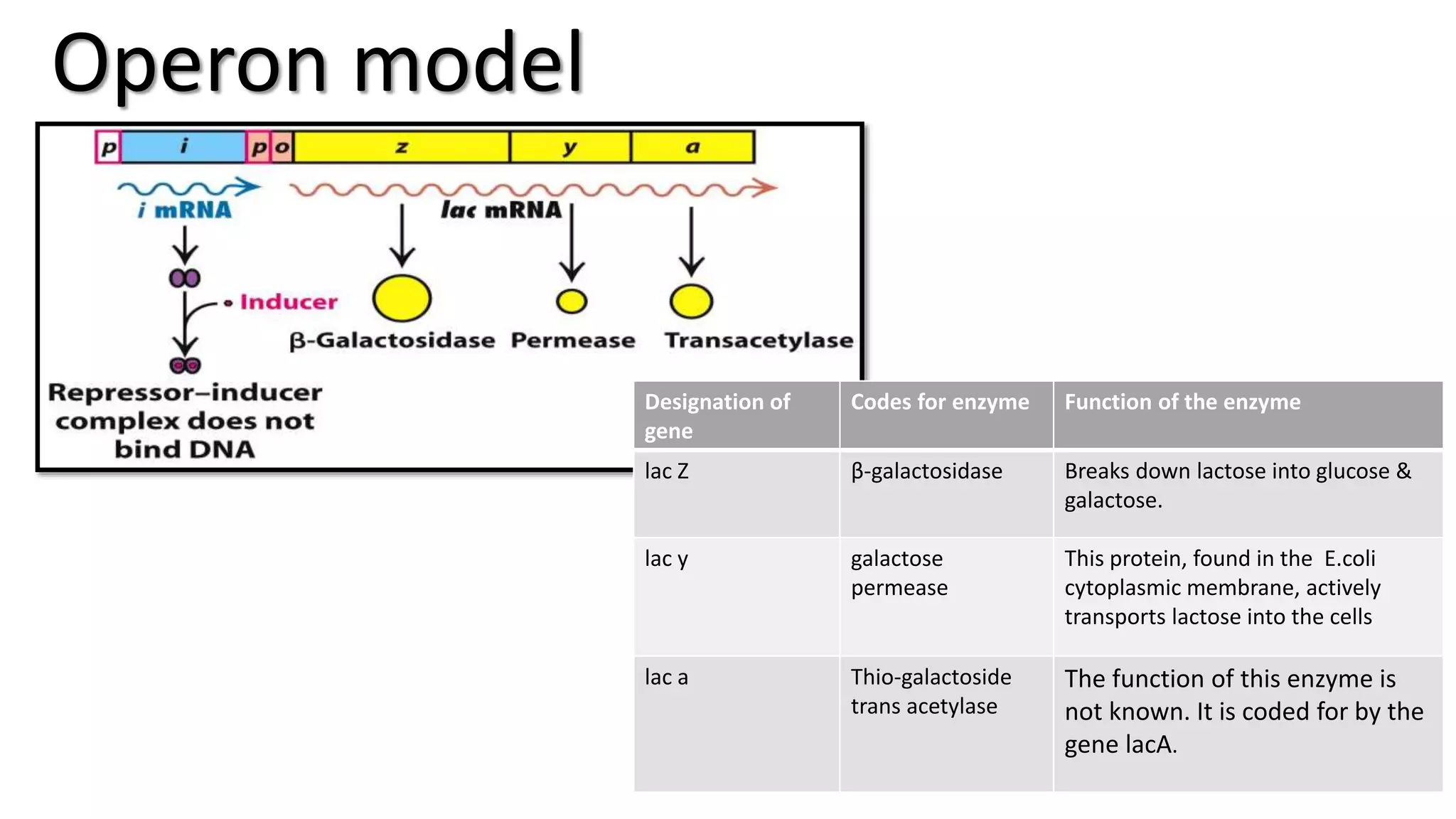
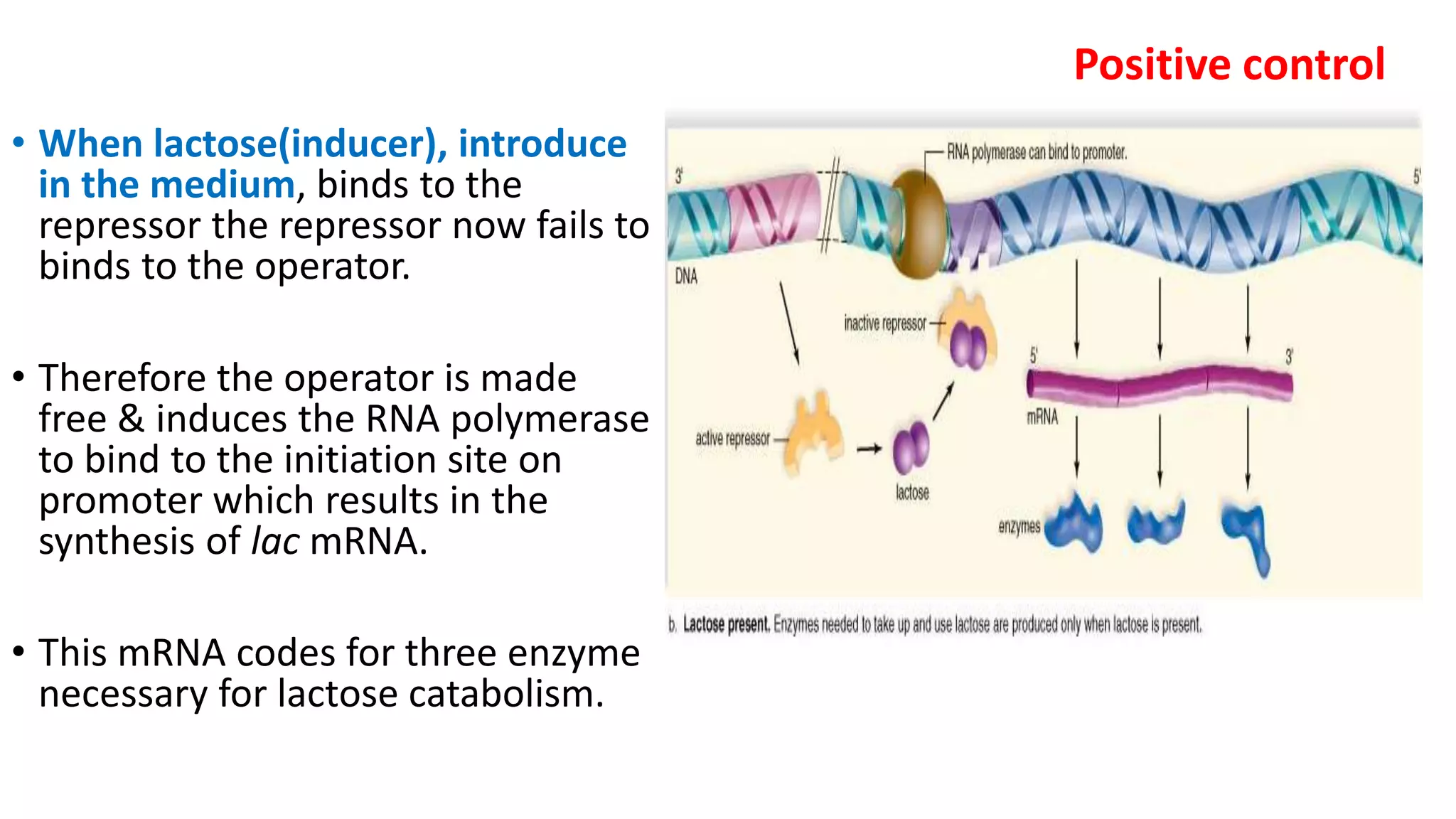
The document summarizes the lac operon in E. coli, which controls the breakdown of lactose. The lac operon contains 3 genes - lacZ, lacY, and lacA - that code for enzymes involved in lactose catabolism. In the absence of lactose, a repressor protein binds to the operator region and prevents transcription. In the presence of lactose, it binds to the repressor and induces transcription of the structural genes. The lac operon demonstrates both negative control by the repressor and positive control through induction by lactose binding. Glucose also regulates the operon through catabolite repression involving cAMP levels.