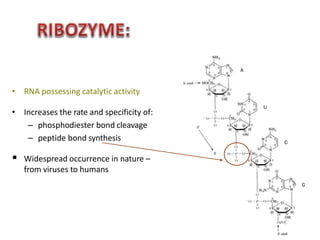
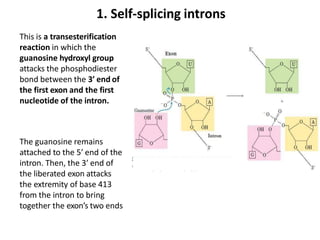
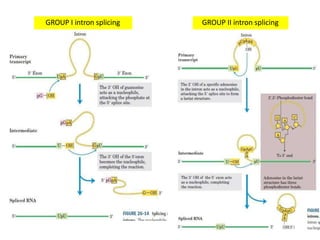
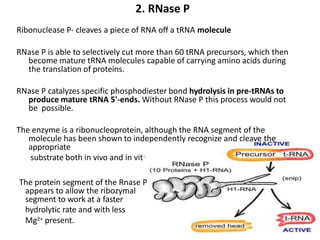
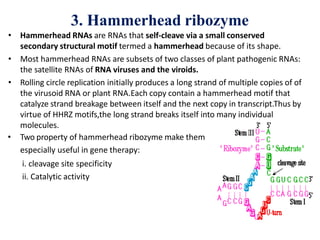
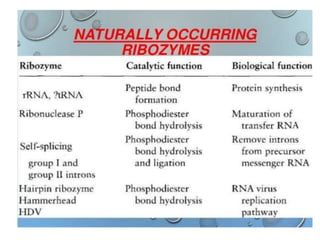
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as enzymes and catalyze biochemical reactions. They were first discovered in 1982 by Thomas Czech and Sidney Altman, who later won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their discovery. Ribozymes increase the rate and specificity of reactions like phosphodiester bond cleavage and peptide bond synthesis. Common types of ribozymes include self-splicing introns, RNase P, hammerhead ribozymes, and hairpin ribozymes. Artificial ribozymes can also be synthesized in the laboratory by mutating natural ribozymes.