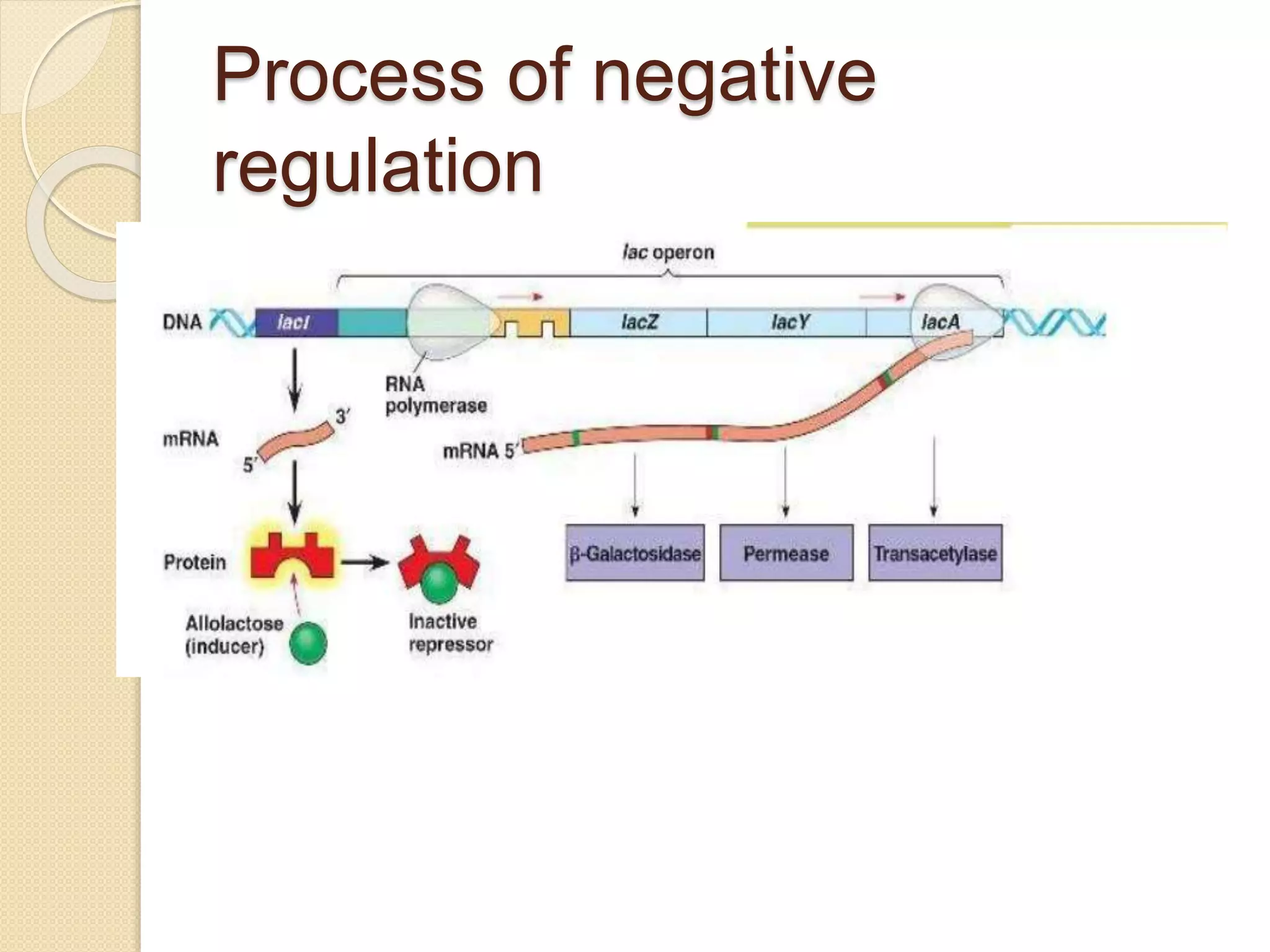
The lac operon contains three genes - lacZ, lacY, and lacA - that encode proteins involved in lactose metabolism. The activity of the lac operon promoter is regulated by the Lac repressor and CAP proteins. Negative regulation occurs when the Lac repressor binds to the operator region and prevents RNA polymerase from binding and initiating transcription. Positive regulation happens when the CAP-cAMP complex binds near the promoter and stimulates RNA polymerase binding, increasing transcription. Together, these two types of regulation allow the lac operon to be turned on or off depending on the presence of lactose in the environment.